Abstract
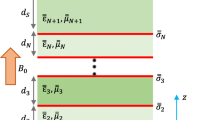
Graphene is an important material for the design of flexible and stretchable electronic and optoelectronic devices on account of its high Young’s modulus and generation of highly confined surface plasmons. In this work, we report the near to far-infrared (FIR) input frequencies required to generate the maximum electric field and magnetic field for the efficient propagation of surface plasmons for differently doped, micron-long, free-standing and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) sandwiched graphene sheets. The effect of the variation of doping of graphene, graphene sheet length and bent angle of the graphene sheet on the propagating electromagnetic field is analysed at the obtained input excitation frequencies using finite element method. Low attenuation of 0.034 and 0.234 dB along with relatively high confinement of ~6 and ~13 nm for the surface plasmons are achieved for micron-long, bent, highly doped, freely suspended and PMMA sandwiched graphene sheets at 193.5 and 190 THz, respectively. The knowledge of these optimized NIR–FIR input excitation frequencies producing maximum electric and magnetic field output at the end of graphene sheet is useful for designing compact and efficient graphene-based flexible and wearable devices for medical imaging applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee C, Wei X, Kysar J W and Hone J 2008 Science 321 385
Bolotin K I, Sikes K J, Jiang Z, Klima M, Fudenberg G, Hone J et al 2008 Solid State Commun. 146 351
Balandin A A, Ghosh S, Bao W, Calizo I, Teweldebrhan D, Miao F et al 2008 Nano Lett. 8 902
Ghosh S, Calizo I, Teweldebrhan D, Pokatilov E P, Nika D L, Balandin A A et al 2008 Appl. Phys. Lett. 92 151911
Nair R R, Blake P, Grigorenko A N, Novoselov K S, Booth T J, Stauber T et al 2008 Science 320 1308
Yan H, Low T, Zhu W, Wu Y, Freitag M, Li X et al 2013 Nat. Photon. 7 394
Yan H, Li X, Chandra B, Tulevski G, Wu Y, Freitag M et al 2012 Nat. Nanotechnol. 7 330
Xia S-X, Zhai X, Wang L-L, Lin Q and Wen S-C 2016 Opt. Express 24 16336
Thongrattanasiri S, Manjavacas A and Garcia de Abajo F J 2012 ACS Nano 6 1766
Thongrattanasiri S, Koppens F H L and de Abajo F J G 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 047401
Guo B, Fang L, Zhang B and Gong J R 2011 Insciences J. 1 80
Fei Z, Rodin A S, Andreev G O, Bao W, McLeod A S, Wagner M et al 2012 Nature 487 82
Tassin P, Koschny T, Kafesaki M and Soukoulis C M 2012 Nat. Photon. 6 259
Jablan M, Buljan H and Soljačić M 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 245435
Li H, Anugrah Y, Koester S J and Li M 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 111110
Cheng Z, Tsang H K, Wang X, Chen X, Xu K and Xu J B 2013 Proc. IEEE Photonics Conference p 460
Kim K S, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee S Y, Kim J M, Kim K S et al 2009 Nature 457 706
Hofmann A I, Cloutet E and Hadziioannou G 2018 Adv. Electron. Mater. 4 1700412
Zhao Y, Duan J, He B and Tang Q 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 776 31
Dudem B, Kim D H, Bharat L K and Yu J S 2018 Appl. Energy 230 865
Koo J H, Kim D C, Shim H J, Kim T H and Kim D H 2018 Adv. Funct. Mater. 28 1801834
Zhang M and Yeow J T 2018 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10 26604
Li D, Hu Y, Zhang N, Lv Y, Lin J, Guo X et al 2017 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 36103
Lu W B, Zhu W, Xu H J, Ni Z H, Dong Z G and Cui T J 2013 Opt. Express 21 10475
Jang H, Park Y J, Chen X, Das T, Kim M S and Ahn J H 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 4184
Koppens F H L, Chang D E and García De A F J 2011 Nano Lett. 11 3370
Nikitin A Y, Guinea F, García-Vidal F J and Martín-Moreno L 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 161407
Nikitin A Y, Guinea F, Garcia-Vidal F J and Martin-Moreno L 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 081405
Gao W, Shu J, Qiu C and Xu Q 2012 ACS Nano 6 7806
Hajian H, Serebryannikov A E, Ghobadi A, Demirag Y, Butun B, Vandenbosch G A et al 2018 Sci. Rep. 8 1
Xiao T-H, Gan L and Li Z-Y 2015 Photonics Res. 3 300
Mikhailov S A and Ziegler K 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 016803
Hanson G W 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 103 064302
Luo X, Qiu T, Lu W and Ni Z 2013 Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 74 351
Jacob G and Raina G 2017 Proc. International Conference on Nextgen Electronic Technologies: Silicon to Software p 225
Vakil A and Engheta N 2011 Science 332 1291
Canadija M, Brcic M and Brnic J 2013 Eng. Rev. 33 9
Acknowledgements
GJ acknowledges the financial support received from Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for performing this study. GJ is grateful to Prof A Nirmala Grace, Director, Centre for Nanotechnology Research, for constant encouragement. GR is thankful for the support from Vellore Institute of Technology, Chennai Campus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacob, G., Raina, G. Efficient surface plasmon propagation on flexible free-standing and PMMA sandwiched graphene at optimized near to far-IR frequencies. Bull Mater Sci 43, 256 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02226-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02226-z