Abstract
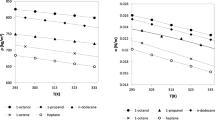
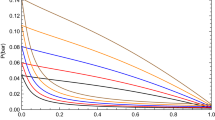
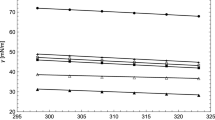
The present study has been dedicated to modeling the surface tension and viscosity of (dimethylsulfoxide + alcohol) mixtures. The self and cross-association have been considered for both alcohol and dimethylsulfoxide, and the Cubic-Plus-Association equation of state is applied to the phase equilibrium calculations. The binary interaction parameters are obtained according to the experimental phase equilibrium data, taking advantage of accurate description of the phase equilibrium. Then the gradient theory is used to describe the surface tension and interface of (dimethylsulfoxide + alcohol) mixtures. Moreover, the Eyring’s rate theory is used to model the viscosity of (dimethylsulfoxide + alcohol) binary system. For more accurate description of the viscosity, an adjustable parameter of the Eyring’s rate theory is fitted based on the experimental viscosity data. The results of this investigation show that the application of association performs well for modeling the surface tension and viscosity of (dimethylsulfoxide + alcohol) mixtures.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a\) :
-
Attractive parameter in CPA EOS [J·m3·mol−2]
- \(a_{0}\) :
-
Adjustable parameter of the CPA EOS
- \(AAD\) :
-
Average absolute deviation (%)
- \(b\) :
-
Covolume in the EOS [m3·mol−1]
- \(A_{r} , B_{r}\) :
-
The adjustable parameters of the gradient theory
- \(c_{1}\) :
-
Adjustable parameter of the CPA EOS
- \(CPA\) :
-
Cubic-Plus-Association
- \(C_{r}\) :
-
An adjustable parameter of the Eyring model
- \(f_{0}\) :
-
Helmholtz free energy density [J·m−3]
- \(g\) :
-
Simplified radial distribution function
- \(k_{ij}\) :
-
Binary interaction parameter for the attractive parameter in the CPA EOS
- \(N\) :
-
The number of experimental points
- \(N_{0}\) :
-
Avogadro constant
- \(P\) :
-
Pressure [Pa]
- \(R\) :
-
Ideal gas constant [J·mol−1·K−1]
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature [K]
- \(T_{c}\) :
-
Critical temperature [K]
- \(T_{r}\) :
-
Reduced temperature
- \(X_{{A_{i} }}\) :
-
The pure component i mole fraction (not bonded at site A)
- \(x_{i}\) :
-
Mole fraction of each component i in the liquid phase
- \(y_{i}\) :
-
Mole fraction of each component i in the vapor phase
- \(z\) :
-
Position in the interface [m]
- \(Z\) :
-
Compressibility factor
- \(\beta^{{A_{i} B_{i} }}\) :
-
The association volume
- \(\Delta^{{A_{i} B_{j} }}\) :
-
Association strength
- \(\varepsilon^{{A_{i} B_{i} }}\) :
-
The association energy [J·mol−1]
- \(\eta\) :
-
Reduced density
- \(\kappa\) :
-
Influence parameter [J·m5·mol−2]
- \(\mu\) :
-
Chemical potential [J·mol−1]
- \(\rho\) :
-
Mole density [mol·m−3]
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Surface tension [N·m−1]
- \(\varOmega\) :
-
Grand thermodynamic potential [J·m−3]
- \(B\) :
-
Bulk
- \(i,j\) :
-
Components i and j
- \(S\) :
-
Surface
- \(assoc\) :
-
Association
- \(calc\) :
-
Calculated result
- \(exp\) :
-
Experimental
- \(L\) :
-
Liquid
- \(phys\) :
-
Physical
- \(ref\) :
-
Reference variable
- \(V\) :
-
Vapor
References
C. Hou, C. Ji, R. Qu, C. Wang, C. Wang, Kinetics of copolymerization and degradation of poly [acrylonitrile-co-(amino ethyl-2-methyl propanoate)]. Eur. Polym. J. 42, 1093–1098 (2006)
D. Yuan, Y. Liu, Electrochemical preparation La–Co magnetic alloy films from dimethylsulfoxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 96, 79–83 (2006)
S.D. Yeo, E. Kiran, Formation of polymer particles with supercritical fluids: a review. J. Supercrit. Fluids 34, 287–308 (2005)
M.K. Pasha, J.R. Dimmock, M.D. Hollenberg et al., Enhanced activity of human N-myristoyltransferase by dimethyl sulfoxide and related solvents in the presence of serine/threonine-containing peptide substrates. Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 1461–1467 (2002)
H. Habibi, A. Hekmat-Nazemi, A. Kamran-Pirzaman et al., Modeling viscosity of alcohols based on the CPA-EoS + f-theory. J. Mol. Liq. 220, 558–565 (2016)
F. Giro, M. Goncalves, A.G. Ferreira et al., Viscosity and density data of the system water + n-pentyl acetate +methanol. Fluid Phase Equilib. 204, 217–232 (2003)
R. Macías-Salinas, F. García-Sánchez, G. Eliosa-Jiménez, An equation-of-state-based viscosity model for non-ideal liquid mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 210, 319–334 (2003)
T.B. Fan, L.S. Wang, A viscosity model based on Peng-Robinson equation of state for light hydrocarbon liquids and gases. Fluid Phase Equilib. 247, 59–69 (2006)
X.Q. Guo, L.S. Wang, S.X. Rong et al., Viscosity model based on equations of state for hydrocarbon liquids and gases. Fluid Phase Equilib. 139, 405–421 (1997)
X.Q. Guo, C.Y. Sun, S.X. Rong et al., Equation of state analog correlations for the viscosity and thermal conductivity of hydrocarbons and reservoir fluids. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 30, 15–27 (2001)
S. Khosharay, Suggestion of mixing rule for parameters of PRμ model for light liquid hydrocarbon mixtures. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 1246–1252 (2014)
S. Khosharay, R. Karimi, K. Khosharay, Modeling the viscosity for (nC5 + nC8), (nC5 + nC10), (nC8 + nC10) and (nC5 + nC8 + nC10) systems with Peng-Robinson viscosity equation of state. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 60, 259–265 (2016)
Z.F. Wang, L.S. Wang, T.B. Fan, Densities and viscosities of ternary mixtures of heptane, octane, nonane, and hexyl benzene from 293.15 K to 313.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 52, 1866–1871 (2007)
S. Khosharay, M. Pierantozzi, G. Di Nicola, Modeling investigation on the viscosity of pure refrigerants and their liquid mixtures by using the Patel-Teja viscosity equation of state. Int. J. refrigeration. 85, 255–267 (2018)
M.A. Monsalvo, A. Baylaucq, S.E. Quiñones-Cisneros et al., High-pressure viscosity behavior of x 1,1,1,2tetrafluoroethane (HFC-134a) + (1 − x) triethylene glycol dimethylether (TriEGDME) mixtures: measurements and modeling. Fluid Phase Equilib. 247, 70–79 (2006)
M.A. Monsalvo, A. Baylaucq, P. Reghem et al., Viscosity measurements and correlations of binary mixtures: 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFC134a) + tetraethylene glycol dimethylether (TEGDME). Fluid Phase Equilib. 233, 1–8 (2005)
S.E. Quiñones-Cisneros, J. García, J. Fernández et al., Phase and viscosity behaviour of refrigerant–lubricant mixtures. Int. J. Refrigeration 28, 714–724 (2005)
S.E. Quiñones-Cisneros, M.L. Huber, U.K. Deiters, Correlation for the viscosity of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) from the triple point to 1000 K and pressures to 50 MPa. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 41, 23102 (2012)
M. Tjahjono, M. Garland, A new modified parachor model for predicting surface compositions of binary liquid mixtures. On the importance of surface volume representation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 345, 528–537 (2010)
H. Lin, Y.Y. Duan, Surface tension of 1,1,1-trifluoroethane (HFC-143a), 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-Heptafluoropropane (HFC-227ea), and their binary mixture HFC-143a/227ea. Int. J. Thermophys. 24, 1495–1508 (2003)
G. Zhao, S. Bi, J. Wu et al., Surface tension of propane (R-290) + 1,1-Difluoroethane (R-152a) from (248 to 328) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 55, 3077–3079 (2010)
S. Enders, H. Kahl, Interfacial properties of water + alcohol mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 263, 160–167 (2008)
S. Sugden, VI-The variation of surface tension with temperature and some related functions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 125, 32–41 (1924)
A. Laaksonen, M. Kulmala, An explicit cluster model for binary nuclei in water–alcohol systems. J. Chem. Phys. 95, 6745–6748 (1991)
A. Bagheri, A. Abolhasani, A.R. Moghadasi et al., Study of surface tension and surface properties of binary systems of DMSO with long chain alcohols at various temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 63, 108–115 (2013)
M.M.H. Bhuiyan, J. Ferdaush, M.H. Uddin, Densities and viscosities of binary mixtures of dimethylsulfoxide + aliphatic lower alkanols (C1–C3) at temperatures from T = 303.15 K to T = 323.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 39, 675–683 (2007)
A. Bagheri, M. Fazli, M. Bakhshaei, Effect of temperature and composition on the surface tension and surface properties of binary mixtures containing DMSO and short chain alcohols. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 101, 236–244 (2016)
R. Tahery, S. Khosharay, Surface tension of binary mixtures of dimethylsulfoxide + methanol, ethanol and propanol between 293.15 and 308.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 247, 354–365 (2017)
G.M. Kontogeorgis, E.C. Voutsas, I.V. Yakoumis et al., An equation of state for associating fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35, 4310–4318 (1996)
G.M. Kontogeorgis, I.V. Yakoumis, H. Meijer et al., Multicomponent phase equilibrium calculations for water–methanol–alkane mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 158–160, 201–209 (1999)
M.B. Oliveira, I.M. Marrucho, J.A.P. Coutinho et al., Surface tension of chain molecules through a combination of the gradient theory with the CPA EoS. Fluid Phase Equilib. 267, 83–91 (2008)
I. Tsivintzelis, G.M. Kontogeorgis, M.L. Michelsen et al., Modeling Phase Equilibria for Acid Gas Mixtures Using the CPA Equation of State. I. Mixtures with H2S. AIChE J. 56, 2965–2981 (2010)
M.B. Oliveira, A.J. Queimada, G.M. Kontogeorgis et al., Evaluation of the CO2 behavior in binary mixtures with alkanes, alcohols, acids and esters using the Cubic-Plus-Association Equation of State. J. Supercrit. Fluids 55, 876–892 (2011)
I. Tsivintzelis, G.M. Kontogeorgis, M.L. Michelsen et al., Modeling phase equilibria for acid gas mixtures using the CPA equation of state. Part II: binary mixtures with CO2. Fluid Phase Equilib. 306, 38–56 (2011)
G. Soave, Equilibrium constants from a modified Redlich-Kwong equation of state. Chem. Eng. Science 27, 1197–1203 (1972)
M.S. Wertheim, Fluids with highly directional attractive forces I. Statistical thermodynamics. J. Statist. Phys. 35, 19–34 (1984)
M.S. Wertheim, Fluids with highly directional attractive forces II. Thermodynamic perturbation theory and integral equations. J. Statist. Phys. 35, 35–47 (1984)
M.S. Wertheim, Fluids with highly directional attractive forces III. Multiple attraction sites. J. Stat. Phys. 42, 459–476 (1986)
M.S. Wertheim, Fluids with highly directional attractive forces IV. Equilibrium polymerization. J. Stat. Phys. 42, 477–492 (1986)
S.H. Huang, M. Radosz, Equation of state for small, large, polydisperse, and associating molecules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 29, 2284–2294 (1990)
E.C. Voutsas, I.V. Yakoumis, D.P. Tassios, Prediction of phase equilibria in water/alcohol/alkane systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 158–160, 151–163 (1999)
A.J. Queimada, C. Miqueu, I.M. Marrucho et al., Modeling vapor–liquid interfaces with the gradient theory in combination with the CPA equation of state. Fluid Phase Equilib. 228–229, 479–485 (2005)
G.T. Dee, B.B. Sauer, The molecular weight and temperature dependence of polymer surface tension: comparison of experiment with interface gradient theory. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 152, 85–103 (1992)
H. Kahl, S. Enders, Calculation of surface properties of pure fluids using density gradient theory and SAFT-EOS. Fluid Phase Equilib. 172, 27–42 (2000)
S. Khosharay, F. Varaminian, Modeling interfacial tension of (CH4 + N2) + H2O and (N2 + CO2) + H2O systems using linear gradient theory. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 724–732 (2013)
S. Khosharay, M. Seyfi Mazraeno, F. Varaminian, Modeling the surface tension of refrigerant mixtures with linear gradient theory. Int. J. Refrigeration. 36, 2223–2232 (2013)
S. Khosharay, M. Seyfi Mazraeno, F. Varaminian et al., A proposed combination model for predicting surface tension and surface properties of binary refrigerant mixtures. Int. J. Refrigeration. 40, 347–361 (2014)
S. Khosharay, M. Abolala, F. Varaminian, Modeling the surface tension and surface properties of (CO2 +H2O) and (H2S + H2O) with gradient theory in combination with sPC–SAFT EOS and a new proposed influence parameter. J. Mol. Liq. 198, 292–298 (2014)
S. Khosharay, Linear gradient theory for modeling investigation on the surface tension of (CH4 + H2O), (N2 + H2O) and (CH4 + N2) + H2O systems. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 23, 474–480 (2015)
S. Khosharay, N. Rezakhani, Using a new proposed influence parameter of gradient theory for CH4/n-alkane binary systems: what advances can be achieved? Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 60, 282–289 (2016)
S. Khosharay, S. Tourang, F. Tajfar, Modeling surface tension and interface of (water + methanol),(water + ethanol), (water + 1-propanol), and (water + MEG) mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 454, 99–110 (2017)
C. Miqueu, B. Mendiboure, A. Graciaa, J. Lachaise, Modelling of the surface tension of pure components with the gradient theory of fluid interfaces: a simple and accurate expression for the influence parameters. Fluid Phase Equilib. 207, 225–246 (2003)
S. Glasstone, H. Ering, K.J. Laidler, The theory of rate process (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1941)
G.K. Folas, J. Gabrielsen, M.L. Michelsen, E.H. Stenby, G.M. Kontogeorgis, Application of the Cubic-Plus-Association (CPA) Equation of State to Cross-Associating Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44, 3823–3833 (2005)
A.N. Campbe, The density and vapour pressure of dimethylsulfoxide at various temperatures and the (hypothetical) critical density. Can. J. Chem. 57, 705–707 (1979)
Z.L. Grigoryan, E.A. Kazoyan, S.A. Markaryan, Thermodynamics of liquid–vapor phase equilibrium in dimethylSulfoxide–alkanol systems in the range of 293.15–323.15 K. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 89, 1790–1794 (2015)
E.A. Kazoyan, A.S. Khachatryan, Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium in the Dimethyl Sulfoxide-Methanol System. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 85, 1335–1338 (2012)
B. Kaczmarek, A. Radecki, Vapor-liquid equilibria in binary systems containing ethanol with hexamethyldisiloxane and dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 34, 195–197 (1989)
C.M. Kinart, W.J. Kinart, A. Bald, The measurements of the surface tension of mixtures of dimethyl sulfoxide with methyl, ethyl and propyl alcohols. Phys. Chem. Liq. 37, 317–321 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, A., Khosharay, S. Investigation on the Surface Tension and Viscosity of (dimethylsulfoxide + alcohol) Mixtures by Using Gradient Theory and Eyring’s Rate Theory. Int J Thermophys 41, 150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02732-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02732-6