Abstract
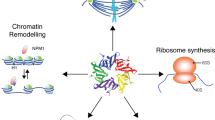
Nucleophosmin/B23/NPM is a multifunctional protein that regulates the most important processes of cell viability and apoptosis. Disturbances in the NPM gene structure and expression of the B23 protein encoded by this gene play an important role in the development and progression of oncological, neurological, and other diseases. The review considers the structure of the NPM gene and the B23 protein, the functions of nucleophosmin, and its role in carcinogenesis from the standpoint of applied and fundamental molecular biological aspects of modern oncology.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adachi, Y., Copeland, T., and Hatanaka, M., Nucleolar targeting signal of Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I specifically binds to nucleolar shuttle protein B23, J. Biol. Chem., 1993, vol. 268, pp. 13930–13934.
Arabi, A., Wu, S., and Ridderstråle, K., c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription, Nat. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 303–310.
Bañuelos, S., Lectez, B., Taneva, S.G., et al., Recognition of intermolecular G-quadruplexes by full length nucleophosmin. Effect of a leukemia-associated mutation, FEBS Lett., 2013, vol. 587, pp. 2254–2259.
Bergstralh, D.T., Conti, B.J., Moore, C.B., et al., Global functional analysis of nucleophosmin in Taxol response, cancer, chromatin regulation, and ribosomal DNA transcription, Exp. Cell Res., 2007, vol. 317, pp. 65–76.
Biggiogera, M., Fakan, S., and Kaufmann, S.H., Simultaneous immunoelectron microscopic visualization of protein B23 and C23 distribution in the HeLa cell nucleolus, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 1371–1374.
Bolli, N., De Marco, M.F., Martelli, M.P., et al., A dosedependent tug of war involving the NPM1 leukaemic mutant, nucleophosmin, and ARF, Leukemia, 2009, vol. 23, pp. 501–509.
Bolli, N., Nicoletti, I., De Marco, M.F., et al., Born to be exported: COOH-terminal nuclear export signals of different strength ensure cytoplasmic accumulation of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants, Cancer Res., 2007, vol. 67, pp. 6230–6237.
Bonetti, P., Davoli, T., Sironi, C., et al., Nucleophosmin and its AML-associated mutant regulate c-Myc turnover through Fbw7γ, J. Cell Biol., 2008, vol. 182, pp. 19–26.
Brandt, R., Nawka, M., and Kellermann, J., Nucleophosmin is a component of the fructoselysine-specific receptor in cell membranes of Mono Mac 6 and U937 monocyte-like cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj., 2004, vol. 1670, pp. 132–136.
Chan, P.K., Chan, F.Y., Morris, S.W., and Xie, Z., Isolation and characterization of the human nucleophosmin/B23 (NPM) gene: identification of the YY1 binding site at the 5' enhancer region, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, vol. 25, pp. 1225–1232.
Chang, J.H. and Olson, M.O., Structure of the gene for rat nucleolar protein B23, J. Biol. Chem., 1990, vol. 265, pp. 18227–18233.
Chang, J.H., Lin, J.Y., Wu, M.H., and Yung, B.Y., Evidence for the ability of nucleophosmin/B23 to bind ATP, Biochem. J., 1998, vol. 329, pp. 539–544.
Chang, T.P., Yu, S.-L., Lin, S.-Y., et al., Tumor Suppressor HLJ1 binds and functionally alters nucleophosmin via activating enhancer binding protein 2α complex formation, Cancer Res., 2010, vol. 70, pp. 1656–1667.
Chiarle, R., Simmons, W.J., Cai, H., et al., Stat3 is required for ALK-mediated lymphomagenesis and provides a possible therapeutic target, Nat. Med., 2005, vol. 11, pp. 623–629.
Ching, R.H., Lau, E.Y., and Ling, P.M., Phosphorylation of nucleophosmin at threonine 234/237 is associated with HCC metastasis, Oncotarget, 2015, vol. 6, pp. 43483–43495.
Choi, J.W., Lee, S.B., Kim, C.K., et al., Lysine 263 residue of NPM/B23 is essential for regulating ATP binding and B23 stability, FEBS Lett., 2008, vol. 582, pp. 1073–1080.
Colombo, E., Alcalay, M., and Pelicci, P.G., Nucleophosmin and its complex network: a possible therapeutic target in hematological diseases, Oncogene, 2011, vol. 30, pp. 2595–2609.
Cordell, J.L., Pulford, K.A., Bigerna, B., et al., Detection of normal and chimeric nucleophosmin in human cells, Blood, 1999, vol. 93, pp. 632–642.
Dabbous, M., Jefferson, M., and Haney, L., Biomarkers of metastatic potential in cultured adenocarcinoma clones, Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 2011, vol. 93, pp. 101–111.
Di Matteo, A., Franceschini, M., and Chiarella, S., Molecules that target nucleophosmin for cancer treatment an update, Oncotarget, 2016, vol. 7, pp. 44821–44840.
Endo, A., Matsumoto, M., and Inada, T., Nucleolar structure and function are regulated by the deubiquitylating enzyme USP36, J. Cell Sci., 2009, vol. 122, pp. 678–686.
Falini, B., Bolli, N., and Liso, A., Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications, Leukemia, 2009a, vol. 23, pp. 1731–1743.
Falini, B., Sportoletti, P., and Martelli, M.P., Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1: diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic perspectives, Curr. Opin. Oncol., 2009b, vol. 21, pp. 573–581.
Falini, B., Macijewski, K., Weiss, T., et al., Multilineage dysplasia has no impact on biologic, clinicopathologic, and prognostic features of AML with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1), Blood, 2010, vol. 115, pp. 3776–3786.
Finch R.A. and Chan, P.K., ATP depletion affects NPM translocation and exportation of rRNA from nuclei, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1996, vol. 222, pp. 553–558.
Foltz, D.R., Jansen, L.E., Black, B.E., et al., The human CENP-A centromeric nucleosome-associated complex, Nat. Cell Biol., 2006, vol. 8, pp. 458–469.
Gjerset, R., DNA damage, p14ARF, nucleophosmin (NPM1/B23), and cancer, J. Mol. Histol., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 239–251.
Grandori, C., Gomez-Roman, N., and Felton-Edkins, Z.A., c-Myc binds to human ribosomal DNA and stimulates transcription of rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I, Nat. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 311–318.
Grisendi, S., Mecucci, C., Falini, B., and Pandolfi, P.P., Nucleophosmin and cancer, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2006, vol. 6, pp. 493–505.
Grummitt, C.G., Townsley, F.M., Johnson, C.M., et al., Structural consequences of nucleophosmin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, pp. 23326–23332.
Gurumurthy, M., Tan, C.H., and Ng, R., Nucleophosmin interacts with HEXIM1 and regulates RNA polymerase II transcription, J. Mol. Biol., 2008, vol. 378, pp. 302–317.
Haindl, M., Harasim, T., Eick, D., and Muller, S., The nucleolar SUMO-specific protease SENP3 reverses SUMO modification of nucleophosmin and is required for rRNA processing, EMBO Rep., 2008, vol. 9, pp. 273–279.
Hamilton, G., Abraham, A.G., and Morton, J., AKT regulates NPM dependent ARF localization and p53mut stability in tumors, Oncotarget, 2014, vol. 5, pp. 6142–6167.
Herrera, J.E., Savkur, R., and Olson, M.O., The ribonuclease activity of nucleolar protein B23, Nucleic Acids Res., 1995, vol. 23, pp. 3974–3979.
Herrera, J.E., Correia, J.J., Jones, A.E., and Olson, M.O.J., Sedimentation analyses of the salt- and divalent metal ion-induced oligomerization of nucleolar protein B23, Biochemistry, 1996, vol. 35, pp. 2668–2673.
Hingorani, K., Szebem, A., and Olson, M.O., Mapping the functional domains of nucleolar protein B23, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, pp. 24451–24457.
Hsu, C.Y. and Yung, B.Y., Over-expression of nucleophosmin/B23 decreases the susceptibility of human leukemia HL-60 cells to retinoic acid-induced differentiation and apoptosis, Int. J. Cancer, 2000, vol. 88, pp. 392–400.
Inder, K.L., Lau, C., Loo, D., et al., Nucleophosmin and nucleolin regulate K-Ras plasma membrane interactions and MAPK signal transduction, J. Biol. Chem., 2009, vol. 284, pp. 28410–28419.
Itahana, K., Bhat, K.P., and Jin, A., Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation, Mol. Cell, 2003, vol. 12, pp. 1151–1164.
Jiang, P.S. and Yung, B.Y., Down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA delays the entry of cells into mitosis, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1999, vol. 257, pp. 865–870.
Joukov, V., Groen, A.C., Prokhorova, T., et al., The BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimer modulates ran-dependent mitotic spindle assembly, Cell, 2006, vol. 127, pp. 539–552.
Karhemo, P.R., Rivinoja, A., Lundin, J., et al., An extensive tumor array analysis supports tumor suppressive role for nucleophosmin in breast cancer, Am. J. Pathol., 2011, vol. 179, pp. 1004–1014.
Koike, A., Nishikawa, H., Wu, W., et al., Recruitment of phosphorylated NPM1 to sites of DNA damage through RNF8-dependent ubiquitin conjugates, Cancer Res., 2010, vol. 70, pp. 6746–6756.
Kotani, H., Ito, M., and Hamaguchi, T., The delta isoform of protein phosphatase type 1 is localized in nucleolus and dephosphorylates nucleolar phosphoproteins, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1998, vol. 249, pp. 292–296.
Krause, A. and Hoffmann, I., Polo-Like kinase 2-dependent phosphorylation of NPM/B23 on serine 4 triggers centriole duplication, PLoS One, 2010, vol. 5, p. 9849.
Kuramitsu, Y., Hayashi, E., and Okada, F., Proteomic analysis for nucleolar proteins related to tumor malignant progression: a comparative proteomic study between malignant progressive cells and regressive cells, Anticancer Res., 2010, vol. 30, pp. 2093–2099.
Kurki, S., Peltonen, K., and Laiho, M., Nucleophosmin, HDM2 and p53: players in UV damage incited nucleolar stress response, Cell Cycle, 2004a, vol. 3, pp. 976–979.
Kurki, S., Peltonen, K., Latonen, L., et al., Nucleolar protein NPM interacts with HDM2 and protects tumor suppressor protein p53 from HDM2-mediated degradation, Cancer Cell, 2004b, vol. 5, pp. 465–475.
Lawson, K., Larentowicz, L., Laury-Kleintop, L., and Gilmour, S.K., B23 is a downstream target of polyamine-modulated CK2, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 2005, vol. 274, pp. 103–114.
Lee, S.B., Xuan Nguyen, T.L., Choi, J.W., et al., Nuclear Akt interacts with B23/NPM and protects it from proteolytic cleavage, enhancing cell survival, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2008, vol. 105, pp. 16584–16589.
Li, Z., Boone, D., and Hann, S.R., Nucleophosmin interacts directly with c-Myc and controls c-Myc-induced hyperproliferation and transformation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2008, vol. 105, pp. 18794–18799.
Lindström, M., NPM/B23: a multifunctional chaperone in ribosome biogenesis and chromatin remodeling, Biochem. Res. Int., 2011, vol. 2011, art. ID 195209.
Lindström, M.S. and Zhang, Y., Ribosomal protein S9 is a novel B23/NPM-binding protein required for normal cell proliferation, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, pp. 15568–15576.
Liu, Q.R. and Chan, P.K., Formation of nucleophosmin/B23 oligomers requires both the amino- and the carboxyl-terminal domains of the protein, Eur. J. Biochem., 1991, vol. 329, pp. 715–721.
Liu, W.H. and Yung, B.Y., Mortalization of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells to be more susceptible to sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity by down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23, Oncogene, 1998, vol. 17, pp. 3055–3064.
Liu, H., Tan, B.C.-M., and Tseng, K.H., Nucleophosmin acts as a novel AP2α-binding transcriptional corepressor during cell differentiation, EMBO Rep., 2007, vol. 8, pp. 394–400.
Lu, Y.Y., Lam, C.Y., and Yung, B.Y., Decreased accumulation and dephosphorylation of themitosis-specific form of nucleophosmin/B23 in staurosporine-induced chromosome decondensation, Biochem J., 1996, vol. 317, pp. 321–327.
Martelli, A.M., Robuffo, I., Bortul, R., et al., Behavior of nucleolar proteins during the course of apoptosis in camptothecin-treated HL60 cells, J. Cell. Biochem., 2000, vol. 78, pp. 264–277.
Mascaux, C., Bex, F., and Martin, B., The role of NPM, p14arf and MDM2 in precursors of bronchial squamous cell carcinoma, Eur. Respir. J., 2008, vol. 32, pp. 678–686.
McCloskey, R., Menges, C., Friedman, A., et al., Human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 upregulation of nucleophosmin is important for proliferation and inhibition of differentiation, J. Virol., 2010, vol. 84, pp. 5131–5139.
Mitrea, D.M. and Kriwacki, R.W., Cryptic disorder: an order-disorder transformation regulates the function of nucleophosmin, Pac. Symp. Biocomput., 2012, pp. 152–163.
Mitrea, D.M., Grace, C.R., Buljan, M., et al., Structural polymorphism in the N-terminal oligomerization domain of NPM1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2014, vol. 111, pp. 4466–4471.
Murano, K., Okuwaki, M., Hisaoka, M., and Nagata, K., Transcription regulation of the rRNA gene by a multifunctional nucleolar protein, B23/nucleophosmin, through its histone chaperone activity, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2008, vol. 28, pp. 3114–3126.
Negi, S.S. and Olson, M.O., Effects of interphase and mitotic phosphorylation on the mobility and location of nucleolar protein B23, J. Cell Sci., 2006, vol. 119, pp. 3676–3685.
Nishimura, Y., Ohkubo, T., Furuichi, Y., and Umekawa, H., Tryptophans 286 and 288 in the C-terminal region of protein B23.1 are important for its nucleolar localization, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2002, vol. 66, pp. 2239–2242.
Okuda, M., The role of nucleophosmin in centrosome duplication, Oncogene, 2002, vol. 21, pp. 6170–6174.
Okuda, M., Horn, H.F., and Tarapore, P., Nucleophosmin/B23 is a target of CDK2/cyclin E in centrosome duplication, Cell, 2000, vol. 103, pp. 127–140.
Okuwaki, M., The structure and functions of NPM1/Nucleophosmin/B23, a multifunctional nucleolar acidic protein, J. Biochem., 2008, vol. 143, pp. 441–448.
Okuwaki, M., Matsumoto, K., Tsujimoto, M., and Nagata, K., Function of nucleophosmin/B23, a nucleolar acidic protein, as a histone chaperone, FEBS Lett., 2001, vol. 506, pp. 272–276.
Okuwaki, M., Tsujimoto, M., and Nagata, K., The RNA binding activity of a ribosome biogenesis factor, nucleophosmin/B23, is modulated by phosphorylation with a cell cycle-dependent kinase and by association with its subtype, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2002, vol. 13, pp. 2016–2030.
Palaniswamy, V., Moraes, K.C.M., Wilusz, C.J., and Wilusz, J., Nucleophosmin is selectively deposited on mRNA during polyadenylation, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2006, vol. 13, pp. 429–435.
Patterson, S.D., Grossman, J.S., D’Andrea, P., and Latter, G.I., Reduced numatrin/B23/nucleophosmin labeling in apoptotic Jurkat T-lymphoblasts, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 9429–9436.
Pearson, J.D., Lee, J.K., Bacani, J.T., et al., NPM-ALK: the prototypic member of a family of oncogenic fusion tyrosine kinases, J. Recept. Signal Transduction, 2012, vol. 2012, p. 123253.
Peter, M., Nakagawa, J., Dorée, M., et al., Identification of major nucleolar proteins as candidate mitotic substrates of cdc2 kinase, Cell, 1990, vol. 60, pp. 791–801.
Pfister, J.A. and D’Mello, S.R., Insights into the regulation of neuronal viability by nucleophosmin/B23, Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood), 2015, vol. 240, pp. 774–786.
Poletto, M., Lirussi, L., Wilson, D.M., III, and Tell, G., Nucleophosmin modulates stability, activity and nucleolar accumulation of base excision repair proteins, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2014, vol. 25, pp. 1641–1652.
Pollock, S.L., Rush, E.A., and Redner, R.L., NPM-RAR, not the RAR-NPM reciprocal t(5;17)(q35;q21) acute promyelocytic leukemia fusion protein, inhibits myeloid differentiation, Leuk. Lymphoma, 2014, vol. 55, pp. 1383–1387.
Prinos, P., Lacoste, M.C., Wong, J., et al., Mutation of cysteine 21 inhibits nucleophosmin/B23 oligomerization and chaperone activity, Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2010, vol. 2, pp. 24–30.
Qi, W., Shakalya, K., and Stejskal, A., NSC348884 a nucleophosmin inhibitor disrupts oligomer formation and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells, Oncogene, 2008, vol. 27, pp. 4210–4220.
Redner, R.L., Chen, J.D., Rush, E.A., et al., The t(5;17) acute promyelocytic leukemia fusion protein NPM-RAR interacts with co-repressor and co-activator proteins and exhibits both positive and negative transcriptional properties, Blood, 2000, vol. 95, pp. 2683–2690.
Ruggero, D. and Pandolfi, P.P., Does the ribosome translate cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2003, vol. 3, pp. 179–192.
Sato, K., Hayami, R., Wu, W., et al., Nucleophosmin/B23 is a candidate substrate for the BRCA1-BARD1 ubiquitin ligase, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, pp. 30919–30922.
Scognamiglio, P.L., Di Natale, C., Leone, M., et al., G-quadruplex DNA recognition by nucleophosmin: new insights from protein dissection, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj., 2014, vol. 1840, pp. 2050–2059.
Shandilya, J., Swaminathan, V., Gadad, S.S., et al., Acetylated NPM1 localizes in the nucleoplasm and regulates transcriptional activation of genes implicated in oral cancer manifestation, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2009, vol. 29, pp. 5115–5127.
Sheng, J. and Zhang, W., Identification biomarkers for cervical cancer in peripheral blood lymphocytes by oligonucleotide microarrays, Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2010, vol. 90, pp. 2611–2615.
Slupianek, A., Nieborowska-Skorska, M., Hoser, G., et al., Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway in nucleophosmin/anaplastic lymphoma kinase-mediated lymphomagenesis, Cancer Res., 2001, vol. 61, pp. 2194–2199.
Smetana, K., Ochs, R., Lischwe, M.A., et al., Immunofluorescence studies on proteins B23 and C23 in nucleoli of human lymphocytes, Exp. Cell Res., 1984, vol. 152, pp. 195–203.
Spector, D.L., Ochs, R.L., and Busch, H., Silver staining, immunofluorescence, and immunoelectron microscopic localization of nucleolar phosphoproteins B23 and C23, Chromosoma, 1984, vol. 90, pp. 139–148.
Staber, P.B., Vesely, P., Haq, N., et al., The oncoprotein NPM-ALK of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma induces JUNB transcription via ERK1/2 and JunB translation via mTOR signaling, Blood, 2007, vol. 110, pp. 3374–3383.
Swaminathan, V., Kishore, A.H., Febitha, K.K., and Kundu, T.K., Human histone chaperone nucleophosmin enhances acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2005, vol. 25, pp. 7534–7545.
Szebeni, A. and Olson, M.O., Nucleolar protein B23 has molecular chaperone activities, Protein Sci., 1999, vol. 8, pp. 905–912.
Szebeni, A., Mehrotra, B., and Baumann, A., Nucleolar protein B23 stimulated neclear import of the HIV-1 Rev protein and NLS-conjugated albumin, Biochemistry, 1997, vol. 36, pp. 3941–3949.
Takemura, M., Ohta, N., and Furuichi, Y., Stimulation of calf thymus DNA polymerase α activity by nucleolar protein B23, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1994, vol. 199, pp. 46–51.
Takemura, M., Sato, K., Nishio, M., et al., Nucleolar protein B23.1 binds to retinoblastoma protein and synergistically stimulates DNA polymerase α activity, J. Biochem., 1999, vol. 125, pp. 904–909.
Tarapore, P., Shinmura, K., and Suzuki, H., Thr199 phosphorylation targets nucleophosmin to nuclear speckles and represses pre-mRNA processing, FEBS Lett., 2006, vol. 580, pp. 399–409.
Tawfic, S., Goueli, S.A., Olson, M.O., and Ahmed, K., Androgenic regulation of the expression and phosphorylation of prostatic nucleolar protein B23, Cell Mol. Biol. Res., 1993, vol. 39, pp. 43–51.
Tawfic, S., Olson, M.O., and Ahmed, K., Role of protein phosphorylation in post-translational regulation of protein B23 during programmed cell death in the prostate gland, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, vol. 270, pp. 21009–21015.
Tokuyama, Y., Horn, H.F., Kawamura, K., et al., Specific phosphorylation of nucleophosmin on Thr(199) by cyclin-dependent kinase 2-cyclin E and its role in centrosome duplication, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 21529–21537.
Tulchin, N., Chambon, M., and Juan, G., BRCA1 protein and nucleolin colocalize in breast carcinoma tissue and cancer cell lines, Am. J. Pathol., 2010, vol. 176, pp. 1203–1214.
Velusamy, T., Kiel, M.J., Sahasrabuddhe, A.A., et al., A novel recurrent NPM1-TYK2 gene fusion in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders, Blood, 2014, vol. 124, pp. 3768–3771.
Wang, W., Budhu, A., Forgues, M., and Wang, X.W., Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication, Nat. Cell Biol., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 823–830.
Wanzel, M., Russ, A.C., Kleine-Kohlbrecher, D., et al., A ribosomal protein L23-nucleophosmin circuit coordinates Miz1 function with cell growth, Nat. Cell Biol., 2008, vol. 10, pp. 1051–1061.
Watanabe, M., Sasaki, M., Itoh, K., et al., JunB induced by constitutive CD30-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen- activated protein kinase signaling activates the CD30 promoter in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and reed-sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma, Cancer Res., 2005, vol. 65, pp. 7628–7634.
White, R.J., RNA polymerases I and III, non-coding RNAs and cancer, Trends Genet., 2008, vol. 24, pp. 622–629.
Wu, M.H. and Yung, B.Y., UV stimulation of nucleophosmin/B23 expression is an immediate-early gene response induced by damaged DNA, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, pp. 48234–48240.
Wu, H.L., Hsu, C.Y., Liu, W.H., and Yung, B.Y., Berberine-induced apoptosis of human leukemia HL-60 cells is associated with down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23 and telomerase activity, Int. J. Cancer, 1999, vol. 81, pp. 923–929.
Yang, C., Maiguel, D.A., and Carrier, F., Identification of nucleolin and nucleophosmin as genotoxic stress-responsive RNA-binding proteins, Nucleic Acids Res., 2002, vol. 30, pp. 2251–2260.
Yang, K., Wang, M., Zhao, Y., et al., A redox mechanism underlying nucleolar stress sensing by nucleophosmin, Nat. Commun., 2016, vol. 7, p. 13599.
Ye, K., Nucleophosmin/B23, a multifunctional protein that can regulate apoptosis, Cancer Biol. Ther., 2005, vol. 4, pp. 918–923.
Yoneda-Kato, N., Look, A.T., Kirstein, M.N., et al., The t(3;5)(q25.1;q34) of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia produces a novel fusion gene, NPM-MLF1, Oncogene, 1996, vol. 12, pp. 265–275.
Yu, Y., Maggi, L.B., Jr., and Brady, S.N., Nucleophosmin is essential for ribosomal protein L5 nuclear export, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2006, vol. 26, pp. 3798–3809.
Yun, J.P., Chew, E.C., and Liew, C.T., Nucleophosmin/B23 is a proliferate shuttle protein associated with nuclear matrix, J. Cell. Biochem., 2003, vol. 90, pp. 1140–1148
Yung, B.Y., Oncogenic role of nucleophosmin/B23, Chang, Gung Med. J., 2007, vol. 30, pp. 285–293.
Zatsepina, O.V., Todorov, I.T., Philipova, R.N., et al., Cell cycle-dependent translocations of a major nucleolar phosphoprotein, B23, and some characteristics of its variants, Eur. J. Cell. Biol., 1997, vol. 73, pp. 58–70.
Zeller, K.I., Haggerty, T.J., and Barrett, J.F., Characterization of nucleophosmin (B23) as a Myc target by scanning chromatin immunoprecipitation, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, vol. 276, pp. 48285–48291.
Zhang, H., Shi, X., Paddon, H., et al., B23/nucleophosmin serine 4 phosphorylation mediates mitotic functions of polo-like kinase 1, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, pp. 35726–35734.
Zhao, X., Ji, J., and Yu, L.R., Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of nucleophosmin and its potential regulation by peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase, J. Mol. Biochem., 2015, vol. 4, pp. 95–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by D. Novikova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponkratova, D.A., Lushnikova, A.A. The Role of Nucleophosmin in Cell Functioning and Tumor Progression. Biol Bull Rev 10, 266–279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086420040064
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086420040064