Abstract
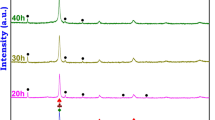
The HfTaTiNbZr high-entropy alloy (HEA) of equimolar concentration is fabricated from powder components by high-energy ball milling (HEBM) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The treatment of the initial powders was performed in a planetary high-energy ball mill for 20, 40, 60, and 90 min. It is shown based on the studied surface morphology, microstructure, and phase composition of HEA samples that the multicomponent powder mixture Hf + Ta + Ti + Nb + Zr is subjected to substantial structural variations during HEBM. Starting from X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) data, it is established that mill treatment for 20 min leads to the formation of a Hf-based solid solution with an fcc structure (Fm3m). Subsequent HEBM for 40 min promotes the formation of a Ta-based solid solution with a bcc structure (Im3m). Peaks of Hf-based and Ta-based solid solutions in the diffraction pattern completely merge after 60-min treatment, forming one common asymmetric peak in an angle range of ~35°–51°. It is revealed that the formation of the HEA with the HfTaTiNbZr composition and bcc structure is observed after 90-min HEBM. The material has a homogeneous structure according to scanning electron microscopy (SEM) data, and the results of energy-dispersive analysis showed that initial elements Hf, Ta, Ti, Nb, and Zr are uniformly distributed in the material bulk. The powders formed after 90-min HEBM are sintered at t = 1150 and 1350°C for 10 min. The results of XRD, SEM, and energy-dispersive spectrometry of SPS-consolidated high-entropy alloys at t = 1350°C show that the material preferentially consists of one phase with the bcc structure and a small amount of Hf2Fe and ZrO. The hardness of the sintered HEA material (10.7 GPa) exceed the hardness of the material consolidated from the mixture of initial elements (6.2 GPa) by a factor 1.8. Density of the samples sintered from initial and HEA powders at t = 1350°C is 9.49 g/cm3 (95.8%) and 9.87 g/cm3 (99.7%), respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cantor, B., Chang, I.T.H., Knight, P., and Vincent, A.J.B., Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, vols. 375–377, pp. 213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.257
Yeh, J.-W., Chen, S.-K., Lin, S.-J., Gan, J.-Y., Chin, T.-S., Shun, T.-T., Tsau, C.-H., and Chang, S.-Y., Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, vol. 6, pp. 299–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
Senkov, O.N., Miracle, D.B., and Chaput, K.J., Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review, J. Mater. Res., 2018, vol. 33, no. 19, pp. 3092–3128.
Ye, Y.F., Wang, Q., Lu, J., Liu, C.T., and Yang, Y., High-entropy alloy: challenges and prospects, Mater. Today, 2016, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 349–362.
Yeh, J.-W., Chen, S.-K., Gan, J.-W., Lin, S.-J., Chin, T.-S., Shun, T.-T., Tsau, C.-H., and Chang, S.-Y., Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu–Co–Ni–Cr–Al–Fe–Ti–V alloys with multi-principal metallic elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 2533–2536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0234-4
Guo, S. and Liu, C.T., Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid solution or amorphous phase, Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int., 2011, vol. 21, pp. 433–446.
Guo, S., Ng, C., Lu, J., and Li, C.T., Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of FCC or BCC phase in high entropy alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 109, no. 103505.
Zhang, Y., Zuo, T.T., Tang, Z., Gao, M.C., Dahmen, K.A., Liaw, P.K., and Lu, Z.P., Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 61, pp. 1–93.
Gali, A. and George, E.P., Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys, Intermetallics, 2013, vol. 39, pp. 74–78.
Otto, F., Dlouhy, A., Somsen, Ch., Bei, H., Eggeler, G., and George, E.P., The influence of temperature and microstructure on tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy, Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 5743–5755.
Kilmametov, A., Kulagin, R., Mazilkin, A., Seils, S., Boll, T., Heilmaier, M., and Hahn, H., High-pressure torsion driven mechanical alloying of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy, Scr. Mater., 2019, vol. 158, pp. 29–33.
Zhu, C., Lu, Z.P., and Nieh, T.G., Incipient plasticity and dislocation nucleation of FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy, Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 2993–3001.
Gludovatz, B., Honenwarter, A., Catoor, D., Chang, E.H., George, E.P., and Ritchie, R.O., A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications, Science, 2014, vol. 345, pp. 1153–1158.
Zhang, Z.J., Mao, M.M., Wang, J., Gludovatz, B., Zhang, Z., Mao, S.X., George, E.P., Yu, Q., and Ritchie, R.O., Nanoscale origins of the damage tolerance of the high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi, Nat. Commun., 2015, vol. 6, no. 10143, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10143
Prusa, F., Senkova, A., Kucera, V., Capek, J., and Vojtech, D., Properties of high-strength ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy prepared by short-term mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2018, vol. 734, pp. 341–352.
Sun, S.J., Tian, Y.Z., Lin, H.R., Dong, X.G., Wang, Y.H., Zhang, Z.J., and Zhang, Z.F., Enhanced strength and ductility of bulk CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy having fully recrystallized ultrafine-grained structure, Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 133, pp. 122–127.
Shahmir, H., He, J., Lu, Z., Kawasaki, M., and Langdona, T.G., Evidence for super-plasticity in a CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy processed by high-pressure torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, vol. 685, pp. 342–348.
Senkov, O.N., Scott, J.M., Senkova, S.V., Miracle, D.B., and Woodward, C.F., Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 6043–6048.
Senkov, O.N., Wilks, G.B., Miracle, D.B., Chuang, C.P., and Liaw, P.K., Refractory high-entropy alloys, Intermetallics, 2010, vol. 18, pp. 758–1765.
He, J.Y., Zhu, C., Zhou, D.Q., Liu, W.H., Nieh, T.G., and Lu, Z.P., Steady state flow of the FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy at elevated temperatures, Intermetallics, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 9–14.
Pickering, E.J., Minoz-Moreno, R., Stone, H.J., and Jones, N.G., Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi, Scr. Mater., 2016, vol. 113, pp. 106–109.
Otto, F., Dlouhý, A., Pradeep, K.G., Kuběnová, M., Raabec, D., Eggeler, G., and Georgea, E.P., Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures, Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 112, pp. 40–52.
Salishchev, G.A., Tikhonovsky, M.A., Shaysultanov, D.G., Stepanov, N.D., Kuznetsov, A.V., Kolodiy, I.V., Tortika, A.S., and Senkov, O.N., Effect of Mn and V on structure and mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys based on CoCrFeNi system, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, vol. 591, pp. 11–21.
Gludovatz, B., George, E.P., and Ritchie, R.O., Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy, J. Met., 2015, vol. 67, no. 10, pp. 2262–2270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1589-z
He, F., Wang, Z., Wu, Q., Li, J., Wang, J., and Liu, C.T., Phase separation of metastable CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperatures, Scr. Mater., 2017, vol. 126, pp. 15–19.
Vaidya, M., Muralikrishna, G.M., and Murty, B.S., High-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: A review, J. Mater. Res, 2019, vol. 34, pp. 664–686.
Rogachev, A.S., Vadchenko, S.G., Kochetov, N.A., Rouvimov, S., Kovalev, D.Yu., Shchukin, A.S., Moskovskikh, D.O., Nepapushev, A.A., and Mukasyan, A.S., Structure and properties of equiatomic CoCrFeNiMn alloy fabricated by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, vol. 805, pp. 1237–1245.
Wu, Y.D., Cai, Y.H., Wang, T., Si, J.J., Zhu, J., Wang, Y.D., and Hui, X.D., A refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 high-entropy alloy with excellent structural stability and tensile properties, Mater. Lett., 2014, vol. 130, pp. 277–280.
Singh, A.K. and Subramaniam, A., On the formation of disordered solid solutions in multi-component alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 587, pp. 113–119.
Idbenali, M., Selhaoui, N., Bouirden, L., and Servant, C., Thermodynamic assessment of the Fe-Hf binary system, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 456, pp. 151–158.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 18-79-10215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by N. Korovin
About this article
Cite this article
Sedegov, A.S., Tsybulin, V.S., Kuskov, K.V. et al. Structural Features of High-Entropy HfTaTiNbZr Alloy Fabricated by High-Energy Ball Milling. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 61, 421–428 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040082
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220040082