Abstract
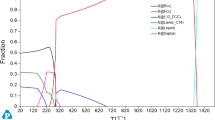
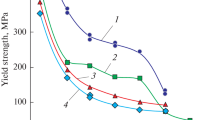
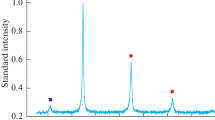
Multicomponent alloys without a base element, also known as highly entropic alloys (HEAs), are of great interest for research. The microstructure of the Fe20Ni20Co20Cu20Al20 alloy in a cast, annealed, and deformed state, as well as its mechanical properties and hot deformation ability, is investigated in this article. This alloy is a typical representative of the high-entropy alloy family. Samples are melted in a vacuum induction furnace in an argon atmosphere and then cast into a copper mold. Differential scanning calorimetry results are used to determine the solidus temperature. The homogenization annealing of cast samples is carried out in a high-temperature furnace in air. The microstructure of the alloy is studied by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. X-ray microanalysis using X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy is used to determine the chemical composition of the phases. It is shown that crystallization results in the formation of three solid solutions with one bcc and two fcc crystalline structures. The mechanical properties are investigated under uniaxial compression. Hardness is also measured. The deformation tests are carried out on a DIL805A/D quenching-deformation dilatometer and a Gleeble System 3800 complex for physical modeling and dynamic thermomechanical testing at temperatures of 900–1100°С and strain rates of 0.01–1.0 s–1 for a true degree of deformation of up to 1. Optimum modes of homogenization annealing for the typical representative of HEAs and optimal deformation modes are selected to obtain high mechanical properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 September 2021
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821221040155
REFERENCES
Yeh, J.W., Chen, S.K., Lin, S.J., Gan, J.Y., Chin, T.S., Shun, T.T., Tsau, C.H., and Chang, S.Y., Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2004, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 299–303.
Miracle, D.B. and Senkov, O.N., A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, no. 122, pp. 448–511.
Portnoi, V.K., Leonov, A.V., Filippova, S.E., Streletskii, A.N., and Logacheva, A.I., Mechanochemical synthesis and heating-induced transformations of a high-entropy of Cr–Fe–Co–Ni–Al–Ti alloy, Inorg. Mater., 2014, vol. 50, no. 12, pp. 1202–1211.
Ivchenko, M.V., Pushin, V.G., Uksusnikov, A.N., and Wanderka, N., Microstructure features of high-entropy equiatomic cast AlCrFeCoNiCu alloys, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2013, vol. 114, no. 6, pp. 514–520.
Wang, J., Liu, Y., Liu, B., Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Li, T., and Zhou, R., Flow behavior and microstructures of powder metallurgical CrFeCoNiMo. Two high entropy alloy during high temperature deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, vol. 689, pp. 233–242.
Louzguine, D.V. and Pol’kin, V.I., Bulk metal glasses: Fabrication, structure, and structural changes under heating, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met., 2016, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 25–32.
Chikova, O.A., Tsepelev, V.S., V’yukhin, V.V., and Shmakova, K.Yu., Kinetic viscosity of molten high entropy alloys Cu–Sn–In–Bi–Pb, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Tsvetn. Metall., 2015, special issue, pp. 57–60.
Senkov, O.N., Senkova, S.V., Miracle, D.B., and Woodward, C., Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 565, pp. 51–62.
Sathiaraj, G.D., Bhattacharjee, P.P., Tsai, C.W., and Yeh, J.W., Effect of heavy cryo-rolling on the evolution of microstructure and texture during annealing of equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy, Intermetallics, 2016, vol. 69, pp. 1–9.
Tung, C.C., Yeh, J.W., Shun, T.T., Chen, S.K., Huang, Y.S., and Cheng, H.C., On the elemental effect of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system, Mater. Lett., 2007, vol. 61, pp. 1–5.
Tomlin, I.A. and Kaloshkin, S.D., High entropy alloys semi-impossible regular solid solutions, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, no. 31, pp. 1231–1234.
Ivchenko, M.V., Pushin, V.G., and Wanderka, N., Highly-entropy equiatomic AlCrFeCoNiCu alloys: Hypotheses and experimental data, Tech. Phys., 2014, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 211–223.
Qiu, X.-W., Microstructure and properties of AlCrFeNiCoCu high entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 555, pp. 246–249.
Stepanova, N.D., Shaysultanova, D.G., Tikhonovsky, M.A., and Salishcheva, G.A., Tensile properties of the Cr–Fe–Ni–Mn non-equiatomic multicomponent alloys with different Cr contents, Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 87, pp. 60–65.
Senkov, O.N., Scott, J.M., Senkova, S.V., Meisenkothen, F., Miracle, D.B., and Woodward, C.F., Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, no. 9, pp. 4062–4074.
Stepanova, N.D., Shaysultanova, D.G., Yurchenkova, N.Yu., Zherebtsova, S.V., Ladygin, A.N., Salishcheva, G.A., and Tikhonovsky, M.A., High temperature deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization in CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2015, vol. 636, pp. 188–195.
He, J.Y., Zhu, C., Zhou, D.Q., Liu, W.H., Nieh, T.G., and Lu, Z.P., Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures, Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 9–14.
Wang, F.J. and Zhang, Y., Effect of Co addition on crystal structure and mechanical properties of Ti0.5CrFeNiAlCo high entropy alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 496, nos. 1–2, pp. 214–216.
Fazakas, E., Zadorozhnyy, V., Varga, L., Inoue, A., Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V., Tian, F., and Vitos, L., Experimental and theoretical study of Ti20Zr20Hf20Nb20X20 (X = V or Cr) refractory high-entropy alloys, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2014, vol. 47, pp. 131–138.
Ma, L.Q., Wang, L.M., Zhang, T., and Inoue, A., Bulk glass formation of Ti−Zr−Hf−Cu−M (M = Fe, Co, Ni) alloys, Mater. Trans., 2002, vol. 43, pp. 277−280.
Nayan, N., Singh, G., Murty, S.V.S.N., Jha, A.K., Pant, B., and George, K.M., Hot deformation behaviour and microstructure control in AlCrCuNiFeCo high entropy alloy, Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 145–153.
Shaysultanov, D.G., Stepanov, N.D., Salishchev, G.A., and Tikhonovsky, M.A., Effect of thermal treatment on the structure and hardness of the high-entropy CoCrFeNiMnVx (x = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1), Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2017, vol. 118, no. 6, pp. 579–590.
Stepanov, N., Tikhonovsky, M., Yurchenko, N., Zyabkin, D., Klimova, M., and Zherebtsov, S., Effect of cryo-deformation on structure and properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy, Intermetallics, 2015, vol. 59, pp. 8–17.
Tong, C.J., Chen, M.R., Chen, S.K., Yeh, J.W., Shun, T.T., Lin, S.J., and Chang, S.Y., Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36, pp. 1263–1271.
Li, S., Wang, Y.P., Ren, M.X., Yang, C., and Fu, H.Z., Effects of Mn, Ti and V on the microstructure and properties of AlCrFeCoNiCu high entropy alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 498, pp. 482–486.
Zhuang, Y.X., Liu, W.J., Chen, Z.Y., Xue, H.D., and He, J.C., Effect of elemental interaction on microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoNiCuAl alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, vol. 556, pp. 395–399.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation as part of the Competitiveness Improvement Program of the National University of Science and Technology “MISiS” (grant no. K2A-2018-060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Aripov, G.R., Bazlov, A.I., Churyumov, A.Y. et al. Study of the Change in the Structure and Properties of High-Entropic Alloys during Thermal and Thermomechanical Processing. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 61, 413–420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040021