Abstract
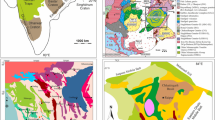
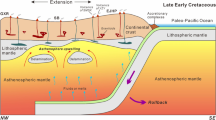
Subduction of Neo-Tethys oceanic lithosphere beneath the Iranian plate during the Mesozoic formed several igneous bodies of ultramafic to intermediate and felsic composition. Intrusion of these magmas into a regional metamorphic sequence (the Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone) caused partial melting and formation of migmatites with meta-pelitic protoliths. The Alvand complex (west Iran) is a unique area comprising migmatites of both mafic and pelitic protoliths. In this area, the gabbroic rocks contain veins of leucosome at their contact with pyroxenite and olivine gabbro. These leucosomes are geochemically and mineralogically different from leucosomes of the meta-pelitic migmatites and clearly show properties of I-type granites. Microscopic observations and whole rock compositions of the mafic migmatite leucosomes show that migmatization occurred through partial melting of biotite, hornblende and plagioclase. Thermobarometric calculations indicate 800 °C and 3.7 kbar for partial melting, although phase diagram modeling demonstrates that the presence of water could decrease the solidus temperature by about 40 °C. Our results suggest an asthenospheric magma upwelling as the source of heat for partial melting of the gabbroic rock during subduction of Neo-Tethys oceanic crust under the western edge of the Iranian plate. The present study also reveals relationships between migmatization and formation of S- and I -type granites in the area.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliani F, Maanijou M, Sabouri Z, Sepah AA (2012) Petrology, geochemistry and geotectonic environment of the Alvand intrusive complex, Hamedan, Iran. Chem Erde 72:363–383
Altherr R, Siebel W (2002) I-type plutonism in a continental back-arc setting: Miocene granitoids and monzonites from the Central Aegean Sea, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 143:397–415
Amidi M, Majidi B (1977) Geology map of Hamedan (1: 250,000). Geological survey of Iran, Tehran
Anders E, Grevesse N (1989) Abundances of the elements: meteoritic and solar. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:197–214
Azizi H, Asahara Y (2013) Juvenile granite in the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, NW Iran: late Jurassic–early cretaceous arc–continent collision. Int Geol Rev 55:1523–1540
Azizi H, Jahangiri A (2008) Cretaceous subduction-related volcanism in the northern Sanandaj-Sirjan zone. Iran J Geodyn 454:178–190
Baharifar A, Moinevaziri H, Bellon H, Piqué A (2004) The crystalline complexes of Hamadan (Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, western Iran): metasedimentary Mesozoic sequences affected by late cretaceous tectono-metamorphic and plutonic events. Compt Rendus Geosci 336:1443–1452
Baharifar A, Whitney DL, Pang K, Chung SY, Iizuka Y (2019) Petrology, geothermobarometry, and P-T path of spinel-bearing symplectite migmatites from the Simin area, Hamedan, Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, Iran. Turk J Earth Sci 28:275–298
Beard JB, Lofgren GE (1991) Dehydration melting and water saturated melting of basaltic and andesitic greenstones and amphibolites at 1, 3 and 6.9 kb. J Petrol 32:365–401
Berberian M (1981) Generalized tectonic map of Iran. Geological Survey of Iran, Tehran
Bhadra S, Bhattacharya A (2007) The barometer tremolite + tschermakite + 2 albite = 2 pargasite + 8 quartz: constraints from experimental data at unit silica activity, with application to garnet-free natural assemblages. Am Mineral 92:491–502
Blundy J, Wood B (2003) Partitioning of trace elements between crystals and melts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 210:383–397
Brown M, Averkin YA, Mclellan EL, Sawyer EW (1995) Melt segregation in migmatites. J Geophys Res 100:655–679
Bucher K, Grapes R (2011) Petrogenesis of metamorphic rocks. Springer, Berlin
de Capitani C, Petrakakis K (2010) The computation of equilibrium assemblage diagrams with Theriak/domino software. Am Mineral 95:1006–1016
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1963) Rock forming minerals, volume 4A, framework silicates. Wiley, New York
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1982) Rock forming minerals, vol 3A, Micas. Longman, London
Diener JFA, White RW, Holland TJB (2007) A new thermodynamic model for clino- and orthoamphiboles in the system Na2O–CaO–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O–O. J Metamorph Geol 25:631–656
Droop GTR (1987) A general equation for estimating Fe3+ concentrations in ferromagnesian silicates and oxides from microprobe analyses using stoichiometric criteria. Mineral Mag 51:431–435
Eshraghi SA, Mahmoudi Gharai M (2003) Geologic map of the Tuyserkan area. (1: 100,000). Geological survey of Iran, Tehran
Farhudi G (1978) A comparison of Zagros geology to island arcs. J Geol 86:323–334
Fornelli A, Piccarreta G, Del Moro A, Acquafredda P (2002) Multi-stage melting in the lower crust of the serre (southern Italy). J Petrol 43:2191–2217
Gao P, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF (2016) Experimental melts from crustal rocks: a lithochemical constraint on granite petrogenesis. Lithos 266–267:133–157
Ghasemi A, Talbot CJ (2006) A new tectonic scenario for the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 26:683–693
Golonka J (2004) Plate tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Eurasia in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. Tectonophysics 38:235–273
Graphchikov AA, Konilov AN, Clemens JD (1999) Biotite dehydration, partial melting, and fluid composition: experiments in the system KAlO2-FeO-MgO-SiO2-H2O-CO2. Am Mineral 84:15–26
Green E, Holland T, Powell R (2007) An order-disorder model for omphacitic pyroxenes in the system jadeite-diopside-hedenbergite-acmite, with applications to eclogitic rocks. Am Mineral 92:1181–1189
Greenfield JE, Clarke GL, White RW (1998) A sequence of partial melting reactions at Mt Stafford, Central Australia. J Metamorph Geol 16:363–378
Hansen E, Johansson L, Andersson J, La Barge L, Harlov D, Möller C, Vincent S (2015) Partial melting in amphibolites in a deep section of the Sveconorwegian Orogen, SW Sweden. Lithos 236:27–45
Harris NBW, Inger S (1992) Trace element modelling of pelite-derived granites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 110:46–56
Harris NBW, Pearce JA, Tindle AG (1986) Geochemical characteristics of collision zone magmatism. In: Coward MP, Ries AC (eds) Collision tectonics. Geological Society Special Publication, London, pp 67–81
Hassanzadeh J, Wernicke B (2016) The Neotethyan Sanadaj–Sirjan zone of Iran as an archetype for passive margin-arc transitions. Tectonics 35:586–621
Hassanzadeh J, Stockli DF, Horton BK, Axen GJ, Stockli LD, Grove M, Walker JD (2008) U-Pb zircon geochronology of late Neoproterozoic–early Cambrian granitoids in Iran: implications for paleogeography, magmatism, and exhumation history of Iranian basement. Tectonophysics 451:71–96
Hawthorn FC, Oberti R (2007) Classification of the amphiboles. Rev Mineral Geochem 67:55–88
Herron MM (1988) Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data. J Sediment Petrol 58:820–829
Hobson A, Bussy F, Hernandez J (1998) Shallow-level migmatization of gabbros in a metamorphic contact aureole, Fuerteventura basal complex, Canary Islands. J Petrol 39:1025–1037
Holland TJB, Blundy J (1994) Non-ideal interactions in calcic amphiboles and their bearing on amphibole-plagioclase thermometry. Contrib Mineral Petrol 116:433–447
Holland TJB, Powell R (2003) Activity–composition relations for phases in petrological calculations: an asymmetric multicomponent formulation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 145:492–501
Hu Z, Zhang Y, Hu R, Wang J, Siebel W, Chen F (2016) Amphibole-bearing migmatite in north Dabie, eastern China: water fluxed melting of the orogenic crust. J Asian Earth Sci 125:100–116
Johannes W, Holtz F, Möller P (1995) REE distribution in some layered migmatites: constraints on their petrogenesis. Lithos 35:139–152
Jørgensen TRC, Tinkham DK, Lesher CM (2019) Low-pressure and high-temperature metamorphism of basalts: insights from the Sudbury impact melt sheet aureole and thermodynamic modelling. J Metamorph Geol 37:271–313
Jung S, Mezger K, Masberg P, Hoffer E, Hoernes S (1998) Petrology of an intrusion-related high-grade migmatite: implications for partial melting of metasedimentary rocks and leucosome-forming processes. J Metamorph Geol 163:425–445
Lundstrom CC, Shaw HF, Ryerson FJ, Phinney DL, Gill JB, Williams Q (1994) Compositional controls on the partitioning of U, Th, Ba, Pb, Sr, and Zr between clinopyroxene and haplobasaltic melts: implications for uranium series disequilibria in basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 128:407–423
Mahmoudi S, Baharifar A (2018) Phase equilibria and P-T-t path of metapelitic rocks in SE-Hamedan, Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, Iran. Mineral Petrol 113:135–154
Mahmoudi S, Corfu F, Masoudi F, Mehrabi B, Mohajjel M (2011) U–Pb dating and emplacement history of granitoid plutons in the northern Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 41:238–249
Mahood GA, Hildreth EW (1983) Large partition coefficients for trace elements in high-silica rhyolites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:11–30
Masberg P, Mihm D, Jung S (2005) Major and trace element and isotopic (Sr, Nd, O) constraints for pan–African crustally contaminated grey granite gneisses from the southern Kaoko belt, Namibia. Lithos 81:25–50
McDermott F, Harris NBW, Hawkesworth CJ (1996) Geochemical constraints on crustal anatexis: a case study from the pan-African Damara granitoids of Namibia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 123:406–423
Middlemost EAK (1994) Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci Rev 37:215–224
Miri M, Sepahi A, Aliani F, Maanijou M (2016) Chemical zoning of Ca-amphiboles in amphibolites, from the Hamedan area, West Iran. Arab J Geosci 9(13):619
Mohajjel M, Fergusson CL (2014) Jurassic to Cenozoic tectonics of the Zagros Orogen in northwestern Iran. Int Geol Revs 56:263–287
Mohajjel M, Fergusson CL, Sahandi MR (2003) Cretaceous-tertiary convergence and continental collision, Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, Western Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 21:397–412
Morimoto N, Fabrise J, Ferguson A, Ginzburg IV, Ross M, Seifert FA, Gottardi G (1988) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Am Mineral 173:1123–1133
O’Connor JT (1965) A classification for quartz-rich igneous rocks based on feldspar ratios. US Geol Surv Prof Pap 525:79–84
Otamendi JE, Ducea MN, Tibaldi AM, Bergantz GW, de la Rosa JD, Vujovich GI (2009) Generation of tonalitic and dioritic magmas by coupled partial melting of gabbroic and metasedimentary rocks within the deep crust of the Famatinian magmatic arc, Argentina. J Petrol 50:841–873
Park AK (1983) Lit-par-lit migmatite fabrics in a metagabbro-anorthosite complex, Sygnefjell, Jotunheim, South Norway. In: Atherton CD, Gribble MP (eds) Migmatites, melting and metamorphism. Shiva, Nantwich, pp 264–276
Patiño Douce AE (1999) What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas? Geol Soc Spec Publ 168:55–75
Pattison DRM (1991) Infiltration–driven dehydration and anatexis in granulite facies metagabbro, Grenville Province, Ontario, Canada. J Metamorph Geol 9:315–332
Pedersen T, Heeremans M, Van Der Beek P (1998) Models of crustal anatexis in volcanic rifts: applications to southern Finland and the Oslo Graben, Southeast Norway. Geophys J Int 132:239–255
Rushmer T (1991) Partial melting of two amphibolites: contrasting experimental results under fluid-absent conditions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 107:41–59
Saki A (2010) Mineralogy, geochemistry and geodynamic setting of the granitoids from NW Iran. Geol J 45:1–16
Saki A (2011) Formation of spinel-cordierite-plagioclase symplectites replacing andalusite in metapelitic migmatites of the Alvand aureole, Iran. Geol Mag 148:423–434
Saki A, Moazzen M, Baharifar A (2012) Migmatite microstructures and partial melting of Hamadan metapelitic rocks, Alvand contact aureole, western Iran. Int Geol Rev 54:1229–1240
Sawyer EW (1998) The role of partial melting and fractional crystallization in determining discordant migmatite leucosome compositions. J Petrol 28:445–473
Sawyer EW (2008) Working with migmatites: nomenclature for the constituent parts. In: Sawyer EW (ed) Working with migmatites. Miner Ass Canada, Quebec, pp 1–28
Schumacher JC (1997) The estimation of the proportion of ferric iron in the electron-microprobe analysis of amphiboles. Can Mineral 35:238–246
Sears JW, George GMS, Winne JC (2005) Continental rift systems and anorogenic magmatism. Lithos 80:147–154
Sepahi AA, Whitney DL, Baharifar AA (2004) Petrogenesis of andalusite-kyanite-sillimanite veins and host rocks, Sanandaj-Sirijan metamorphic belt, Hamadan, Iran. J Metamorph Geol 22:119–134
Sepahi AA, Jafari SR, Mani-Kashani S (2009) Low pressure migmatites from the Sanandaj-Sirjan Metamorphic Belt in the Hamedan region, Iran. Geol Carpath 602:107–119
Sepahi AA, Borzoei K, Salami S (2013) Mineral chemistry and thermobarometry of plutonic, metamorphic and anatectic rocks from the Tueyserkan area (Hamedan, Iran). Geol Q 57:515–526
Sepahi AA, Shahbazi H, Siebel W, Ranin A (2014) Geochronology of plutonic rocks from the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, Iran and new zircon and titanite U–Th–Pb age for granitoids from the Marivan pluton. Geochronometria 413:207–215
Sepahi AA, Jafari SR, Osanai Y, Shahbazi H, Moazzen M (2019) Age, petrologic significance and provenance analysis of the Hamedan low-pressure migmatites; Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, West Iran. Int Geol Rev 61(12):1446–1461
Shahbazi H, Siebel W, Pourmoafee M, Ghorbani M, Sepahi A, Shang C, Vosough Abedini M (2010) Geochemistry and U–Pb zircon geochronology of the Alvand plutonic complex in Sanandaj–Sirjan zone Iran: new evidence for Jurassic magmatism. J Asian Earth Sci 39:668–683
Shakerardakani F, Neubauer F, Masoudi F, Mehrabi B, Liu X, Dong Y, Mohajjel M, Monfaredi B, Friedl G (2015) Pan-African basement and Mesozoic gabbro in the Zagros orogenic belt in the Dorud–Azna region NW Iran: laser- ablation ICP–MS zircon ages and geochemistry. Tectonophysics 647:146–171
Slagstad T, Jamieson RA, Culshaw NG (2005) Formation, crystallization, and migration of melt in the mid-orogenic crust: Muskoka domain migmatites, Grenville province, Ontario. J Petrol 465:893–919
Springer W, Seck HA (1997) Partial fusion of basic granulites at 5 to 15 kbar: implications for the origin of TTG magmas. Contrib Mineral Petrol 127:30–45
Stöcklin J (1974) Possible ancient continental margins in Iran. In: Burk CA, Drake CL (eds) The geology of continental margins. Springer, Berlin, pp 873–887
Sylvester PJ (1998) Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 45:29–44
Thompson RN (1982) British tertiary province. Scott J Geol 18:49–107
Thompson AB, Ellis DJ (1994) CaO+MgO+Al2O3+SiO2+H2O to 35 kbar: amphibole, talc and zoisite dehydration and melting reactions in the silica-excess part of the system and their possible significance in subduction zones, amphibolite melting and magma fractionation. Am J Sci 294:1229–1289
Vernon RH (2004) A practical guide to rock microstructure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vernon RH, Richards SW, Collins WJ (2001) Migmatite-granite relationships: origin of the Cooma ganodiorite magma, Lachlan Fold Belt, Australia. Phys Chem Earth 26:267–271
Wallis D, Phillips RJ, Lloyd GE (2014) Evolution of the eastern Karakoram metamorphic complex, Ladakh, NW India, and its relationship to magmatism and regional tectonics. Tectonophysics 626:41–52
Weinberg RF, Hasalová P (2014) Water–fluxed melting of the continental crust: a review. Lithos 212-215:158–188
White RW, Powell R, Holland TJB (2001) Calculation of partial melting equilibria in the system Na2O–CaO–K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O (NCKFMASH). J Metamorph Geol 19:139–153
White RW, Powell R, Holland TJB (2007) Progress relating to calculation of partial melting equilibria for metapelites. J Metamorph Geol 25:511–527
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95:185–187
Wimmenauer W, Bryhni I (2007) A systematic nomenclature for metamorphic rocks: 6. Migmatites and related rocks. A proposal on behalf of the IUGS subcommission on the systematics of metamorphic rocks (SCMR). Recommendations web version. https://www.bgs.ac.uk/scmr/products.html
Wolf MB, Wyllie PJ (1994) Dehydration-melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar: the effects of temperature and time. Contrib Mineral Petrol 115:369–383
Wolff PE, Koepke J, Feig ST (2013) The reaction mechanism of fluid-induced partial melting of gabbro in the oceanic crust. Eur J Mineral 25:279–298
Yajam S, Monterro P, Scarrow JH, Ghalamghash J, Razavi SMH, Bea F (2015) The spatial and compositional evolution of the late Jurassic Ghorveh-Dehgolan plutons of the Zagros Orogen, Iran: SHRIMP zircon U-Pb and Sr and Nd isotope evidence. Geol Acta 13:25–43
Yang TN, Chen JL, Liang MJ, Xin D, Aghazadeh M, Hou ZQ, Zhang HR (2018) Two plutonic complexes of the Sanandaj-Sirjan magmatic-metamorphic belt record Jurassic to early cretaceous subduction of an old neo-Tethys beneath the Iran microplate. Gondwana Res 62:246–268
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Activation laboratories, Ontario, Canada, for ICP-MS analyses and Potsdam University, Germany, for EPMA analyses. We wish to thank Kim Jessop and an anonymous expert for constructive reviews and journal editors Andreas Möller and Lutz Nasdala for helpful comments that greatly improved the manuscript. This research was supported by the Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz (grant SCU.EG98.44295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: A. Möller
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saki, A., Miri, M. & Oberhänsli, R. High temperature – low pressure metamorphism during subduction of Neo-Tethys beneath the Iranian plate: evidence for mafic migmatite formation in the Alvand complex (western Iran). Miner Petrol 114, 539–557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-020-00721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-020-00721-z