Abstract
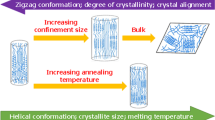
Thermal properties such as melting temperature can well reflect the microstructure of the polymer material, and have practical implications in the application of nanofibers. In this work, we investigated the melting temperature of individual electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) nanofibers with diameters ranging from smaller than 200 nm to greater than 2 µm by the local thermal analysis technique. The PVDF fibers obtained under four different conditions were found to crystallize into α and β phases, and the fiber mats showed typical values in the crystallinity and Tm with no significant difference among the four. However, analyses at single fiber level revealed broad distribution in diameter and Tm for the fibers produced under identical electrospinning condition. The Tm of individual nanofibers was found to remain constant at large diameters and increase quickly when reducing the fiber diameter toward the nanoscale, and Tm values of 220–230 °C were observed for the thinnest nanofibers, much higher than the typical values reported for bulk PVDF. The Tm and molecular orientation at different positions along a beaded fiber were analyzed, showing a similar distribution pattern with a minimum at the bead center and higher values when moving toward both directions. The results indicate that molecular orientation is the driving mechanism for the observed correlation between the Tm and the diameter of the nanofibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reneker, D. H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223.
Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 581–586.
Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S. K.; Zhang, F.; Huang, C. Electrospun nanofibers membranes for effective air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353.
Al-Attabi, R.; Dumée, L. F.; Kong, L.; Schütz, J. A.; Morsi, Y. High efficiency poly(acrylonitrile) electrospun nanofiber membranes for airborne nanomaterials filtration. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700572.
Zeng, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Liang, Q.; Bian, X.; Yang, L.; Jing, X. Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 227–231.
Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21.
Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nano/micro scale poly(L-lactic acid) aligned fibers and their potential in neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610.
Sill, T. J.; von Recum, H. A. Electrospinning: applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 0008, 29, 1989–2006.
Hu, J.; Kai, D.; Ye, H.; Tian, L.; Ding, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Loh, X. J. Electrospinning of poly(glycerol sebacate)-based nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 70, 1089–1094.
Wong, S. C.; Baji, A.; Leng, S. Effect of fiber diameter on tensile properties of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymer 2008, 49, 4713–4722.
Pai, C. L.; Boyce, M. C.; Rutledge, G. C. Mechanical properties of individual electrospun PA 6(3)T fibers and their variation with fiber diameter. Polymer 2011, 52, 2295–2301.
Greenfeld, I.; Sui, X.; Wagner, H. D. Stiffness, strength, and toughness of electrospun nanofibers: effect of flow-induced molecular orientation. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 6518–6530.
Mathew, G.; Hong, J. P.; Rhee, J. M.; Leo, D. J.; Nah, C. Preparation and anisotropic mechanical behavior of highly-oriented electrospun poly(butylene terephthalate) fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 2017–2021.
Chew, S. Y.; Hufnagel, T. C.; Lim, C. T.; Leong, K. W. Mechanical properties of single electrospun drug-encapsulated nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3880–3891.
Chan, K. H. K.; Wong, S. Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Lim, P. C.; Lim, C. T.; Kotaki, M.; He, C. B. Effect of molecular orientation on mechanical property of single electrospun fiber of poly. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 13179–13185.
Arinstein, A.; Zussman, E. Electrospun polymer nanofibers: mechanical and thermodynamic perspectives. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 691–707.
Stachewicz, U.; Bailey, R. J.; Wang, W.; Barber, A. H. Size dependent mechanical properties of electrospun polymer fibers from a composite structure. Polymer 2012, 53, 5132–5137.
Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Orientation and partial disentanglement in individual electrospun fibers: diameter dependence and correlation with mechanical properties. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4511–4519.
Papkov, D.; Zou, Y.; Andalib, M. N.; Goponenko, A.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Dzenis, Y. A. Simultaneously strong and tough ultrafine continuous nanofibers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3324–3331.
Wang, W.; Barber, A. H. Diameter-dependent melting behaviour in electrospun polymer fibres. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 225701.
Doshi, J.; Reneker, D. H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160.
Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Turng, L. S.; Li, Q. Crystalline morphology of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) nanofibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4939–4949.
Kołbuk, D.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Kowalewski, T. A. Optical birefringence and molecular orientation of electrospun polycaprolactone fibers by polarizing-interference microscopy. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 275–283.
Damaraju, S. M.; Wu, S.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T. L. Structural changes in PVDF fibers due to electrospinning and its effect on biological function. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 045007.
Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Wachtel, E.; Koga, T.; Sokolov, J.C.; Rafailovich, M. H. Electrospinning of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate)/clay nanocomposite fibers. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 2501–2508.
Arinstein, A.; Liu, Y.; Rafailovich, M.; Zussman, E. Shifting of the melting point for semi-crystalline polymer nanofibers. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 93, 46001.
Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zussman, E.; Korach, C. S.; Zhao, W.; Rafailovich, M. Diameter-dependent modulus and melting behavior in electrospun semicrystalline polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4439–4444.
Zheng, Y. R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X. L.; Li, H. H.; Ren, Z. J.; Yan, S. K. Enhanced αγ′ transition of poly(vinylidene fluoride) by step crystallization and subsequent annealing. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 598–603.
Baji, A.; Mai, Y. W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Electrospinning induced ferroelectricity in poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3068–3071.
Hansen, B. J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z. L. Hybrid nanogenerator for concurrently harvesting biomechanical and biochemical energy. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3647–3652.
Chang, C.; Tran, V. H.; Wang, J.; Fuh, Y. K.; Lin, L. Direct-write piezoelectric polymeric nanogenerator with high energy conversion efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 726–731.
Zhou, J.; Berry, B.; Douglas, J. F.; Karim, A.; Snyder, C. R.; Soles, C. Nanoscale thermal-mechanical probe determination of ‘softening transitions’ in thin polymer films. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 495703.
Wu, X.; Shi, S.; Yu, Z.; Russell, T. P.; Wang, D. AFM nanomechanical mapping and nanothermal analysis reveal enhanced crystallization at the surface of a semicrystalline polymer. Polymer 2018, 146, 188–195.
Middendorf, D.; Bindrich, U.; Mischnick, P.; Franke, K.; Heinz, V. AFM-based local thermal analysis is a suitable tool to characterize the impact of different grinding techniques on sucrose surface properties. J. Food Eng. 2018, 235, 50–58.
Ago, M., Jakes, J.E.; Johansson, L.; Park, S.; Rojas, O. J. Interfacial properties of lignin-based electrospun nanofibers and films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6849–6856.
Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Su, Z. Molecular orientation in individual electrospun nanofibers studied by polarized AFM-IR. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9639–9645.
Chowdhury, M.; Stylios, G. Effect of experimental parameters on the morphology of electrospun Nylon 6 fibres. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 70–78.
Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Hsieh, Y. Direct fabrication of highly nanoporous polystyrene fibers via electrospinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 521–528.
Martins, P.; Lopes, A. C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706.
Boccaccio, T.; Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Piaggio, P. Characterization of PVDF membranes by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 315–329.
Kochervinskii, V. V. The structure and properties of block poly(vinylidene fluoride) and systems based on it. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1996, 65, 865–913.
Bormashenko, Y.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, E. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796.
Imamura, R.; Silva, A. B.; Gregorio Jr., R. γ→β Phase transformation induced in poly(vinylidene fluoride) by stretching. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 3242–3246.
Gregorio Jr., R. Determination of the α, ε, and γ crystalline phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films prepared at different conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3272–3279.
Esterly, D. M.; Love, B. J. Phase transformation to β-poly(vinylidene fluoride) by milling. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 91–97.
Gregorio, J. R.; Cestari, M. Effect of crystallization temperature on the crystalline phase content and morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 1994, 32, 859–870.
Lee, S. H.; Cho, H. H. Crystal structure and thermal properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)-carbon fiber composite films with various drawing temperatures and speeds. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 1146–1151.
Nakagawa, K.; Ishida, Y. Annealing effects in poly(vinylidene fluoride) as revealed by specific volume measurements, differential scanning calorimetry, and electron microscopy. J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Phys. Ed. 1973, 11, 2153–2171.
Maccone, P.; Brinati, G.; Arcella, V. Environmental stress cracking of poly(vinylidene fluoride) in sodium hydroxide. Effect of chain regularity. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 761–767.
Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. Electrospinning of ethyl-cyanoethyl cellulose/tetrahydrofuran solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 242–246.
Ero-Phillips, O.; Jenkins, M.; Stamboulis, A. Tailoring crystallinity of electrospun plla fibres by control of electrospinning parameters. Polymers 2012, 4, 1331–1348.
Nandi, A.K.; Mandelkern, L. The influence of chain structure on the equilibrium melting temperature of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 1991, 29, 1287–1297.
Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Zhuang, Y.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y. M. Crystalline polymorphism in poly(vinylidenefluoride) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 94–126.
Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Molecular orientation in electrospun fibers: from mats to single fibers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9473–9493.
Wang, C.; Tsou, S. Y.; Lin, H. S. Brill transition of nylon-6 in electrospun nanofibers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1799–1809.
Iguchi, M.; Tonami, H.; Kawai, T. Crystallization of polyethylene under molecular orientation. Kolloid-Z.u.Z.Polymere 1967, 221, 28–40.
Yan, J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, C.; Fu, H.; An, S.; Jiang, Y. Crystalline structure changes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers during stretching process. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2019, 50, 752–760.
Yoshioka, T.; Dersch, R.; Tsuji, M.; Schaper, A. K. Orientation analysis of individual electrospun PE nanofibers by transmission electron microscopy. Polymer 2010, 51, 2383–2389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2476-9
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21674118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2020_2476_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Melting Temperature of Individual Electrospun Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Fibers Studied by AFM-based Local Thermal Analysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZQ., Zhong, ZX., Ma, YY. et al. Melting Temperature of Individual Electrospun Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Fibers Studied by AFM-based Local Thermal Analysis. Chin J Polym Sci 39, 219–227 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2476-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2476-9