Abstract
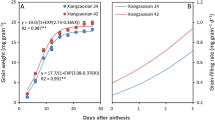
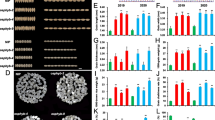
The Wx gene is the major gene controlling amylose synthesis in rice endosperm. In a previous study, we were able to separate the Wxa allele into two functional Wx alleles, Wxg2 and Wxg3, according to their amylose phenotypes and a T/C nucleotide polymorphism in exon 10. Subsequent studies revealed that this Wx allelic variation also plays a vital role in regulating other important starch properties. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms related to the rice grain proteome have remained unclear. To elucidate this, we used two rice single-segment substitution lines harboring different Wx alleles, Wxg2 and Wxg3, in comparative proteomic studies. On the basis of iTRAQ quantitative proteomics, we identified a total of 185 proteins as differentially accumulated between the Wxg2 and Wxg3 lines. Gene Ontology functional analysis revealed that a high proportion of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) are involved in metabolic and cellular biological processes. Further functional and pathway enrichment analyses indicated that relevant functions of the DEPs on protein degradation and binding may play important roles in distinguishing the Wxg2 and Wxg3 alleles. The present results may provide comprehensive insights into the molecular regulatory mechanisms of starch biosynthesis as influenced by the Wxg2 and Wxg3 alleles in rice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen MH, Bergman CJ, Pinsona SRM, Fjellstrom RG (2008) Waxy gene haplotypes: associations with apparent amylose content and the effect by the environment in an international rice germplasm collection. J Cereal Sci 47(3):536–545
Crofts N, Abe N, Oitome NF, Matsushima R, Hayashi M, Tetlow IJ, Emes MJ, Nakamura Y, Fujita N (2015) Amylopectin biosynthetic enzymes from developing rice seed form enzymatically active protein complexes. J Exp Bot 66(15):4469–4482
Fujita N (2014) Starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Agri-Biosc Monogr 4:1–18
Fulton DC, Stettler M, Mettler T, Vaughan CK, Li J, Francisco P, Gil M, Reinhold H, Eicke S, Messerli G, Dorken G, Halliday K, Smith AM, Smith SM, Zeeman SC (2008) Beta-amylase 4, a noncatalytic protein required for starch breakdown, acts upstream of three active beta-amylases in Arabidopsis chloroplasts. Plant Cell 20(4):1040–1058
Han Y, Cao H, Jiang J, Xu Y, Du J, Wang X, Yuan M, Wang Z, Xu Z, Chong K (2008) Rice ROOT ARCHITECTURE ASSOCIATED1 binds the proteasome subunit RPT4 and is degraded in a d-box and proteasome-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 148(2):843–855
Hayashi M, Crofts N, Oitome NF, Fujita N (2018) Analyses of starch biosynthetic protein complexes and starch properties from developing mutant rice seeds with minimal starch synthase activities. BMC Plant Biol 18(1):59
Hellmann H (2002) Plant development: regulation by protein degradation. Science 297(5582):793–797
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Liu F, Marsh RS, Kim S, Gan Q, Tetlow IJ, Emes MJ, James MG, Myers AM (2008) Starch biosynthetic enzymes from developing maize endosperm associate in multisubunit complexes. Plant Physiol 146(4):1892–1908
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Lin Q, Grimaud F, Planchot V, Keeling PL, James MG, Myers AM (2009) Proteins from multiple metabolic pathways associate with starch biosynthetic enzymes in high molecular weight complexes: a model for regulation of carbon allocation in maize amyloplasts. Plant Physiol 149(3):1541–1559
Hur YJ, Yi YB, Lee JH, Chung YS, Jung HW, Yun DJ, Kim KM, Park DS, Kim DH (2012) Molecular cloning and characterization of OsUPS, a U-box containing E3 ligase gene that respond to phosphate starvation in rice (Oryza sativa). Mol Biol Rep 39(5):5883–5888
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436(7052):793–800
Juliano BO (1985) Criteria and test for rice grain quality. In: Juliano BO (ed) Rice chemistry and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc., St. Paul, pp 443–513
Kurepa J, Smalle JA (2008) Structure, function and regulation of plant proteasomes. Biochimie 90(2):324–335
Li XM, Chao DY, Wu Y, Huang X (2015) Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermotolerance and adaptation of African rice. Nat Genet 47(7):827–833
Lim SD, Hwang JG, Han AR, Park YC, Lee C, Ok YS, Jang CS (2014) Positive regulation of rice RING E3 ligase OSHIR1 in arsenic and cadmium uptakes. Plant Mol Biol 85(4–5):365–379
Lin Q, Wang D, Dong H, Gu S, Cheng Z, Gong J, Qin Z, Jiang L, Li G, Wang JL, Wu F, Guo X, Zhang X, Lei C, Wang H, Wan J (2012) Rice APC/CTE controls tillering by mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1. Nat Commun 3:752
Liu F, Makhmoudova A, Lee EA, Wait R, Emes MJ, Tetlow IJ (2009) The amylose extender mutant of maize conditions novel protein–protein interactions between starch biosynthetic enzymes in amyloplasts. J Exp Bot 60(15):4423–4440
Liu F, Ahmed Z, Lee EA, Donner E, Liu Q, Ahmed R, Morell MK, Emes MJ, Tetlow IJ (2012) Allelic variants of the amylose extender mutation of maize demonstrate phenotypic variation in starch structure resulting from modified protein–protein interactions. J Exp Bot 63(3):1167–1183
Liu Q, Ning Y, Zhang Y, Yu N, Zhao C, Zhan X, Wu W, Chen D, Wei X, Wang GL, Cheng S, Cao L (2017) OsCUL3a negatively regulates cell death and immunity by degrading OsNPR1 in rice. Plant Cell 29(2):345–359
Lohmeier-Vogel EM, Kerk D, Nimick M, Wrobel S, Vickerman L, Muench DG, Moorhead GBG (2008) Arabidopsis At5g39790 encodes a chloroplast-localized, carbohydrate-binding, coiled-coil domain-containing putative scaffold protein. BMC Plant Biol 8(1):120
Matsushita A, Inoue H, Goto S, Nakayama A, Sugano S, Hayashi N, Takatsuji H (2013) Nuclear ubiquitin proteasome degradation affects WRKY45 function in the rice defense program. Plant J 73(2):302–313
Mikami I, Uwatoko N, Ikeda Y, Yamaguchi J, Hirano HY, Suzuki Y, Sano Y (2008) Allelic diversification at the wx locus in landraces of Asian rice. Theor Appl Genet 116(7):979–989
Nakamura Y, Ono M, Sawada T, Crofts N, Fujita N, Steup M (2017) Characterization of the functional interactions of plastidial starch phosphorylase and starch branching enzymes from rice endosperm during reserve starch biosynthesis. Plant Sci 264:83–95
Pang Y, Zhou X, Chen Y, Bao J (2018) Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing seeds in two indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars with different starch quality. J Agric Food Chem 66(11):3030–3037
Park YC, Lim SD, Moon Jun-Cheol, Jang CS (2019) A rice really interesting new gene H2-type E3 ligase, OsSIRH2-14, enhances salinity tolerance via ubiquitin/26S proteasome-mediated degradation of salt-related proteins. Plant Cell Environ 42(11):3061–3076
Peng C, Wang Y, Liu F, Ren Y, Zhou K, Lv J, Zheng M, Zhao S, Zhang L, Wang C, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo X, Bao Y, Wan J (2014) FLOURY ENDOSPERM6 encodes a CBM48 domain-containing protein involved in compound granule formation and starch synthesis in rice endosperm. Plant J 77(6):917–930
Sano Y (1984) Differential regulation of waxy gene expression in rice endosperm. Theor Appl Genet 68(5):467–473
Shi C, Ren Y, Liu L, Wang F, Zhang H, Tian P, Pan T, Wang Y, Jing R, Liu T, Wu F (2019) Ubiquitin specific protease 15 has an important role in regulating grain width and size in rice. Plant Physiol 181(1):381–391
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown ring-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39(5):623–630
Teng B, Zeng R, Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zhu H, Ding X, Li W, Zhang G (2012) Detection of allelic variation at the Wx locus with single-segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 30(1):583–595
Teng B, Zhang Y, Wu J, Cong X, Wang R, Han Y, Luo Z (2013) Association between allelic variation at the Waxy locus and starch physicochemical properties using single-segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Starch/Stärke 65(11–12):1069–1077
Teng B, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Wu J, Li Z, Luo Z, Yang J (2015) Comparison of amylopectin structure and activities of key starch synthesis enzymes in the grains of rice single-segment substitution lines with different Wx alleles. Plant Growth Regul 77(2):117–124
Teng B, Zhang Y, Du S, Wu J, Li Z, Luo Z, Yang J (2017) Crystalline, thermal and swelling properties of starches from single-segment substitution lines with different Wx alleles in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Sci Food Agric 97(1):108–114
Teng B, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Du S, Xi M, Song F, Ni J, Luo Z, Ni D (2018) Effects of different Wx alleles on amylopectin molecular structure and enzymatic hydrolysis properties of rice starch. Int J Food Prop 21(1):2772–2784
Tetlow IJ, Wait R, Lu ZX, Akkasaeng R, Bowsher CG, Esposito S, Kosar-Hashemi B, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2004) Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions. Plant Cell 16(3):694–708
Tetlow IJ, Beisel KG, Cameron S, Makhmoudova A, Liu F, Bresolin NS, Wait R, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2008) Analysis of protein complexes in wheat amyloplasts reveals functional interactions among starch biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Physiol 146(4):1878–1891
Wang ZY, Wu ZL, Xing YY, Zheng FG, Guo XL, Zhang WG, Hong MM (1990) Nucleotide sequence of rice waxy gene. Nucleic Acids Res 18(19):5898
Wang ZY, Zheng FQ, Shen GZ, Gao JP, Snusted DP, Li MG, Zhang JL, Hong MM (1995) The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J 7(4):613–622
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77(1):95–101
Zhang J, Nallamilli BR, Mujahid H, Peng Z (2010) OsMADS6 plays an essential role in endosperm nutrient accumulation and is subject to epigenetic regulation in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J 64(4):604–617
Zhang XQ, Hou P, Zhu HT, Li GD, Liu XG, Xie XM (2013) Knockout of the VPS22 component of the ESCRT-II complex in rice (Oryza sativa L.) causes chalky endosperm and early seedling lethality. Mol Biol Rep 40(5):3475–3481
Zhang Z, Zhao H, Huang F, Long J, Song G, Lin W (2019) The 14-3-3 protein GF14f negatively affects grain filling of inferior spikelets of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J 99(2):344–358
Zhou H, Wang L, Liu G, Meng X, Jing Y, Shu X, Kong X, Sun J, Yu H, Smith SM, Wu D, Li J (2016) Critical roles of soluble starch synthase SSIIIa and granule-bound starch synthase waxy in synthesizing resistant starch in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(45):12844–12849
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Program of Rice Genetic Breeding Key Laboratory of Anhui province, the Program of Rice Molecular Breeding International Joint Research Center and Joint Laboratory of Rice Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Temasek Academy of Life Sciences (SDKF-201901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BT and CZ conceived and designed the experiments; BT, CZ, and YZ performed the experiments and analyzed the data; BT wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, B., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, C. Quantitative analysis of allelic differences in the grain proteome between the Wxg2 and Wxg3 alleles in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 216, 150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02685-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02685-9