Abstract
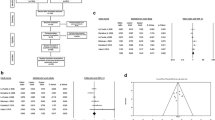
Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a destructive neuropsychiatric illness affecting millions of people worldwide. The correlation between RELN gene polymorphisms and SCZ was investigated by previous researches, though the results remained conflicting. Based on the available studies, we conducted this meta-analysis to provide a more comprehensive outcome on whether the RELN gene polymorphisms (rs7341475 and rs262355) are associated with SCZ. A total of 15 studies with 25,403 subjects (9047 cases and 16,356 controls) retrieved from PubMed, ScienceDirect, EMBASE, Wiley, BMC, Cochrane, Springer, MDPI, SAGE, and Google Scholar up to June 2020 were included. Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.3. The heterogeneity was checked using I2 statistics and Q-test, whereas publication bias was also measured. The rs7341475 polymorphism showed a significantly lower risk for SCZ for the allele (A vs. G: OR = 0.93, 95%CI = 0.87–0.99), codominant 1 (AG vs. GG: OR = 0.92, 95%CI = 0.85–0.99), dominant model (AA+AG vs. GG: OR = 0.92, 95%CI = 0.86–0.98), and over dominant model (AG vs. AA+GG: OR = 0.92, 95%Cl = 0.86–0.99). The allele, codominant model 1, and dominant models remained statistically significant after the correction of the Bonferroni (p < 0.025). Subgroup analysis confirmed the association of allele and dominant models in the Caucasian after Bonferroni correction. For rs262355 polymorphism, a significantly increased risk of SCZ was found only in Caucasians for codominant 2, dominant, and allele models, but significance exists only for the allele model after Bonferroni correction. Publication bias was found in the case of codominant 2 and recessive models for rs7341475 in the overall population, but this publication was not found after performing the Bonferroni correction or after performing the subgroup analysis. No such publication was found for rs262355. The results suggest that RELN rs7341475 is associated with a lower risk of SCZ in the overall population and Caucasian population, but rs262355 is associated with an increased risk of SCZ only in the Caucasian population.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arioka Y, Shishido E, Kubo H, Kushima I, Yoshimi A, Kimura H, Ishizuka K, Aleksic B, Maeda T, Ishikawa M, Kuzumaki N, Okano H, Mori D, Ozaki N (2018) Single-cell trajectory analysis of human homogenous neurons carrying a rare RELN variant. Transl Psychiatry 8(1):129
Bai W, Fu Y, Yu X, Zhu B, Duan R, Yu Y, Kou C (2019) Association between RELN polymorphisms and schizophrenia in a Han population from Northeast China. Psychiatr Genet 29(6):232–236
Bocharova AV, Stepanov VA, Marusin AV et al (2017) Association study of genetic markers of schizophrenia and its cognitive endophenotypes. Genetika 53(1):100–108
Cai LS, Huang JW (2018) Schizophrenia and risk of dementia: a meta-analysis study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 14:2047–2055
Chen N, Bao Y, Xue Y, Sun Y, Hu D, Meng S, Lu L, Shi J (2017) Meta-analyses of RELN variants in neuropsychiatric disorders. Behav Brain Res 332:110–119
Costain G, Lionel AC, Merico D, Forsythe P, Russell K, Lowther C, Yuen T, Husted J, Stavropoulos DJ, Speevak M, Chow EWC, Marshall CR, Scherer SW, Bassett AS (2013) Pathogenic rare copy number variants in community-based schizophrenia suggest a potential role for clinical microarrays. Hum Mol Genet 22(22):4485–4501
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M et al (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Esan OB, Ojagbemi A, Gureje O (2012) Epidemiology of schizophrenia--an update with a focus on developing countries. Int Rev Psychiatry 24(5):387–392
Falkai P, Rossner MJ, Schulze TG, Hasan A, Brzózka MM, Malchow B, Honer WG, Schmitt A (2015) Kraepelin revisited: schizophrenia from degeneration to failed regeneration. Mol Psychiatry 20(6):671–676
Folsom TD, Fatemi SH (2013) The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuropharmacology 68:122–135
Fromer M, Pocklington AJ, Kavanagh DH, Williams HJ, Dwyer S, Gormley P, Georgieva L, Rees E, Palta P, Ruderfer DM, Carrera N, Humphreys I, Johnson JS, Roussos P, Barker DD, Banks E, Milanova V, Grant SG, Hannon E, Rose SA, Chambert K, Mahajan M, Scolnick EM, Moran JL, Kirov G, Palotie A, McCarroll SA, Holmans P, Sklar P, Owen MJ, Purcell SM, O’Donovan MC (2014) De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature 506(7487):179–184
Galaktionova DI, Gareeva AE, Khusnutdinova EK et al (2014) The association of polymorphisms in SLC18A1, TPH1 and RELN genes with risk of paranoid schizophrenia. Mol Biol (Mosk) 48(4):629–639
Goeman JJ, Solari A (2014) Multiple hypothesis testing in genomics. Stat Med 33(11):1946–1978
Guidotti A, Grayson DR, Caruncho HJ (2016) Epigenetic RELN dysfunction in schizophrenia and related neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 10:89
Halldorsdottir T, Binder EB (2017) Gene × environment interactions: from molecular mechanisms to behavior. Annu Rev Psychol 68:215–241
Herz J, Chen Y (2006) Reelin, lipoprotein receptors and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:850–859
Hong J, Bang M (2020) Anti-inflammatory strategies for schizophrenia: a review of evidence for therapeutic applications and drug repurposing. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 18(1):10–24
Huang T, Shu Y, Cai YD (2015) Genetic differences among ethnic groups. BMC Genomics 16:1093
Ishii K, Kubo KI, Nakajima K (2016) Reelin and neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 10:229
Kähler AK, Djurovic S, Kulle B, Jönsson EG, Agartz I, Hall H, Opjordsmoen S, Jakobsen KD, Hansen T, Melle I, Werge T, Steen VM, Andreassen OA (2008) Association analysis of schizophrenia on 18 genes involved in neuronal migration: MDGA1 as a new susceptibility gene. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(7):1089–1100
Kahn RS, Sommer IE, Murray RM, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Cannon TD, O’Donovan M, Correll CU, Kane JM, van Os J, Insel TR (2015) Schizophrenia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15067
Li W, Song X, Zhang H, Yang Y, Jiang C, Xiao B, Li W, Yang G, Zhao J, Guo W, Lv L (2011) Association study of RELN polymorphisms with schizophrenia in Han Chinese population. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(6):1505–1511
Li M, Luo XJ, Xiao X, Shi L, Liu XY, Yin LD, Ma XY, Yang SY, Pu XF, Yu J, Diao HB, Shi H, Su B (2013) Analysis of common genetic variants identifies RELN as a risk gene for schizophrenia in Chinese population. World J Biol Psychiatry 14(2):91–99
Li W, Guo X, Xiao S (2015) Evaluating the relationship between reelin gene variants (rs7341475 and rs262355) and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Lett 16(609):42–47
Lichtenstein P, Yip BH, Björk C, Pawitan Y, Cannon TD, Sullivan PF, Hultman CM (2009) Common genetic determinants of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in Swedish families: a population-based study. Lancet 373(9659):234–239
Liu Y, Chen PL, McGrath J, Wolyniec P, Fallin D, Nestadt G, Liang KY, Pulver A, Valle D, Avramopoulos D (2010) Replication of an association of a common variant in the Reelin gene (RELN) with schizophrenia in Ashkenazi Jewish women. Psychiatr Genet 20(4):184–186
Liu XY, Li M, Yang SY, Su B, Yin LD (2011) Association of RELN SNP rs7341475 with schizophrenia in the Chinese population. Dongwuxue Yanjiu 32(5):499–503
Lu YF, Goldstein DB, Angrist M, Cavalleri G (2014) Personalized medicine and human genetic diversity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 4(9):a008581
Luo X, Chen S, Xue L, Chen JH, Shi YW, Zhao H (2019) SNP variation of RELN gene and schizophrenia in a Chinese population: a hospital-based case-control study. Front Genet 10:175
Mallet J, Le Strat Y, Dubertret C et al (2020) Polygenic risk scores shed light on the relationship between schizophrenia and cognitive functioning: review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med 9(2):341
Man DW (2006) Cognitive functions among Hong Kong Chinese people with schizophrenia. Int J Rehabil Res 29(3):261–265
McCutcheon RA, Krystal JH, Howes OD (2020) Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry 19(1):15–33
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A (2016) Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev 5(1):210
Perkovic MN, Erjavec GN, Strac DS et al (2017) Theranostic biomarkers for schizophrenia. Int J Mol Sci 18(4):733
Prasad S, Bhatia T, Kukshal P, Nimgaonkar VL, Deshpande SN, Thelma BK (2017) Attempts to replicate genetic associations with schizophrenia in a cohort from north India. NPJ Schizophr 3(1):28
Prohaska A, Racimo F, Schork AJ, Sikora M, Stern AJ, Ilardo M, Allentoft ME, Folkersen L, Buil A, Moreno-Mayar JV, Korneliussen T, Geschwind D, Ingason A, Werge T, Nielsen R, Willerslev E (2019) Human disease variation in the light of population genomics. Cell 177(1):115–131
Quattrocchi CC, Wannenes F, Persico AM, Ciafré SA, D’Arcangelo G, Farace MG, Keller F (2002) Reelin is a serine protease of the extracellular matrix [published correction appears in J Biol Chem 2002 Mar 29;277(13):11616]. J Biol Chem 277(1):303–309
Ripke S, Neale B, Corvin A et al (2014) Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 511(7510):421–427
Rogers JT, Rusiana I, Trotter J, Zhao L, Donaldson E, Pak DTS, Babus LW, Peters M, Banko JL, Chavis P, Rebeck GW, Hoe HS, Weeber EJ (2011) Reelin supplementation enhances cognitive ability, synaptic plasticity, and dendritic spine density. Learn Mem 18(9):558–564
Shifman S, Johannesson M, Bronstein M, Chen SX, Collier DA, Craddock NJ, Kendler KS, Li T, O’Donovan M, O’Neill FA, Owen MJ, Walsh D, Weinberger DR, Sun C, Flint J, Darvasi A (2008) Genome-wide association identifies a common variant in the reelin gene that increases the risk of schizophrenia only in women. PLoS Genet 4(2):e28
Sobue A, Kushima I, Nagai T, Shan W, Kohno T, Aleksic B, Aoyama Y, Mori D, Arioka Y, Kawano N, Yamamoto M, Hattori M, Nabeshima T, Yamada K, Ozaki N (2018) Genetic and animal model analyses reveal the pathogenic role of a novel deletion of RELN in schizophrenia. Sci Rep 8(1):13046
Sozuguzel MD, Sazci A, Yildiz M (2019) Female gender specific association of the Reelin (RELN) gene rs7341475 variant with schizophrenia. Mol Biol Rep 46(3):3411–3416
Stepanov VA, Bocharova AV, Saduakassova KZ, Marusin AV, Koneva LA, Vagaitseva KV, Svyatova GS (2015) Replicative study of susceptibility to childhood-onset schizophrenia in Kazakhs. Genetika 51(2):227–235
Tissir F, Goffinet AM (2003) Reelin and brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(6):496–505
Tost H, Lipska BK, Vakkalanka R, Lemaitre H, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Kleinman JE, Marenco S, Weinberger DR (2010) No effect of a common allelic variant in the reelin gene on intermediate phenotype measures of brain structure, brain function, and gene expression. Biol Psychiatry 68(1):105–107
Viertiö S, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Perälä J, Saarni SI, Koskinen S, Sihvonen M, Lönnqvist J, Suvisaari J (2012) Activities of daily living, social functioning and their determinants in persons with psychotic disorder. Eur Psychiatry 27(6):409–415
Walsh T, McClellan JM, McCarthy SE et al (2008) Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science 320(5875):539–543
Wedenoja J, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Suvisaari J, Loukola A, Paunio T, Partonen T, Varilo T, Lönnqvist J, Peltonen L (2010) Replication of association between working memory and Reelin, a potential modifier gene in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 67(10):983–991
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell DL, et al. (2014) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses
World health organization (WHO), (2020) Schizophrenia, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia; 2020 [Accessed 2.06.20]
Yang XB, Kang C, Liu H, Yang J (2013) Association study of the reelin (RELN) gene with Chinese Va schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet 23(3):138
Zhou Z, Hu Z, Zhang L et al (2016) Identification of RELN variation p.Thr3192Ser in a Chinese family with schizophrenia. Sci Rep 6:24327
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM and MAA and MSI were equally involved in the conduction of the meta-analysis. SM and MAA did the initial literature search. The manuscript was initially drafted by SM and MAA, whereas MSI designed the concept, analyzed the data, and revised the manuscript. The final manuscript was read and accepted by all contributors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 4837 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marzan, S., Aziz, M. & Islam, M.S. Association Between REELIN Gene Polymorphisms (rs7341475 and rs262355) and Risk of Schizophrenia: an Updated Meta-analysis. J Mol Neurosci 71, 675–690 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01696-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01696-4