Abstract
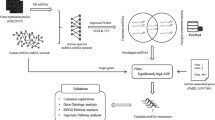
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) includes a heterogeneous group of disorders with different contributing genetics and epigenetics factors. Aberrant expression of miRNAs has been detected in ASD children compared with normally developed children. Due to the heterogeneity of this disorder, there is no consensus on ASD-associated miRNAs; thus, it is necessary to develop a model for comprehensive assessment of the role of miRNAs in ASD. We interrogated the PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science databases until the end of 2019 to identify ASD-associated miRNAs. In addition, mRNA-coding genes that contribute to the pathogenesis of ASD were downloaded from the SFARI GENE (https://gene.sfari.org/). The obtained 201 miRNAs and 478 target mRNAs were imported into the Cytoscape software suite to construct a miRNA-mRNA network. A protein-protein interaction network was constructed for target mRNAs using the CluPedia program in Cytoscape. Using this approach, we detected five modules that were associated with neurexins and neuroligins, glutamatergic synapse, cell adhesion molecules, NOTCH, MECP2 and circadian clock pathways, L1CAM interactions, and neurotransmitter release cycle. Taken together, functional analysis of these genes led to determination of critical pathways related to CNS disorders. Thus, the suggested approach in the current study resulted in the identification of the most relevant pathways in the pathogenesis of ASD that can be used as biomarkers or therapeutic targets.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitha A, Thanseem I (2015) microRNA and autism. Adv Exp Med Biol 888:71–83 Epub 2015/12/15. eng
Carlsson ML (1998) Hypothesis: is infantile autism a hypoglutamatergic disorder? Relevance of glutamate - serotonin interactions for pharmacotherapy. J Neural Transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 105(4–5):525–535 Epub 1998/08/28. eng
Du Y, Li X-S, Chen L, Chen G-Y, Cheng Y (2020) A network analysis of epigenetic and transcriptional regulation in a neurodevelopmental rat model of schizophrenia with implications for translational research. Schizophr Bull 46(3):612–622
Fatemi SH (2008) The hyperglutamatergic hypothesis of autism. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(3):911 author reply 2-3. Epub 2007/12/28. eng
Fischer-Zirnsak B, Segebrecht L, Schubach M, Charles P, Alderman E, Brown K, Cadieux-Dion M, Cartwright T, Chen Y, Costin C, Fehr S, Fitzgerald KM, Fleming E, Foss K, Ha T, Hildebrand G, Horn D, Liu S, Marco EJ, McDonald M, McWalter K, Race S, Rush ET, Si Y, Saunders C, Slavotinek A, Stockler-Ipsiroglu S, Telegrafi A, Thiffault I, Torti E, Tsai ACH, Wang X, Zafar M, Keren B, Kornak U, Boerkoel CF, Mirzaa G, Ehmke N (2019) Haploinsufficiency of the Notch ligand DLL1 causes variable neurodevelopmental disorders. Am J Hum Genet 105(3):631–639
Loomes R, Hull L, Mandy WPL (2017) What is the male-to-female ratio in autism spectrum disorder? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 56(6):466–474 Epub 2017/05/27. eng
McPartland JC, Reichow B, Volkmar FR (2012) Sensitivity and specificity of proposed DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(4):368–383
Pinato L, Spilla CSG, Markus RP, Cruz-Machado SDS (2019) Dysregulation of Circadian Rhythms in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr Pharm Des
Reichelt AC, Dachtler J (2015) The role of neurexins and neuroligins in autism. Springer, The Molecular Basis of Autism, pp 361–381
Rojas DC (2014) The role of glutamate and its receptors in autism and the use of glutamate receptor antagonists in treatment. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 121(8):891–905 Epub 04/22. eng
Rylaarsdam L, Guemez-Gamboa A (2019) Genetic causes and modifiers of autism spectrum disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 13:385 eng
Shen L, Lin Y, Sun Z, Yuan X, Chen L, Shen B (2016) Knowledge-guided bioinformatics model for identifying autism spectrum disorder diagnostic microRNA biomarkers. Sci Rep 6:39663
Wen Z, Cheng T-L, Li G-Z, Sun S-B, Yu S-Y, Zhang Y et al (2017) Identification of autism-related MECP2 mutations by whole-exome sequencing and functional validation. Molecular autism 8(1):43
Ye H, Liu J, Wu JY (2010) Cell adhesion molecules and their involvement in autism spectrum disorder. Neuro-Signals. 18(2):62–71 Epub 2011/01/08. eng
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noroozi, R., Dinger, M.E., Fatehi, R. et al. Identification of miRNA-mRNA Network in Autism Spectrum Disorder Using a Bioinformatics Method. J Mol Neurosci 71, 761–766 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01695-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01695-5