Abstract
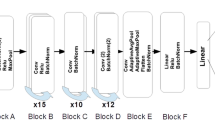
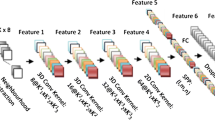
Over the past few decades, hyperspectral image (HSI) classification has garnered increasing attention from the remote sensing research community. The largest challenge faced by HSI classification is the high feature dimensions represented by the different HSI bands given the limited number of labeled samples. Deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), in particular, have been shown to be highly effective in several computer vision problems such as object detection and image classification. In terms of accuracy and computational cost, one of the best CNN architectures is the Inception model i.e., the winner of the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition (ILSVRC) 2014 challenge. Another architecture that has significantly improved image recognition performance is the Residual Network (ResNet) architecture i.e., the winner of the ILSVRC 2015 challenge. Inspired by the incredible performance introduced by the Inception and ResNet architectures, we investigate the possibility of combining the core ideas of these two models into a hybrid architecture to improve the HSI classification performance. We tested this combined model on four standard HSI datasets, and it shows competitive results compared with other existing HSI classification methods. Our hybrid deep ResNet-Inception architecture obtained accuracies of 95.31% on the Pavia University dataset, 99.02% on the Pavia Centre scenes dataset, 95.33% on the Salinas dataset and 90.57% on the Indian Pines dataset.
Zusammenfassung
Ein hybrides Deep ResNet- und Inception-Modell für die hyperspektrale Bildklassifikation. In den letzten Jahrzehnten ist die Aufmerksamkeit für die Klassifizierung von Hyperspektralen Bilddaten (HSI) in der Fernerkundung gestiegen. Die größte Herausforderung ist dabei die hohe Dimension an Merkmalen, die die verschiedenen HSI-Bänder angesichts der begrenzten Anzahl an Referenzdaten darstellen. Insbesondere Deep Learning und Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) haben sich bei verschiedenen computergestützten Visualisierungsproblemen als äußerst effektiv erwiesen. In Bezug auf Genauigkeit und Rechenaufwand ist eine der besten CNN-Architekturen das Inception-Modell, der Gewinner der ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition (ILSVRC) 2014. Eine weitere Architektur, die die Bilderkennung erheblich verbessert hat, ist die Residual Network (ResNet) Architektur, der Gewinner der ILSVRC 2015. Inspiriert durch die Leistung, die durch die Inception- und ResNet-Architekturen eingeführt wurde, untersuchen wir die Möglichkeit, die Kernideen dieser beiden Modelle in einer hybriden Architektur zu kombinieren, um die HSI-Klassifikation zu verbessern. Wir testeten dieses kombinierte Modell an vier Standard HSI-Datensätzen, und es zeigt sehr gute Ergebnisse im Vergleich zu anderen bestehenden HSI-Klassifikationsmethoden. Unsere hybride tiefe ResNet-Inception-Architektur erzielte Genauigkeiten von 95,31% für den Datensatz der Pavia-Universität, 99,02% für den Datensatz Pavia-Zentrum, 95,33% für den Salinas-Datensatz und 90,57% für die Indian Pines Daten.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hamid O, Ar M, Jiang H, Deng L, Penn G, Yu D (2014) Convolutional neural networks for speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Language Process 22(10):1533–1545
Buitinck L, Louppe G, Blondel M, Pedregosa F, Mueller A, Grisel O, Niculae V, Prettenhofer P, Gramfort A, Grobler J, Layton R, VanderPlas J, Joly A, Holt B, Varoquaux G (2013) API design for machine learning software: experiences from the scikit-learn project. In: ECML PKDD workshop: languages for data mining and machine learning, pp 108–122
Carreiras JM, Jones J, Lucas RM, Shimabukuro YE (2017) Mapping major land cover types and retrieving the age of secondary forests in the Brazilian Amazon by combining single-date optical and radar remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 194:16–32
Chen Y, Lin Z, Zhao X, Wang G, Gu Y (2014) Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Obser Remote Sens 7(6):2094–2107
Chen Y, Jiang H, Li C, Jia X, Ghamisi P (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(10):6232–6251
Chicco D, Sadowski P, Baldi P (2014) Deep autoencoder neural networks for gene ontology annotation predictions. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM conference on bioinformatics, computational biology, and health informatics, ACM, pp 533–540
Choi E, Schuetz A, Stewart WF, Sun J (2016) Using recurrent neural network models for early detection of heart failure onset. J Am Med Inform Assoc 24(2):361–370
Chollet F, et al (2015) Keras
Ciregan D, Meier U, Schmidhuber J (2012) Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE conference on, IEEE, pp 3642–3649
Deng L, Yu D et al (2014) Deep learning: methods and applications. Found Trends Signal Process 7(3–4):197–387
Ertürk A, Iordache MD, Plaza A (2016) Sparse unmixing-based change detection for multitemporal hyperspectral images. IEEE J Select Topics Appl Earth Obser Remote Sens 9(2):708–719
Garcia-Garcia A, Orts-Escolano S, Oprea S, Villena-Martinez V, Garcia-Rodriguez J (2017) A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv:170406857
Garg V, Kumar AS, Aggarwal S, Kumar V, Dhote P, Thakur PK, Nikam BR, Sambare R, Siddiqui A, Muduli PR et al (2017) Spectral similarity approach for mapping turbidity of an inland waterbody. J Hydrol
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, pp 249–256
Graves A, Jaitly N, Mohamed Ar (2013a) Hybrid speech recognition with deep bidirectional lstm. In: Automatic speech recognition and understanding (ASRU), 2013 IEEE workshop on, IEEE, pp 273–278
Graves A, Mohamed A, Hinton G (2013b) Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: Acoustics, speech and signal processing (icassp), 2013 IEEE international conference on, IEEE, pp 6645–6649
Grupo de Inteligencia Computacional (2014) Ehu. http://www.ehu.eus/ccwintco/index.php/Hyperspectral_Remote_Sensing_Scenes
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Hu W, Huang Y, Wei L, Zhang F, Li H (2015) Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. J Sens
Jakob S, Zimmermann R, Gloaguen R (2017) The need for accurate geometric and radiometric corrections of drone-borne hyperspectral data for mineral exploration: Mephysto–a toolbox for pre-processing drone-borne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens 9(1):88
Kingma D, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:14126980
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Kussul N, Lavreniuk M, Skakun S, Shelestov A (2017) Deep learning classification of land cover and crop types using remote sensing data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(5):778–782
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Li Y, Hu J, Zhao X, Xie W, Li J (2017a) Hyperspectral image super-resolution using deep convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing
Li Y, Zhang H, Shen Q (2017b) Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3d convolutional neural network. Remote Sens 9(1):67
Mesnil G, Dauphin Y, Yao K, Bengio Y, Deng L, Hakkani-Tur D, He X, Heck L, Tur G, Yu D et al (2015) Using recurrent neural networks for slot filling in spoken language understanding. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Language Process (TASLP) 23(3):530–539
Mou L, Ghamisi P, Zhu XX (2017) Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens
Olmanson LG, Brezonik PL, Bauer ME (2013) Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The mississippi river and its tributaries in minnesota. Remote Sens Environ 130:254–265
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:14091556
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Tao C, Pan H, Li Y, Zou Z (2015) Unsupervised spectral-spatial feature learning with stacked sparse autoencoder for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(12):2438–2442
Wang L, Zhang J, Liu P, Choo KKR, Huang F (2017) Spectral-spatial multi-feature-based deep learning for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Soft Comput 21(1):213–221
Yu S, Jia S, Xu C (2017) Convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Neurocomputing 219:88–98
Zhang L, Zhang L, Du B (2016) Deep learning for remote sensing data: a technical tutorial on the state of the art. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Magn 4(2):22–40
Zhao W, Du S (2016) Spectral-spatial feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification: A dimension reduction and deep learning approach. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(8):4544–4554
Zhong Sh, Liu Y, Liu Y (2011) Bilinear deep learning for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM international conference on Multimedia, ACM, pp 343–352
Zhong Z, Li J, Luo Z, Chapman M (2017a) Spectral-spatial residual network for hyperspectral image classification: a 3-d deep learning framework. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens
Zhong Z, Li J, Ma L, Jiang H, Zhao H (2017b) Deep residual networks for hyperspectral image classification. In: 2017 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), Institute of electrical and electronics engineers
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, University of Tabuk, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia under grant number S-0181-1439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was performed in the different locations of the authors affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alotaibi, B., Alotaibi, M. A Hybrid Deep ResNet and Inception Model for Hyperspectral Image Classification. PFG 88, 463–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41064-020-00124-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41064-020-00124-x