Abstract
Objectives
The study was designed to determine the presence of Helicobacter genus and three species of H. pylori, H. bilis, and H. canis, in the duodenum, ileum, colon, and liver of stray cats. Moreover, the histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses have been performed.
Methods
Samples were taken from the duodenum, ileum, colon, and liver of 30 cats for molecular and histopathological evaluations. Polymerase chain reaction was carried out for the detection of the Helicobacter genus in the mentioned samples. Then, species-specific primers were used in Helicobacter-positive samples.
Results
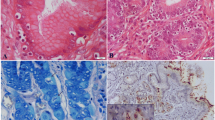
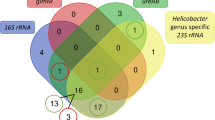
Helicobacter genus prevalence rates in the duodenum, ileum, colon, and liver samples were 50%, 60%, 50%, and 43.3%, respectively. Helicobacter pylori, H. canis, and H. bilis were isolated from at least one tissue of 18 (60%), 13 (43.3%), and 8 (26.7%) of the cats, respectively. Immunohistochemical findings confirmed the presence of bacteria in the intestinal crypt or the mucosal layer of duodenum, ileum, colon, and hepatic sinusoids.
Conclusion
In the present study, the concurrent infection of duodenum and liver was noticeable. Furthermore, the high prevalence of H. pylori in cats, as a well-known human pathogen, should be considered. High incidence of Helicobacter in gut and liver of Ahvaz stray cats is noticeable. According to the zoonotic importance of Helicobacter, more studies in the field of treatment and prevention are highly recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable for that section.
References
Abdi FS, Jamshidi S, Moosakhani F, Sasani F (2014) Detection of Helicobacter spp. DNA in the colonies biopsies of stray dogs: molecular and histopathological investigations. Diagn Pathol 9:50
Akhtardanesh B, Mohammadi M, Jamshidi S et al (2006) Clinical significance of helicobacter infection in gastric mucosa of cats. Onl J Vet Res 10(2):177–201
Araujo IC, Mota SB, De Aquino MHC et al (2010) Helicobacter species detection and histopathological changes in stray cats from Niteroi. J Feline Med Surg 12(6):509–511
Boomkens SY, Kusters JG, Hoffmann G, Pot RG, Spee B, Penning LC, Egberink HF, van den Ingh T, Rothuizen J (2004) Detection of Helicobacter pylori in bile of cats. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 42(3):307–311
Burkitt MD, Duckworth CA, Williams JM, Pritchard DM (2017) Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric pathology: insights from in vivo and ex vivo models. Dis Model Mech 10:89–104
Canejo-Teixeira R, Oliveira M, Pissarra H, Niza MMRE, Vilela CL (2014) A mixed population of Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter bizzozeronii and “Helicobacter heilmannii” in the gastric mucosa of a domestic cat. Ir Vet J 67:25
Castiglioni V, Vailati Facchini R, Mattiello S, Luini M, Gualdi V, Scanziani E, Recordati C (2012) Enterohepatic Helicobacter genus in colonic biopsies of dogs: molecular, histopathological and immunohistochemical investigations. Vet Microbiol 159(1–2):107–114
Clayton CL, Kleanthous H, Coates PJ, Morgan DD, Tabaqchali S (1992) Sensitive detection of Helicobacter pylori by using polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 30(1):192–200
Dag S, Sözmen M, Cihan M et al (2016) Gastric helicobacter like organism in stray cats: identification, prevalence, and pathologic association. Pak Vet J 36(2):199–203
Day MJ, Bilzer T, Mansell J, Wilcock B, Hall EJ, Jergens A, Minami T, Willard M, Washabau R (2008) Histopathological standards for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal inflammation in endoscopic biopsy samples from the dog and cat: a report from the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization Group. J Comp Pathol 138:S1–S43
Ekman E, Fredriksson M, Trowald-Wigh G et al (2013) Helicobacter spp. in the saliva, stomach, duodenum and faeces of colony dogs. Vet J 195:127–129
Feng T, Elson CO (2011) Adaptive immunity in the host-microbiota dialog. Mucosal Immunol 4(1):15–21
Fox JG (2012) Enteric bacterial infections. In: Green CE (ed) Infectious diseases of the dog and cat, 4th edn. Saunders, Elsevier Health Sciences, Georgia, p 374
Fox JG, Yan LL, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Shames B, Murphy JC, Hayward A, Belcher JC, Mendes EN (1995) Helicobacter bilis sp. nov., a novel Helicobacter species isolated from bile, livers, and intestines of aged, inbred mice. J Clin Microbiol 33:445–454
Fox JG, Shen Z, Muthupalani S, Rogers AR, Kirchain SM, Dewhirst FE (2009) Chronic hepatitis, hepatic dysplasia, fibrosis, and biliary hyperplasia in hamsters naturally infected with a novel Helicobacter classified in the H. bilis cluster. J Clin Microbiol 47:3673–3681
Germani Y, Dauga C, Duval P, Huerre M, Levy M, Pialoux G, Sansonetti P, Grimont PAD (1997) Strategy for the detection of Helicobacter species by amplification of 16S rRNA genes and identification of H. felis in a human gastric biopsy. Res Microbiol 148(4):315–326
Ghil HM, Yoo JH, Jung WS, Chung TH, Youn HY, Hwang CY (2009) Survey of Helicobacter infection in domestic and feral cats in Korea. J Vet Sci 10(1):67–72
Greiter-Wilke A, Scanziani E, Soldati S, McDonough SP, McDonough PL, Center SA, Rishniw M, Simpson KW (2006) Association of Helicobacter with cholangiohepatitis in cats. J Vet Intern Med 20(4):822–827
Krzysiek-Maczka G, Targosz A, Szczyrk U et al (2018) Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in cancer- associated fibroblast- induced epithelial - mesenchymal transition in vitro. Helicobacter 23:e12538
Matsukura NS, Yokomuro S, Yamada T et al (2002) Association between Helicobacter bilis in bile and biliary tract malignancies: H. bilis in bile from Japanese and Thai patients with benign and malignant diseases in the biliary tract. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:842–847
Mladenova – Hristove I, Grekova O, Patel A (2017) Zoonotic potential of Helicobacter SPP. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 50: 265–269
Recordati C, Gualdi V, Craven M, Sala L, Luini M, Lanzoni A, Rishniw M, Simpson KW, Scanziani E (2009) Spatial distribution of Helicobacter spp. in the gastrointestinal tract of dogs. Helicobacter 14(3):180–191
Rieder F, Fiocchi C (2009) Intestinal fibrosis in IBD-a dynamic, multifactorial process. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(4):228–235
Rossi M, Hänninen ML, Revez J, Hannula M, Zanoni RG (2008) Occurrence and species level diagnostics of Campylobacter spp., enteric Helicobacter spp. and Anaerobiospirillum spp. in healthy and diarrheic dogs and cats. Vet microbial 129(3–4):304–314
Scanziani E, Simpson KW, Monestiroli S, Soldati S, Strauss-Ayali D, Piero FD (2001) Histological and immunohistochemical detection of different Helicobacter species in the gastric mucosa of cats. J Vet Diagn Investig 13(1):3–12
Sjödin S, Trowald-Wigh G, Fredriksson M (2011) Identification of Helicobacter DNA in feline pancreas, liver, stomach, and duodenum: comparison between findings in fresh and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples. Res Vet Sci 91:28–30
Shojaee Tabrizi A, Derakhshandeh A, Esfandiari A, Ali AZ (2015) Identification of Helicobacter spp. in gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and hepatobiliary system of stray cats. Iran J Vet Res 16(4):374–376
Takemura LS, Camargo PL, Alfieri AA, Bracarense APFRL (2009) Helicobacter spp. in cats: association between infecting species and epithelial proliferation within the gastric lamina propria. J Comp Pathol 141(2):127–134
Takemura LS, Marcasso RA, Lorenzetti E, Alfieri AA, Bracarense APL (2019) Helicobacter infection in the hepatobiliary system and hepatic lesions: a possible association in dogs. Braz J Microbiol 50:297–305
Takemura, LS. (2012) Molecular characterization of Helicobacter spp. in hepatobiliar system from dogs and cats with hepatic lesions. 100f. Thesis (Doctor’s Degree in Animal Science) - Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Londrina
Ward JM, Anver MR, Haines DC, Benveniste RE (1994) Chronic active hepatitis in mice caused by Helicobacter hepaticus. Am J Pathol 145:959–968
Warren A, Center S, Mc Donough S et al (2011) Histopathologic features, immunophenotyping, clonality, and eubacterial fluorescence in situ hybridization in cats with lymphocytic cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis. Vet Pathol 48(3):627–641
Weiss DJ, Gagne JM, Armstrong PJ (1996) Relationship between inflammatory hepatic disease and inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis, and nephritis in cats. J Am Vet Med A 209(6):1114–1116
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the research council of Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz for their financial support. Also, the authors thank technicians Miss and Mr. Behdarvand in the pathology laboratory for their technical assistance in Pathology Lab, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz.
Code availability
Not applicable for that section.
Funding
The research was supported by research council of Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BE performed the sampling, PCR, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry. AR designed and performed histopathology, immunohistochemistry, interpreted the data. NMB conducted PCR techniques. BMN checked the animals in the small animal department and, after ensuring and deciding for euthanasia, collected the samples. SKD and AR wrote the manuscript, and all authors critically revised it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study has been approved by the laboratory animal ethics framework of Shahid Chamran University Research Council.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Miliane Moreira Soares de Souza.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elyasi, B., Rezaie, A., Moori Bakhtiari, N. et al. Helicobacter genus in the intestine and liver of stray cats: the molecular, histopathological, and immunohistochemical study. Braz J Microbiol 51, 2123–2132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00359-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-020-00359-1