Abstract
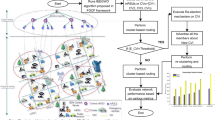
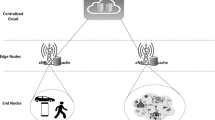
Service caching can improve the QoS of computationally intensive vehicle applications by pre-storing the necessary application programs and related data for computing tasks on edge servers. In this paper, we propose a new vehicle edge computing framework based on software defined networks, which introduces the reputation to measure the contribution of each vehicle as the basis for providing different quality of services. The process is divided into two phases: in the first phase, the vehicle requests the offload application task from the edge server; and in the second phase, the edge server makes the service caching decision after processing the task. We design the whole interaction process as a kind of incentive mechanism based on reputation via using Stackelberg game modeling, and analyze the optimal strategy for both sides of the game by reverse induction. Furthermore, we also prove the existence and uniqueness of Stackelberg equilibrium in two-stage game, and a genetic optimization algorithm is designed to quickly obtain the optimal strategy for both sides of the game. Experimental results show that the proposed scheme not only brings more profits to the edge server side, but also reduces the average delay by 76 % compared with the ordinary mobile edge computing scheme.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas N, Zhang Y, Taherkordi A, Skeie T (2018) Mobile edge computing: a survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 5(1):450–464
Wang S, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang L, Yang J, Wang W (2017) A survey on mobile edge networks: convergence of computing, caching and communications. IEEE Access 5:6757–6779
Grewe D, Wagner M, Arumaithurai M, Psaras I, Kutscher D (2017) Information-centric mobile edge computing for connected vehicle environments: challenges and research directions. In: ACM Special interest group on data communication, pp 7–12
Zhou L (2016) Mobile device-to-device video distribution: theory and application. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 12(3):38
Tordsson J, Montero RS, Moreno-Vozmediano R, et al (2012) Cloud brokering mechanisms for optimized placement of virtual machines across multiple providers. Futur Gener Comput Syst 28(2):358–367
Sarrigiannis I, Ramantas K, Kartsakli E, Mekikis P-V, Antonopoulos A, Verikoukis C (2020) Online VNF lifecycle management in a MEC-enabled 5g iot architecture. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 7 (5):4183–4194
Xuan H, Wei S, Feng Y, Liu D, Li Y (2019) Bi-level programming model and algorithm for VNF deployment with data centers placement. IEEE Access 7:185760–185772
Mekikis P, Ramantas K, Antonopoulos A, Kartsakli E, Sanabriarusso L, Serra J, Pubill D, Verikoukis C (2020) NFV-Enabled experimental platform for 5g tactile internet support in industrial environments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 16(3):1895–1903
Baktir AC, Ozgovde A, Ersoy C (2017) How can edge computing benefit from software-defined networking: a survey, use cases, and future directions. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 19(4):2359–2391. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2717482. Fourthquarter
Sukjin C, Joonwoo K, Sangheon P (2018) Optimal task offloading and resource allocation in software-defined vehicular edge computing. In: 2018 International conference on information and communication technology convergence (ICTC), pp 251–256
Xie Q, Wang Q, Yu N, Huang H, Jia X (2018) Dynamic service caching in mobile edge networks. Mobile adhoc and sensor systems 73–79
Zhao T, Hou IH, Wang S, Chan K (2018) Red/led: an asymptotically optimal and scalable online algorithm for service caching at the edge. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 36 (8):1857–1870
Chen L, Xu J, Ren S, Zhou P (2018) Spatio-temporal edge service placement: a bandit learning approach. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 17(12):8388–8401
Zeng F, Chen Q, Meng L, Wu J (2020) Volunteer assisted collaborative offloading and resource allocation in vehicular edge computing. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 1–11
Wang Y, Li Y, Wang W, et al (2016) A locality-based mobile caching policy for d2d-based content sharing network. In: GLOBECOM 2016—2016 IEEE global communications conference, pp 1–6
Su Z, Hui Y, Guo S (2016) D2d-based content delivery with parked vehicles in vehicular social networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 23(4):90–95
Zhou Z, Yu H, Xu C, et al (2018) Dependable content distribution in d2d-based cooperative vehicular networks: a big data-integrated coalition game approach. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 19(3):953–964
Wang S, Zhang Z, Yu R, et al (2017) Low-latency caching with auction game in vehicular edge computing. In: International conference on communications, pp 1–6
Hui Y, Su Z, Luan TH, et al (2019) Content in motion: an edge computing based relay scheme for content dissemination in urban vehicular networks. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 20(8):3115–3128
Chen M, Hao Y, Hu L, et al (2017) Green and mobility-aware caching in 5g networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 16(12):8347–8361
Su Z, Xu Q, Hou F, et al (2017) Edge caching for layered video contents in mobile social networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(10):2210–2221
Muller S, Atan O, Mihaela VDS, et al (2017) Context-aware proactive content caching with service differentiation in wireless networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 16(2):1024–1036
Kwak J, Kim Y, Le LB, et al (2018) Hybrid content caching in 5G wireless networks: cloud versus edge caching. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 17(5):3030–3045
Zhao H, Wang Y, Sun R (2018) Task proactive caching based computation offloading and resource allocation in mobile-edge computing systems. In: 2018 14th international wireless communications & mobile computing conference (IWCMC). IEEE, pp 232–237
Xu J, Chen L, Zhou P (2018) Joint service caching and task offloading for mobile edge computing in dense networks. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, pp 207–215
Li M, Rui L, Qiu X, Guo S, Yu X (2019) Design of a service caching and task offloading mechanism in smart grid edge network. In: International conference on wireless communications and mobile computing, pp 249–254
Tran T X, Chan K, Pompili D (2019) COSTA: cost-aware service caching and task offloading assignment in mobile-edge computing. Sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks 1–9
Bi S, Huang L, Zhang YA (2020) Joint optimization of service caching placement and computation offloading in mobile edge computing system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 19(7):4947–4963
Zhang K, Mao Y, Leng S, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2016) Optimal delay constrained offloading for vehicular edge computing networks. In: International conference on communications, pp 1–6
Kao Y, Krishnamachari B, Ra M, Bai F (2017) Hermes: latency optimal task assignment for resource-constrained mobile computing. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 16(11):3056–3069
Deng X, Li J, Liu E, Zhang H (2020) Task allocation algorithm and optimization model on edge collaboration. J Syst Archit 101778
Deng X, Luo J, He L, Liu Q, Li X, Cai L (2019) Cooperative channel allocation and scheduling in multi-interface wireless mesh networks. Peer-to-peer Networking and Applications 12(1):1–12
Zeng F, Ren Y, Deng X, Li W (2018) Cost-effective edge server placement in wireless metropolitan area networks. Sensors 19(1):32
Jammal M, Singh T, Shami A, Asal R, Li Y (2014) Software defined networking: state of the art and research challenges. Comput Netw 72:74–98
Huang X, Yu R, Kang J, Zhang Y (2017) Distributed reputation management for secure and efficient vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Access 5:25408–25420
Zhang H, Xiao Y, Bu S, Niyato D, Yu R, Han Z (2017) Computing resource allocation in three-tier IoT fog networks: a joint optimization approach combining stackelberg game and matching. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 4(5):1204–1215
Wang R, Zeng F, Yao L, Wu J (2020) Game-theoretic algorithm designs and analysis for interactions among contributors in mobile crowdsourcing with word of mouth. IEEE Internet of Things Journal (Early Access) https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2989745
Maharjan S, Zhu Q, Zhang Y, Gjessing S, Basar T (2013) Dependable demand response management in the smart grid: a Stackelberg game approach. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 4(1):120–132
Rosen JB (1965) Existense and uniqueness of equilibrium points for concaven-person N-person games. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 520–534
Zhang K, Mao Y, Leng S, Zhao Q, Li L, Peng X, Pan L, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2016) Energy-efficient offloading for mobile edge computing in 5G heterogeneous networks. IEEE Access 4:5896–5907
Hao Y, Chen M, Hu L, et al (2018) Energy efficient task caching and offloading for mobile edge computing. IEEE Access 6(99):11365–11373
You C, Huang K, Chae H, Kim B (2017) Energy-Ecient Resource allocation for mobile edge computation offloading. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 16(3):1397–1411
Chen M, Liang B, Dong M (2017) Joint offoading decision and resource allocation for multi-user multi-task mobile cloud. In: International conference on communications, pp 1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, F., Chen, Y., Yao, L. et al. A novel reputation incentive mechanism and game theory analysis for service caching in software-defined vehicle edge computing. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 467–481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00985-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00985-4