Abstract
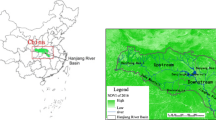
How vegetation phenology responds to climate change is a key to the understanding of the mechanisms driving historic and future changes in regional terrestrial ecosystem productivity. Based on the 250-m and 8-day moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) data for 2000–2014 in the Three-River Source Region (TRSR) of Qinghai Province, China, i.e., the hinterland of the Tibetan Plateau, we extracted relevant vegetation phenological information (e.g., start, end, and length of growing season) and analyzed the changes in the TRSR vegetation in response to climate change. The results reveal that, under the increasingly warm and humid climate, the start of vegetation growing season (SOS) advanced 1.03 day yr−1 while the end of vegetation growing season (EOS) exhibited no significant changes, which led to extended growing season length. It is found that the SOS was greatly affected by the preceding winter precipitation, with progressively enhanced precipitation facilitating an earlier SOS. Moreover, as the variations of SOS and its trend depended strongly on topography, we estimated the elevation break-points for SOS. The lower the elevations were, the earlier the SOS started. In the areas below 3095-m elevation, the SOS delay changed rapidly with increasing elevation; whereas above that, the SOS changes were relatively minor. The SOS trend had three elevation break-points at 2660, 3880, and 5240 m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, R. Y., J. Chen, M. G. Shen, et al., 2015: An improved logistic method for detecting spring vegetation phenology in grasslands from MODIS EVI time-series data. Agric. Forest Meteor., 200, 9–20, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.09.009.
Chen, X. Q., S. An, D. W. Inouye, et al., 2015: Temperature and snowfall trigger alpine vegetation green-up on the world’s roof. Global Change Biol., 21, 3635–3646, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12954.
Ding, M. J., Q. Chen, L. H. Li, et al., 2016a: Temperature dependence of variations in the end of the growing season from 1982 to 2012 on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. GISci. Remote Sens., 53, 147–163, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/15481603.2015.1120371.
Ding, M. J., L. H. Li, Y. Nie, et al., 2016b: Spatio-temporal variation of spring phenology in Tibetan Plateau and its linkage to climate change from 1982 to 2012. J. Mt. Sci., 13, 83–94, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3600-0.
Fan, D. Q., W. Q. Zhu, Z. T. Zheng, et al., 2015: Change in the green-up dates for Quercus mongolica in Northeast China and its climate-driven mechanism from 1962 to 2012. PLoS One, 10, e0130516, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130516.
Fu, G., and Z. M. Zhong, 2016: Initial response of phenology and aboveground biomass to experimental warming in a maize system of the Tibet. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 25, 1093–1097, doi: https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2016.07.001. (in Chinese)
Hutchinson, M. F., 1991: The application of thin plate smoothing splines to continent-wide data assimilation. BMRC Research Report No. 27, Data Assimilation Systems, J. D. Jasper, Ed., Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, 104–113.
Hutchinson, M. F., 1998: Interpolation of rainfall data with thin plate smoothing splines—Part II: Analysis of topographic dependence. J. Geogr. Inf. Decis. Anal., 2, 152–167.
Jeong, S. J., C. H. Ho, H. J. Gim, et al., 2011: Phenology shifts at start vs. end of growing season in temperate vegetation over the Northern Hemisphere for the period 1982–2008. Global Change Biol., 17, 2385–2399, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02397.x.
Jin, Z. N., Q. L. Zhuang, J. S. He, et al., 2013: Phenology shift from 1989 to 2008 on the Tibetan Plateau: An analysis with a process-based soil physical model and remote sensing data. Climatic Change, 119, 435–449, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-013-0722-7.
Jönsson, P., and L. Eklundh, 2004: TIMESAT—a program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci., 30, 833–845, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2004.05.006.
Justice, C. O., J. R. G. Townshend, B. N. Holben, et al., 1985: Analysis of the phenology of global vegetation using meteorological satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens., 6, 1271–1318, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168508948281.
Liu, J. Y., X. L. Xu, and Q. Q. Shao, 2008: Grassland degradation in the “Three-River Headwaters” region, Qinghai Province. J. Geogr. Sci., 18, 259–273, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0259-2.
Piao, S. L., M. D. Cui, A. P. Chen, et al., 2011: Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. Forest Meteor., 151, 1599–1608, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.06.016.
Qiu, B. W., J. P. Zhong, Z. H. Tang, et al., 2017: Greater phenological sensitivity on the higher Tibetan Plateau: New insights from weekly 5 km EVI2 datasets. Int. J. Biometeorol., 61, 807–820, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-016-1259-z.
Shao, Q. Q., J. W. Fan, J. Y. Liu, et al., 2017: Target-based assessment on effects of first-stage ecological conservation and restoration project in Three-River Source Region, China and policy recommendations. Bull. Chinese Acad. Sci., 32, 35–14, doi: https://doi.org/10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2017.01.005. (in Chinese)
Shen, M. G., Y. H. Tang, J. Chen, et al., 2011: Influences of temperature and precipitation before the growing season on spring phenology in grasslands of the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Forest Meteor., 151, 1711–1722, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.07.003.
Shen, M. G., G. X. Zhang, N. Cong, et al., 2014: Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Forest Meteor., 189–190, 71–80, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.01.003.
Shen, M. G., S. L. Piao, N. Cong, et al., 2015: Precipitation impacts on vegetation spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Global Change Biol., 21, 3647–3656, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12961.
Tan, J. B., A. N. Li, and G. B. Lei, 2016: Contrast on Anusplin and Cokriging meteorological spatial interpolation in southeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteor., 35, 875–886. (in Chinese)
Wang, C. Z., H. D. Guo, L. Zhang, et al., 2015: Assessing phenological change and climatic control of alpine grasslands in the Tibetan Plateau with MODIS time series. Int. J. Biometeorol., 59, 11–23, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-014-0817-5.
Wang, H. S., D. S. Liu, H. Lin, et al., 2015: NDVI and vegetation phenology dynamics under the influence of sunshine duration on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol., 35, 687–698, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4013.
Wang, J., J. Dong, Y. Yi, et al., 2017: Decreasing net primary production due to drought and slight decreases in solar radiation in China from 2000 to 2012. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci., 122, 261–278, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JG003417.
Wang, J. B., J. W. Wang, H. Ye, et al., 2017: An interpolated temperature and precipitation dataset at 1-km grid resolution in China (2000–2012). China Sci. Data, 2, 73–80, doi: https://doi.org/10.11922/csdata.170.2016.0112. (in Chinese)
Wu, J., S. P. Serbin, X. T. Xu, et al., 2017: The phenology of leaf quality and its within-canopy variation is essential for accurate modeling of photosynthesis in tropical evergreen forests. Global Change Biol., 23, 4814–4827, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13725.
Zhang, G. L., Y. J. Zhang, J. W. Dong, et al., 2013: Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 4309–4314, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1210423110.
Zhao, J. J., Y. Y. Wang, Z. X. Zhang, et al., 2016: The variations of land surface phenology in Northeast China and its responses to climate change from 1982 to 2013. Remote Sens., 8, 400, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050400.
Zhu, J. T., Y. J. Zhang, and W. F. Wang, 2016: Interactions between warming and soil moisture increase overlap in reproductive phenology among species in an alpine meadow. Biol. Lett., 12, 20150749, doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2015.0749.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0500203 and 2017YFC0503803), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971507), and Science and Technology Program of Qinghai Province (2018-ZJ-T09).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, J., Dong, J. et al. Variations of Vegetation Phenology Extracted from Remote Sensing Data over the Tibetan Plateau Hinterland during 2000–2014. J Meteorol Res 34, 786–797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9211-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9211-x