Abstract
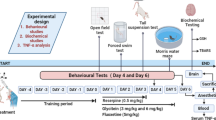
Pain and depression are often co-existing pathological states that promote mutual severity resulting in limited efficacy of current treatment strategies. Thus, there is a need to develop an efficacious alternate treatment regimen for pain-depression dyad. Skimmetin and osthole are molecules of natural origin that have been explored for an anti-hyperglycemic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, and anti-diabetic activities in preclinical studies. in animal models. The current study has been designed to explore the beneficial effect of skimmetin/osthole in reserpine-induced pain-depression dyad in mice. Female Swiss albino mice (n = 6) were challenged with reserpine (0.5 mg/kg s.c.) for the first 3 days to induce a pain-depression dyad-like state. Skimmetin (10 mg/kg i.p.) and osthole (10 mg/kg i.p.) were administered for 5 days consecutively, starting from the first day of study. Reserpine treatment significantly reduced the pain threshold in the pressure application measurement (PAM) and electronic von frey (eVF) test. In forced swim test (FST) and Morris water maze (MWM) test mice displayed an increased immobility time and latency to reach platform respectively. Biochemical results showed an increased level of TNF-α, IL-1β, TBARS, glutamate, and reduced level of GSH, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the reserpine treated group. Reserpine treatment also increased brain MAO-A activity. Skimmetin/osthole treatment was found to attenuate the behavioral and biochemical alterations induced by reserpine. The results of the current investigation delineated that skimmetin/osthole may exert anti-nociceptive, anti-depressant, and improved cognition via inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative stress-mediated neurotransmitter dysregulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora V, Chopra K (2013) Possible involvement of oxido-nitrosative stress induced neuro-inflammatory cascade and monoaminergic pathway: underpinning the correlation between nociceptive and depressive behaviour in a rodent model. J Affect Disord 151:1041–1052
Arora V, Kuhad A, Tiwari V, Chopra K (2011) Curcumin ameliorates reserpine-induced pain–depression dyad: Behavioural, biochemical, neurochemical and molecular evidences. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:1570–1581
Bai YM, Chiou WF, Su TP, Li CT, Chen MH (2014) Pro-inflammatory cytokine associated with somatic and pain symptoms in depression. J Affect Disord 155:28–34
Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Katon W, Kroenke K (2003) Depression and pain comorbidity: a literature review. Arch Intern Med 163:2433–2445
Campbell LC, Clauw DJ, Keefe FJ (2003) Persistent pain and depression: a biopsychosocial perspective. Biol Psychiatry 54:399–409
Chang CC (1964) A sensitive method for spectrophotofluorometric assay of catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 3:643–649
Chavan SS, Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ (2017) Mechanisms and therapeutic relevance of neuro-immune communication. Immunity 46:927–942
Chou KL (2007) Reciprocal relationship between pain and depression in older adults: evidence from the English longitudinal study of ageing. J Affect Disord 102:115–123
Coderre TJ, Kumar N, Lefebvre CD, Yu JS (2005) Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate. J Neurochem 94:1131–1139
Cooper TE, Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA (2017) Gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD012188
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:46–56
Deuis JR, Dvorakova LS, Vetter I (2017) Methods used to evaluate pain behaviors in rodents. Front Mol Neurosci 10:284
Doboszewska U, Wlaź P, Nowak G, Radziwoń-Zaleska M, Cui R, Młyniec K (2017) Zinc in the monoaminergic theory of depression: its relationship to neural plasticity. Neural Plast 2017:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3682752
Errante LA, Petroff OA (2003) Acute effects of gabapentin and pregabalin on rat forebrain cellular GABA, glutamate, and glutamine concentrations. Seizure 12:300–306
Felger JC, Li L, Marvar PJ, Woolwine BJ, Harrison DG, Raison CL, Miller AH (2013) Tyrosine metabolism during interferon-alpha administration: association with fatigue and CSF dopamine concentrations. Brain Behav Immun 31:153–160
Felger JC, Lotrich FE (2013) Inflammatory cytokines in depression: neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurosci 246:199–229
Fiore NT, Austin PJ (2016) Are the emergence of affective disturbances in neuropathic pain states contingent on supraspinal neuroinflammation? Brain Behav Immun 56:397–411
Fishbain DA, Detke MJ, Wernicke J, Chappell AS, Kajdasz DK (2008) The relationship between antidepressant and analgesic responses: findings from six placebo-controlled trials assessing the efficacy of duloxetine in patients with major depressive disorder. Curr Med Res Opin 24:3105–3115
Goldberg JS, Bell CE Jr, Pollard DA (2014) Revisiting the monoamine hypothesis of depression: a new perspective. Perspect Medicin chem 6:S11375
Goldlust A, Su TZ, Welty DF, Taylor CP, Oxender DL (1995) Effects of anticonvulsant drug gabapentin on the enzymes in metabolic pathways of glutamate and GABA. Epilepsy Res 22:1–1, 11
Haase J, Brown E (2015) Integrating the monoamine, neurotrophin and cytokine hypotheses of depression—a central role for the serotonin transporter? Pharmacol Therapeut 147:1–1, 11
Haroon E, Raison CL, Miller AH (2012) Psychoneuroimmunology meets neuropsychopharmacology: translational implications of the impact of inflammation on behavior. Neuropsychopharmacol 37:137–162
Hayley S, Merali Z, Anisman H (2003) Stress and cytokine-elicited neuroendocrine and neurotransmitter sensitization: implications for depressive illness. Stress 6:19–32
Iyer RN, Bradberry CW (1996) Serotonin-mediated increase in prefrontal cortex dopamine release: pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:40–47
Izumi F, Oka M, Yoshida H, Imaizumi R (1967) Effect of reserpine on monoamine oxidase activity in Guinea pig heart. Life Sci 6:2333–2343
Jackson KC, St. Onge EL (2003) Antidepressant pharmacotherapy: considerations for the pain clinician. Pain Practice 3:135–143
Jeanjean AP, Moussaoui SM, Maloteaux JM, Laduron PM (1995) Interleukin-1 beta induces long-term increase of axonally transported opiate receptors and substance P. Neurosci 68:151–157
Kaur A, Singh L, Singh N, Bhatti MS, Bhatti R (2019) Ameliorative effect of imperatorin in chemically induced fibromyalgia: role of NMDA/NFkB mediated downstream signaling. Biochem Pharmacol 166:56–69
Kaur S, Kaur A, Singh G, Bhatti R (2018) Mercurius solubilis attenuates scopolamine-induced memory deficits and enhances the motor coordination in mice. Int J Neurosci 128:219–230
Kia S, Choy E (2017) Update on treatment guideline in fibromyalgia syndrome with focus on pharmacology. Biomedicines 5:20
Krishnan R, Cella D, Leonardi C, Papp K, Gottlieb AB, Dunn M, Chiou CF, Patel V, Jahreis A (2007) Effects of etanercept therapy on fatigue and symptoms of depression in subjects treated for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis for up to 96 weeks. Br J Dermatol 157:1275–1277
Lam CS, Li JJ, Tipoe GL, Youdim MB, Fung ML (2017) Monoamine oxidase a upregulated by chronic intermittent hypoxia activates indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and neurodegeneration. PLoS One 12:e0177940
Liu SB, Zhao R, Li XS, Guo HJ, Tian Z, Zhang N, Gao GD, Zhao MG (2014) Attenuation of reserpine-induced pain/depression dyad by gentiopicroside through downregulation of GluN2B receptors in the amygdala of mice. NeuroMolecular Med 16:350–359
Marks DM, Shah MJ, Patkar AA, Masand PS, Park GY, Pae CU (2009) Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors for pain control: premise and promise. Curr Neuropharmacol 7:331–336
Mazimba O (2017) Umbelliferone: sources, chemistry and bioactivities review. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 55:223–232
McMahon SB, Cafferty WB, Marchand F (2005) Immune and glial cell factors as pain mediators and modulators. Exp Neurol 192:444–462
Morris RG (1981) Spatial localization does not depend on the presence of local cues. Learn Motiv 12:239–260
Müller N, Schwarz MJ, Dehning S, Douhe A, Cerovecki A, Goldstein-Müller B, Spellmann I, Hetzel G, Maino K, Kleindienst N, Möller HJ (2006) The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol Psychiatry 11:680–684
Nekovarova T, Yamamotova A, Vales K, Stuchlik A, Fricova J, Rokyta R (2014) Common mechanisms of pain and depression: are antidepressants also analgesics? Front Behav Neurosci 25;8:99
Ossipov MH, Dussor GO, Porreca F (2010) Central modulation of pain. J Clin Invest 120:3779–3787
Ozaktay AC, Kallakuri S, Takebayashi T, Cavanaugh JM, Asik I, DeLeo JA, Weinstein JN (2006) Effects of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor on sensitivity of dorsal root ganglion and peripheral receptive fields in rats. Eur Spine J 15:1529–1537
Patel, P.R., Hegde, M.L., Theruvathu, J., Mitra, S.A., Boldogh, I. and Sowers, L., 2015. Norepinephrine reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damage in ovarian surface epithelial cells. Journal of bioanalysis & biomedicine, 7(3), p.75
Petroff OA, Manor D, Behar KL (1997) Gabapentin decreases cortical glutamate rapidly in a rat model. Epilepsy Res
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA Jr, Chiu IM (2017) Nociceptor sensory neuron–immune interactions in pain and inflammation. Trends Immunol 38:5–19
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266:730–732
Radha GV, Sadhana B, Trideva Sastri K, Ganapaty S (2019) Bioactive Umbelliferone and its derivatives: An update. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 8:59–66
Raison CL, Borisov AS, Majer M, Drake DF, Pagnoni G, Woolwine BJ, Vogt GJ, Massung B, Miller AH (2009) Activation of central nervous system inflammatory pathways by interferon-alpha: relationship to monoamines and depression. Biol Psychiatry 65:296–303
Reynolds JL, Ignatowski TA, Sud R, Spengler RN (2004) Brain-derived tumor necrosis factor-α and its involvement in noradrenergic neuron functioning involved in the mechanism of action of an antidepressant. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:1216–1225
Rose MA, Kam PC (2002) Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management. Anaesthesia. 57:451–462
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre JV, Woolf CJ (2001) Interleukin-1β-mediated induction of cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 410:471–475
Sheng J, Liu S, Wang Y, Cui R, Zhang X (2017) The link between depression and chronic pain: neural mechanisms in the brain. Neural Plast 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9724371
Sluka KA, Clauw DJ (2016) Neurobiology of fibromyalgia and chronic widespread pain. Neuroscience 338:114–129
Smith RS (1991) The macrophage theory of depression. Med Hypotheses 35:298–306
Sousa FS, Birmann PT, Baldinotti R, Fronza MG, Balaguez R, Alves D, Brüning CA, Savegnago L (2018) α-(phenylselanyl) acetophenone mitigates reserpine-induced pain–depression dyad: behavioral, biochemical and molecular docking evidences. Brain Res Bull 142:129–137
Subakanmani S, Murugan S, Devi PU (2016) Evaluation of antidepressant like effects of Ethanolic Hypericum hookerianum and its Glycosidic flavonoid enriched extract in reserpine induced Swiss albino mice. Asian Journal of Biochemistry 11:1–3
Wang Z, Wang Q, Wang C, Xu X, Yu H (2017) Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates periorbital allodynia and neuroinflammation in a model of traumatic brain injury. J Inflamm 14:13
Welty DF, Schielke GP, Vartanian MG, Taylor CP (1993) Gabapentin anticonvulsant action in rats: Disequilib- rium with peak drug concentration in plasma and brain microdialysate. Epilepsy Res 16:175–181
WHO (2017) Depression: let’s talk" says WHO, as depression tops list of causes of ill health. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-03-2017--depression-let-s-talk-says-who-as-depression-tops-list-of-causes-of-ill-health.
Wozniak KM, Rojas C, Wu Y, Slusher BS (2012) The role of glutamate signaling in pain processes and its regulation by GCP II inhibition. Curr Med Chem 19:1323–1334
Youdim MBH, Sandler M (1968) Activation of monoamine oxidase and inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase by reserpine. Eur J Pharmacol 4:105–108
Yu C, Li P, Qi D, Wang L, Qu HL, Zhang YJ, Wang XK, Fan HY (2017) Osthole protects sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via down-regulating NF-κB signal pathway. Oncotarget 8:4796–4813
Zhang JM, An J (2007) Cytokines, inflammation and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin 45:27–37
Zhang ZR, Leung WN, Cheung HY, Chan CW (2015) Osthole: a review on its bioactivities, pharmacological properties, and potential as alternative medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/919616
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for funding received under EMR (EMR/2016/005878) and DST-PURSE. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support received from the University Grants Commission under RUSA scheme.
Funding
Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (EMR/2016/005878), DST-PURSE and University Grants Commission, RUSA 2.0 scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The entire study involving the use of mice was approved by the Institutional. Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No. 226/CPCSEA/2016/07) and the experiments were conducted according to ethical guidelines of the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, L., Kaur, A., Garg, S. et al. Skimmetin/osthole mitigates pain-depression dyad via inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative stress-mediated neurotransmitter dysregulation. Metab Brain Dis 36, 111–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00604-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00604-4