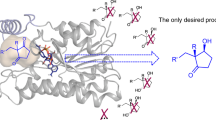
Abstract
Since the first discovery of old yellow enzyme 1 (OYE1) from Saccharomyces pastorianus in 1932, biocatalytic asymmetric reduction of activated alkenes by OYEs has become a valuable reaction in organic synthesis. To access stereocomplementary C=C-bond bioreduction, the mining of novel OYEs and especially the protein engineering of existing OYEs have been performed, which successfully achieved the stereocomplementary reduction in several cases and further raise the potential of applications. In this review, we analyzed the structures, active sites, and substrate recognition of OYEs, which are the bases for their substrate specificity and stereospecificity. Sequence similarity network of OYEs superfamily was also constructed to investigate the scope of characterized OYEs. The structure-guided engineering to switch the stereoselectivity of OYEs and thus access stereocomplementary bioreduction over the last decade (2009–2020) was then reviewed and discussed, which might give new insights into the mining and engineering of related biocatalysts.
Key points
• The sequence similarity network of OYEs superfamily was constructed and annotated.
• The structures and active sites of OYEs from different classes were compared.
• “Left/right” binding mode was used to explain the stereopreferences of OYEs.
• Structure-guided engineering of OYEs to switch their stereoselectivity was reviewed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato ED, Stewart JD (2015) Applications of protein engineering to members of the old yellow enzyme family. Biotechnol Adv 33(5):624–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.04.011
Aregger D, Peters C, Buller RM (2020) Characterization of the novel ene reductase Ppo-Er1 from paenibacillus polymyxa. Catalysts 10(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020254
Barna TM, Khan H, Bruce NC, Barsukov I, Scrutton NS, Moody PCE (2001) Crystal structure of pentaerythritol tetranitrate reductase: “flipped” binding geometries for steroid substrates in different redox states of the enzyme. J Mol Biol 310(2):433–447. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4779
Bechtold M, Brenna E, Femmer C, Gatti FG, Panke S, Parmeggiani F, Sacchetti A (2012) Biotechnological development of a practical synthesis of ethyl (S)-2-ethoxy-3-(p-methoxyphenyl)propanoate (EEHP): over 100-fold productivity increase from yeast whole cells to recombinant isolated enzymes. Org Process Res Dev 16(2):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1021/op200085k
Biegasiewicz KF, Cooper SJ, Gao X, Oblinsky DG, Kim JH, Garfinkle SE, Joyce LA, Sandoval BA, Scholes GD, Hyster TK (2019) Photoexcitation of flavoenzymes enables a stereoselective radical cyclization. Science 364(6446):1166–1169. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw1143
Bornscheuer UT, Huisman GW, Kazlauskas RJ, Lutz S, Moore JC, Robins K (2012) Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis. Nature 485(7397):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11117
Bougioukou DJ, Kille S, Taglieber A, Reetz MT (2009) Directed evolution of an enantioselective enoate-reductase: testing the utility of iterative saturation mutagenesis. Adv Synth Catal 351(18):3287–3305. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200900644
Breithaupt C, Strassner J, Breitinger U, Huber R, Macheroux P, Schaller A, Clausen T (2001) X-ray structure of 12-oxophytodienoate reductase 1 provides structural insight into substrate binding and specificity within the family of OYE. Structure 9(5):419–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00602-5
Breithaupt C, Kurzbauer R, Lilie H, Schaller A, Strassner J, Huber R, Macheroux P, Clausen T (2006) Crystal structure of 12-oxophytodienoate reductase 3 from tomato: self-inhibition by dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(39):14337–14342. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606603103
Brenna E, Crotti M, Gatti FG, Monti D, Parmeggiani F, Powell Iii RW, Santangelo S, Stewart JD (2015) Opposite enantioselectivity in the bioreduction of (Z)-β-aryl-β-cyanoacrylates mediated by the tryptophan 116 mutants of old yellow enzyme 1: synthetic approach to (R)- and (S)-β-aryl-γ-lactams. Adv Synth Catal 357(8):1849–1860. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201500206
Brigé A, Van Den Hemel D, Carpentier W, De Smet L, Van Beeumen JJ (2006) Comparative characterization and expression analysis of the four old yellow enzyme homologues from Shewanella oneidensis indicate differences in physiological function. Biochem J 394(1):335–344. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050979
Contente ML, Zambelli P, Galafassi S, Tamborini L, Pinto A, Conti P, Molinari F, Romano D (2015) A new chemoenzymatic approach to the synthesis of Latanoprost and Bimatoprost. J Mol Catal B Enzym 114:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.05.022
Crotti M, Parmeggiani F, Ferrandi EE, Gatti FG, Sacchetti A, Riva S, Brenna E, Monti D (2019) Stereoselectivity switch in the reduction of α-alkyl-β-arylenones by structure-guided designed variants of the ene reductase OYE1. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00089
Devine PN, Howard RM, Kumar R, Thompson MP, Truppo MD, Turner NJ (2018) Extending the application of biocatalysis to meet the challenges of drug development. Nat Rev Chem 2(12):409–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-018-0055-1
Fox KM, Karplus PA (1994) Old yellow enzyme at 2 Å resolution: overall structure, ligand binding, and comparison with related flavoproteins. Structure 2(11):1089–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(94)00111-1
Fryszkowska A, Toogood H, Sakuma M, Stephens GM, Gardiner JM, Scrutton NS (2011) Active site modifications in pentaerythritol tetranitrate reductase can lead to improved product enantiopurity, decreased by-product formation and altered stereochemical outcome in reactions with α, β-unsaturated nitroolefins. Catal Sci Technol 1(6):948–957. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CY00092B
Fu Y, Castiglione K, Weuster-Botz D (2013) Comparative characterization of novel ene-reductases from cyanobacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(5):1293–1301. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24817
Griese JJ, Jakob RP, Schwarzinger S, Dobbek H (2006) Xenobiotic reductase a in the degradation of quinoline by Pseudomonas putida 86: physiological function, structure and mechanism of 8-hydroxycoumarin reduction. J Mol Biol 361(1):140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.007
Guo J, Zhang R, Ouyang J, Zhang F, Qin F, Liu G, Zhang W, Li H, Ji X, Jia X, Qin B, You S (2018) Stereodivergent synthesis of carveol and dihydrocarveol through ketoreductases/ene-reductases catalyzed asymmetric reduction. ChemCatChem 10(23):5496–5504. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201801391
Hall M, Bommarius AS (2011) Enantioenriched compounds via enzyme-catalyzed redox reactions. Chem Rev 111(7):4088–4110. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200013n
Hall M, Stueckler C, Ehammer H, Pointner E, Oberdorfer G, Gruber K, Hauer B, Stuermer R, Kroutil W, Macheroux P, Faber K (2008) Asymmetric bioreduction of C=C bonds using enoate reductases OPR1, OPR3 and YqjM: enzyme-based stereocontrol. Adv Synth Catal 350(3):411–418. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200700458
Hubbard PA, Liang X, Schulz H, Kim J-JP (2003) The crystal structure and reaction mechanism of Escherichia coli 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase. J Biol Chem 278(39):37553–37560. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304642200
Hulley ME, Toogood HS, Fryszkowska A, Mansell D, Stephens GM, Gardiner JM, Scrutton NS (2010) Focused directed evolution of pentaerythritol tetranitrate reductase by using automated anaerobic kinetic screening of site-saturated libraries. ChemBioChem 11(17):2433–2447. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201000527
Khairy H, Wübbeler JH, Steinbüchel A (2016) The NADH:flavin oxidoreductase Nox from Rhodococcus erythropolis MI2 is the key enzyme of 4,4′-dithiodibutyric acid degradation. Lett Appl Microbiol 63(6):434–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12662
Khan H, Harris RJ, Barna T, Craig DH, Bruce NC, Munro AW, Moody PCE, Scrutton NS (2002) Kinetic and structural basis of reactivity of pentaerythritol tetranitrate reductase with NADPH, 2-cyclohexenone, nitroesters, and nitroaromatic explosives. J Biol Chem 277(24):21906–21912. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M200637200
Kitzing K, Fitzpatrick TB, Wilken C, Sawa J, Bourenkov GP, Macheroux P, Clausen T (2005) The 1.3 Å crystal structure of the flavoprotein YqjM reveals a novel class of old yellow enzymes. J Biol Chem 280(30):27904–27913. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M502587200
Kosjek B, Fleitz FJ, Dormer PG, Kuethe JT, Devine PN (2008) Asymmetric bioreduction of α,β-unsaturated nitriles and ketones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 19(12):1403–1406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2008.05.023
Kress N, Rapp J, Hauer B (2017) Enantioselective reduction of citral isomers in NCR ene reductase: analysis of an active-site mutant library. ChemBioChem 18(8):717–720. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700011
Litman ZC, Wang Y, Zhao H, Hartwig JF (2018) Cooperative asymmetric reactions combining photocatalysis and enzymatic catalysis. Nature 560(7718):355–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0413-7
Nett N, Duewel S, Richter AA, Hoebenreich S (2017) Revealing additional stereocomplementary pairs of old yellow enzymes by rational transfer of engineered residues. ChemBioChem 18(7):685–691. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201600688
Nizam S, Gazara RK, Verma S, Singh K, Verma PK (2014) Comparative structural modeling of six old yellow enzymes (OYEs) from the necrotrophic fungus Ascochyta rabiei: insight into novel OYE classes with differences in cofactor binding, organization of active site residues and stereopreferences. PLoS One 9(4):e95989. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095989
Oberdorfer G, Steinkellner G, Stueckler C, Faber K, Gruber K (2011) Stereopreferences of old yellow enzymes: structure correlations and sequence patterns in enoate reductases. ChemCatChem 3(10):1562–1566. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201100141
Oberdorfer G, Gruber K, Faber K, Hall M (2012) Stereocontrol strategies in the asymmetric bioreduction of alkenes. Synlett 23(13):1857–1864. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1316591
Okamoto N, Yamaguchi K, Mizohata E, Tokuoka K, Uchiyama N, Sugiyama S, Matsumura H, Inaka K, Urade Y, Inoue T (2011) Structural insight into the stereoselective production of PGF2α by old yellow enzyme from Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biochem 150(5):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvr096
Padhi SK, Bougioukou DJ, Stewart JD (2009) Site-saturation mutagenesis of tryptophan 116 of Saccharomyces pastorianus old yellow enzyme uncovers stereocomplementary variants. J Am Chem Soc 131(9):3271–3280. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8081389
Peters C, Frasson D, Sievers M, Buller R (2019) Novel old yellow enzyme subclasses. ChemBioChem 20(12):1569–1577 371002/cbic.201800770
Pietruszka J, Schölzel M (2012) Ene reductase-catalysed synthesis of (R)-profen derivatives. Adv Synth Catal 354(4):751–756. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201100743
Pompeu YA, Sullivan B, Walton AZ, Stewart JD (2012) Structural and catalytic characterization of Pichia stipitis OYE 2.6, a useful biocatalyst for asymmetric alkene reductions. Adv Synth Catal 354(10):1949–1960. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201200213
Pompeu YA, Sullivan B, Stewart JD (2013) X-ray crystallography reveals how subtle changes control the orientation of substrate binding in an alkene reductase. ACS Catal 3(10):2376–2390. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400622e
Powell IIIRW, Buteler MP, Lenka S, Crotti M, Santangelo S, Burg MJ, Bruner S, Brenna E, Roitberg AE, Stewart JD (2018) Investigating Saccharomyces cerevisiae alkene reductase OYE 3 by substrate profiling, X-ray crystallography and computational methods. Catal Sci Technol 8(19):5003–5016. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CY00440D
Qin F, Qin B, Mori T, Wang Y, Meng L, Zhang X, Jia X, Abe I, You S (2016) Engineering of Candida glabrata Ketoreductase 1 for asymmetric reduction of α-halo ketones. ACS Catal 6(9):6135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b01552
Qin F, Qin B, Zhang W, Liu Y, Su X, Zhu T, Ouyang J, Guo J, Li Y, Zhang F, Tang J, Jia X, You S (2018) Discovery of a switch between prelog and anti-prelog reduction toward halogen-substituted acetophenones in short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases. ACS Catal 8(7):6012–6020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b00807
Reed T, Lushington GH, Xia Y, Hirakawa H, Travis DM, Mure M, Scott EE, Limburg J (2010) Crystal structure of histamine dehydrogenase from Nocardioides simplex. J Biol Chem 285(33):25782–25791. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.084301
Reich S, Hoeffken HW, Rosche B, Nestl BM, Hauer B (2012) Crystal structure determination and mutagenesis analysis of the ene reductase NCR. ChemBioChem 13(16):2400–2407. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201200404
Reich S, Kress N, Nestl BM, Hauer B (2014) Variations in the stability of NCR ene reductase by rational enzyme loop modulation. J Struct Biol 185(2):228–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2013.04.004
Robescu MS, Niero M, Hall M, Cendron L, Bergantino E (2020) Two new ene-reductases from photosynthetic extremophiles enlarge the panel of old yellow enzymes: CtOYE and GsOYE. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(5):2051–2066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10287-2
Rüthlein E, Classen T, Dobnikar L, Schölzel M, Pietruszka J (2015) Finding the selectivity switch – a rational approach towards stereocomplementary variants of the ene reductase YqjM. Adv Synth Catal 357(8):1775–1786. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201500149
Sandoval BA, Kurtoic SI, Chung MM, Biegasiewicz KF, Hyster TK (2019) Photoenzymatic catalysis enables radical-mediated ketone reduction in ene-reductases. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(26):8714–8718. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201902005
Scholtissek A, Tischler D, Westphal AH, Van Berkel WJH, Paul CE (2017) Old yellow enzyme-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation: linking family roots with improved catalysis. Catalysts 7(5):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7050130
Stueckler C, Winkler CK, Hall M, Hauer B, Bonnekessel M, Zangger K, Faber K (2011) Stereo-controlled asymmetric bioreduction of α,β-dehydroamino acid derivatives. Adv Synth Catal 353(7):1169–1173. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201100042
Thorpe TW, France SP, Hussain S, Marshall JR, Zawodny W, Mangas-Sanchez J, Montgomery SL, Howard RM, Daniels DSB, Kumar R, Parmeggiani F, Turner NJ (2019) One-pot biocatalytic cascade reduction of cyclic enimines for the preparation of diastereomerically enriched N-heterocycles. J Am Chem Soc 141(49):19208–19213. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b10053
Toogood HS, Scrutton NS (2014) New developments in ‘ene’-reductase catalysed biological hydrogenations. Curr Opin Chem Biol 19:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.01.019
Toogood HS, Scrutton NS (2018) Discovery, characterization, engineering, and applications of ene-reductases for industrial biocatalysis. ACS Catal 8(4):3532–3549. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b00624
Toogood HS, Gardiner JM, Scrutton NS (2010) Biocatalytic reductions and chemical versatility of the old yellow enzyme family of flavoprotein oxidoreductases. ChemCatChem 2(8):892–914. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201000094
Toogood HS, Mansell D, Gardiner JM, Scrutton NS (2012) 7.11 reduction: enantioselective bioreduction of C–C double bonds. In: Carreira EM, Yamamoto H (eds) Comprehensive chirality. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 216–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095167-6.00713-8
Trickey P, Basran J, Lian L-Y, Z-w C, Barton JD, Sutcliffe MJ, Scrutton NS, Mathews FS (2000) Structural and biochemical characterization of recombinant wild type and a C30A mutant of trimethylamine dehydrogenase from Methylophilus methylotrophus (sp. W3A1). Biochemistry 39(26):7678–7688. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9927181
Walton AZ, Conerly WC, Pompeu Y, Sullivan B, Stewart JD (2011) Biocatalytic reductions of Baylis–Hillman adducts. ACS Catal 1(9):989–993. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs200223f
Walton AZ, Sullivan B, Patterson-Orazem AC, Stewart JD (2014) Residues controlling facial selectivity in an alkene reductase and semirational alterations to create stereocomplementary variants. ACS Catal 4(7):2307–2318. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs500429k
Winkler CK, Clay D, Turrini NG, Lechner H, Kroutil W, Davies S, Debarge S, O'Neill P, Steflik J, Karmilowicz M, Wong JW, Faber K (2014) Nitrile as activating group in the asymmetric bioreduction of β-cyanoacrylic acids catalyzed by ene-reductases. Adv Synth Catal 356(8):1878–1882. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201301055
Winkler CK, Faber K, Hall M (2018) Biocatalytic reduction of activated CC-bonds and beyond: emerging trends. Curr Opin Chem Biol 43:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.12.003
Xu D, Kohli RM, Massey V (1999) The role of threonine 37 in flavin reactivity of the old yellow enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(7):3556–3561. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.7.3556
Ying X, Yu S, Huang M, Wei R, Meng S, Cheng F, Yu M, Ying M, Zhao M, Wang Z (2019) Engineering the enantioselectivity of yeast old yellow enzyme OYE2y in asymmetric reduction of (E/Z)-citral to (R)-citronellal. Molecules 24(6):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061057
Zallot R, Oberg N, Gerlt JA (2019) The EFI web resource for genomic enzymology tools: leveraging protein, genome, and metagenome databases to discover novel enzymes and metabolic pathways. Biochemistry 58(41):4169–4182. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00735
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971207, 81602993), LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1907153), and Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2016QNRC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QS, HW, and JL conducted structural comparison and summarized the stereo-switch of OYEs. SL, JG, and HL conducted phylogenetic analysis and sequence similarity network of OYEs. XJ, HH, ZZ, and SY contributed ideas for literature analysis. BQ contributed ideas for literature analysis and wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Q., Wang, H., Liu, J. et al. Old yellow enzymes: structures and structure-guided engineering for stereocomplementary bioreduction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 8155–8170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10845-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10845-z