Abstract
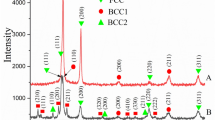
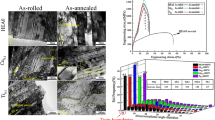
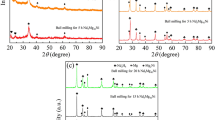
A relatively new approach to obtaining metal materials containing several principal elements in equiatomic concentrations which look promising for replacing commercially used alloys is proposed. Such materials are called high-entropy alloys (HEAs). Studies show that HEAs tend to form a simple solid-solution structure and can also contain ordered intermetallic phases. Such a method of forming metal materials can be regarded as a background for producing new HEAs with elevated performance characteristics. Most studies focus on the relationship between microstructure and measured properties; significantly less attention is paid to studying and developing new effective methods for creating HEAs. In this paper, we study the possibility of obtaining CoCrFeNiMn–(X) HEAs by centrifugal metallothermic SHS. Chemical and technological modes of modifying cast CoCrFeNiMn alloy during synthesis (in situ) by introducing alloying components into the starting exothermic compositions are tested for the first time. The microstructure and phase composition of NiCrCoFeMn alloys synthesized from mixtures containing Ti–Si–B(C) or Al are characterized. The microstructure of CoCrFeNiMn–(Ti–Si–B(C)) HEAs is found to consist of an HEA-based matrix and new structural inclusions of carbides and borides of titanium. High-Al CoCrFeNiMn–Al HEAs are represented by a composite structure containing NiAl as a basis and dispersion nanoprecipitates (~100 nm) of a Cr- and Fe-based solid solution.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Reed, R.C., The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Cambridge, New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2006. http://www.cambridge.org/9780521859042.
Kolobov, Yu.R., Kablov, E.N., and Kozlov, E.V., Struktura i svoistva intermetallidnykh materialov s nanofaznym uprochneniem (Structure and Properties of Intermetallic Materials with Nanophase Hardening), Moscow: National Univ. of Science and Technology MISiS, 2008.
Yeh, J.W., Chen, S.K., Lin, S.J., Gan, J.Y., Chin, T.S., Shun, T.T., Tsau, C.H., and Chang, S.Y., Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 299–303.
Yeh, J.W., Recent progress in high-entropy alloys, Ann. Chim. Sci. Mater., 2006, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 633–648.
Gorr, B., Azim, M., Christ, H.-J., Mueller, T., Schliephake, D., and Heilmaier, M., Phase equilibria, microstructure, and high temperature oxidation resistance of novel refractory high-entropy alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 624, no. 9, pp. 270–278.
Tong, C.J., Chen, M.R., Chen, S.K., Yeh, J.W., Shun, T.T., Lin, S.J., and Chang, S.Y., Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36, pp. 1263–1271.
Miracle, D.B. and Senkov, O.N., A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 122, pp. 448–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
Gorsse, S., Miracle, D.B., and Senkov, O.N., Mapping the world of complex concentrated alloys, Acta Mater., 2017, vol. 135, pp. 177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.06.027
Tsai, M.-H. and Yeh, J.-W., High-entropy alloys: A critical review, Mater. Res. Lett., 2014, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.912690
Zhang, Y., Zuo, T.T., Tang, Z., Gao, M.C., Dahmen, K.A., Liaw, P.K., and Lu, Z.P., Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 61, pp. 1–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
Tsai Ming-Hung, Physical properties of high entropy alloys, Entropy, 2013, vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 5338–5345.
Yeh J.-W., Gao, M.C., Yeh, J.-W., Liaw, P.K., and Zhang, Y., Overview of high-entropy alloys, in: High-Entropy Alloys, Fundamentals and Applications, Springer, 2016, pp. 1–19.
Miracle, D.B., Miller, J.D., Senkov, O.N., Woodward, Ch., Uchic, M.D., and Tiley, J., Exploration and development of high entropy alloys for structural applications, Entropy, 2014, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 494–525.
Zhijun Wang, Sheng Guo, Qing Wang, Zhiyuan Liu, Jincheng Wang, Yong Yang, and Liu, C.T., Nanoindentation characterized initial creep behavior of a high-entropy-based alloy CoFeNi, Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 53, pp. 183–186.
Senkov, O.N., Wilks, G.B., Miracle, D.B., Chuang, C.P., and Liaw, P.K., Refractory high-entropy alloys, Intermetallics, 2010, vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 1758–1765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2010.05.014
Senkov, O.N., Wilks, G.B., Scott, J.M., and Miracle, D.B., Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys, Intermetallics, 2011, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 698–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2011.01.004
Juan, C.-Ch., Tseng, K.-K., Hsu, W.-L., Tsai, M.-H., Tsai, Ch.-W., Lin, Ch.-M., Chen, S.-K., Lin, S.-J., and Yeh, J.-W., Solution strengthening of ductile refractory HfMoxNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloys, Mater. Lett., 2016, vol. 175, pp. 284–287.
Senkov, O.N. and Woodward, C.F., Microstructure and properties of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, vol. 529, no. 1, pp. 311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.09.033
Senkov, O.N., Senkova, S.V., Woodward, C., and Miracle, D.B., Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system: microstructure and phase analysis, Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 1545–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.11.032
Senkov, O.N., Senkova, S.V., Miracle, D.B., and Woodward, C., Mechanical properties of low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 565, pp. 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.12.018
Han, Z.D., Luan, H.W., Liu, X., Chen, N., Li, X.Y., Shao, Y., and Yao, K.F., Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2018, vol. 712, no. 17, pp. 380–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2017.12.004
Guo, N.N., Wang, L., Luo, L.S., Li, X.Z., Chen, R.R., Su, Y.Q., Guo, J.J., and Fu, H.Z., Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory high entropy (Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi)BCC/M5Si3 in-situ compound, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 660, pp. 197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.11.091
Juan, C.-C., Tsai, M.-H., Tsai, C.-W., Lin, C.-M., Wang, W.-R., Yang, C.-C., Chen, S.-K., Lin, S.-J., and Yeh, J.-W., Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys, Intermetallics, 2015, vol. 62, pp. 76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTERMET.2015.03.013
Stepanov, N.D., Yurchenko, N.Yu., Shaysultanov, D.G., Salishchev, G.A., and Tikhonovsky, M.A., Effect of Al on structure and mechanical properties of AlxNbTiVZr (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5) high entropy alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 31, pp. 1184–1193. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000032
Otto, F., Dlouhý, A., Somsen, C., Bei, H., Eggeler, G., and George, E.P., The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy, Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, no. 15, pp. 5743–5755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.06.018
Gludovatz, B., George, E.P., and Ritchie, R.O., Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy, JOM, 2015, vol. 67, no. 10, pp. 2262–2270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1589-z
Otto, F., Dlouhý, A., Pradeep, K.G., Kuběnová, M., Raabe, D., Eggeler, G., and George, E.P., Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures, Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 112, pp. 40–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.04.005
Zhu, G., Liu, Y., and Ye, J., Early high-temperature oxidation behavior of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with multi-component AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy binder, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2014, vol. 44, pp. 35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.01.005
Stepanov, N.D., Yurchenko, N.Y., Sokolovsky, V.S., Tikhonovsky, M.A., and Salishchev, G.A., An AlNbTiVZr0.5 high-entropy alloy combining high specific strength and good ductility, Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 161, pp. 136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.099
Sanin, V.N., Ikornikov, D.M., Andreev, D.E., and Yukhvid, V.I., Centrifugal SHS metallurgy of nickel aluminide based eutectic alloys, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met., 2014, vol. 55, no. 6, pp. 613–619. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821214060212
Sanin, V., Andreev, D., Ikornikov, D., and Yukhvid, V., Cast intermetallic alloys and composites based on them by combined centrifugal casting - SHS process, Open J. Met., 2013, vol. 3, no. 2B, pp. 12–24. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojmetal.2013.32A2003
Sanin, V.N., Yukhvid, V.I., Ikornikov, D.M, Andreev, D.E., Sachkova, N.V., and Alymov, M.I., SHS metallurgy of high-entropy transition metal alloys, 2016, vol. 470, no. 2, pp. 145–149. https://doi.org/10.1134/S001250161610002X
Klimova, M., Stepanov, N., Shaysultanov, D., Chernichenko, R., Yurchenko, N., Sanin, V., and Zherebtsov, S., Microstructure and mechanical properties evolution of the Al, C-containing CoCrFeNiMn-type high-entropy alloy during cold rolling, Materials, 2018, vol. 11, no. 1, p. 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010053
Kashaev, N., Ventzke, V., Stepanov, N., Shaysultanov, D., Sanin, V., and Zherebtsov, S., Laser beam welding of a CoCrFeNiMn-type high entropy alloy produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis, Intermetallics, 2018, vol. 96, pp. 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2018.02.014
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 19-08-01108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Golosova
About this article
Cite this article
Sanin, V.N., Ikornikov, D.M., Golosova, O.A. et al. Centrifugal Metallothermic SHS of Cast Co–Cr–Fe–Ni–Mn–(Х) Alloys. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 61, 436–445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040070
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040070