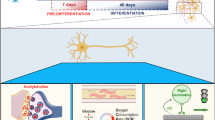
Abstract
Septal innervation of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons to the hippocampus is critical for normal learning and memory and is severely degenerated in Alzheimer’s disease. To understand the molecular events underlying physiological cholinergic synaptogenesis and remodeling, as well as pathological loss, we developed an optimized primary septal-hippocampal co-culture system. Hippocampal and septal tissue were harvested from embryonic Sprague–Dawley rat brain and cultured together at varying densities, cell ratios, and in the presence of different growth factors. We identified conditions that produced robust septal-hippocampal synapse formation. We used confocal microscopy with primary antibodies and fluorescent ligands to validate that this system was capable of generating developmentally mature cholinergic synapses. Such synapses were comprised of physiological synaptic partners and mimicked the molecular composition of in vivo counterparts. This co-culture system will facilitate the study of the formation, plasticity, and dysfunction of central mammalian cholinergic synapses.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Original raw data will be available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author for academic/non-commercial purposes.
Abbreviations
- αBTX:
-
α-Bungarotoxin
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease
- BFCN:
-
Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- BMP9:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 9
- ChAT:
-
Choline acetyltransferase
- CHT1:
-
High-affinity choline transporter
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DIV:
-
Day in vitro
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GAD65:
-
Glutamate decarboxylase 65
- Geph:
-
Gephyrin
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule associated protein 2
- MLA:
-
Methyllycaconitine
- nAChR:
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- nMDP:
-
Normalized mean deviation product
- PSD-93:
-
Postsynaptic density 93
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density 95
- VAChT:
-
Vesicular acetylcholine transporter
- VGAT:
-
Vesicular GABA transporter
References
Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX (1993) Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:1455–1473
Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX (2004) The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and their function in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Prog Brain Res 145:109–120
Andrä J, Lachmann I, Luppa H (1988) A comparison of the localization of acetylcholinesterase in the rat brain as demonstrated by enzyme histochemistry and immunohistochemistry. Histochemistry 88:595–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00570330
Ballinger EC, Ananth M, Talmage DA, Role LW (2016) Basal forebrain cholinergic circuits and signaling in cognition and cognitive decline. Neuron 91:1199–1218
Banker GA, Cowan WM (1977) Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res 126:397–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7
Baron JA (1986) Cigarette smoking and Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 36:1490–1496. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.36.11.1490
Cheng Q, Yakel JL (2014) Presynaptic α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors enhance hippocampal mossy fiber glutamatergic transmission via PKA activation. J Neurosci 34:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2973-13.2014
Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR (1983) Alzheimer’s disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 219:1184–1190
Dani JA (2015) Chapter one-neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor structure and function and response to nicotine. Int Rev Neurobiol 124:3–19
El Ayadi A, Stieren ES, Barral JM et al (2012) Ubiquilin-1 regulates amyloid precursor protein maturation and degradation by stimulating K63-linked polyubiquitination of lysine 688. Proc Nat Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206786109
Elias GM, Funke L, Stein V et al (2006) Synapse-specific and developmentally regulated targeting of AMPA receptors by a family of MAGUK scaffolding proteins. Neuron 52:307–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.012
Emerit MB, Segovia J, Alho H et al (1989) Hippocampal membranes contain a neurotrophic activity that stimulates cholinergic properties of fetal rat septal neurons cultured under serum-free conditions. J Neurochem 52:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb02547.x
Eslamizade MJ, Madjd Z, Rasoolijazi H et al (2016) Impaired memory and evidence of histopathology in CA1 pyramidal neurons through injection of Aβ1-42 peptides into the frontal cortices of rat. Basic Clin Neurosci 7:31–41
Fabian-Fine R, Skehel P, Errington ML et al (2001) Ultrastructural distribution of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 21:7993–8003
Ghosheh OA, Dwoskin LP, Miller DK, Crooks PA (2001) Accumulation of nicotine and its metabolites in rat brain after intermittent or continuous peripheral administration of [2’-(14)C]nicotine. Drug Metab Dispos 29:645–651
Gorlewicz A, Krawczyk K, Szczepankiewicz AA et al (2020) Colocalization colormap—an ImageJ plugin for the quantification and visualization of colocalized signals. Neuroinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-020-09465-9
Gray R, Rajan AS, Radcliffe KA et al (1996) Hippocampal synaptic transmission enhanced by low concentrations of nicotine. Nature 383:713
Gritti I, Henny P, Galloni F et al (2006) Stereological estimates of the basal forebrain cell population in the rat, including neurons containing choline acetyltransferase, glutamic acid decarboxylase or phosphate-activated glutaminase and colocalizing vesicular glutamate transporters. Neuroscience 143:1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.024
Haam J, Zhou J, Cui G, Yakel JL (2018) Septal cholinergic neurons gate hippocampal output to entorhinal cortex via oriens lacunosum moleculare interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E1886–E1895. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712538115
Hampel HJ, Cuello AC, Farlow MR et al (2017) Revisiting the cholinergic hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: emerging evidence from translational and clinical research. Alzheimer Dementia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.08.016
Hartikka J, Hefti F (1988) Development of septal cholinergic neurons in culture: plating density and glial cells modulate effects of NGF on survival, fiber growth, and expression of transmitter-specific enzymes. J Neurosci 8:2967–2985
Huang LZ, Parameswaran N, Bordia T et al (2009) Nicotine is neuroprotective when administered before but not after nigrostriatal damage in rats and monkeys. J Neurochem 109:826–837. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06011.x
Jaskolski F, Mulle C, Manzoni OJ (2005) An automated method to quantify and visualize colocalized fluorescent signals. J Neurosci Methods 146:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.01.012
Johansson S, Friedman W, Arhem P (1992) Impulses and resting membrane properties of small cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol 445:129–140. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018915
Kojima M, Ikeuchi T, Hatanaka H (1994) Nerve growth factor induces trkA mRNA expression in cultured basal forebrain cholinergic neurons from 17-day fetal rats. Neurosci Lett 169:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(94)90353-0
Lee Y, Lee JS, Lee KJ et al (2017) Polo-like kinase 2 phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein regulates activity-dependent amyloidogenic processing. Neuropharmacology 117:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.02.027
Lopez-Coviella I, Follettie MT, Mellott TJ et al (2005) Bone morphogenetic protein 9 induces the transcriptome of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6984–6989. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0502097102
Luchicchi A, Bloem B, Viana JN et al (2014) Illuminating the role of cholinergic signaling in circuits of attention and emotionally salient behaviors. Front Synaptic Neurosci 6:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00024
Mintz CD, Smith SC, Barrett KMS, Benson DL (2012) Anesthetics interfere with the polarization of developing cortical neurons. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 24:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0b013e31826a03a6
Morens DM, Grandinetti A, Reed D et al (1995) Cigarette smoking and protection from parkinson’s disease: false association or etiologic clue? Neurology 45:1041–1051
Morley BJ, Mervis RF (2013) Dendritic spine alterations in the hippocampus and parietal cortex of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice. Neuroscience 233:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.025
Newhouse PA, Sunderland T, Tariot PN et al (1988) Intravenous nicotine in Alzheimer’s disease: a pilot study. Psychopharmacology 95:171–175
Pak DT, Yang S, Rudolph-Correia S et al (2001) Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by SPAR, a PSD-95-associated RapGAP. Neuron 31:289–303
Park HJ, Lee PH, Ahn YW et al (2007) Neuroprotective effect of nicotine on dopaminergic neurons by anti-inflammatory action. Eur J Neurosci 26:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05636.x
Parker MJ, Zhao S, Bredt DS et al (2004) PSD93 regulates synaptic stability at neuronal cholinergic synapses. J Neurosci 24:378–388. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3865-03.2004
Peacock JH, Rush DF, Mathers LH (1979) Morphology of dissociated hippocampal cultures from fetal mice. Brain Res 169:231–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(79)91027-8
Rubboli F, Court JA, Sala C et al (1994) Distribution of nicotinic receptors in the human hippocampus and thalamus. Eur J Neurosci 6:1596–1604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00550.x
Ryan RE, Ross SA, Drago J, Loiacono RE (2001) Dose-related neuroprotective effects of chronic nicotine in 6-hydroxydopamine treated rats, and loss of neuroprotection in α4 nicotinic receptor subunit knockout mice. Br J Pharmacol 132:1650–1656
Schmitz TW, Nathan Spreng R, Weiner MW et al (2016) Basal forebrain degeneration precedes and predicts the cortical spread of Alzheimer’s pathology. Nat Commun 7:13249. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13249
Schnitzler AC, Lopez-Coviella I, Blusztajn JK (2008) Purification and culture of nerve growth factor receptor (p75)-expressing basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Nat Protoc 3:34–40
Schock SC, Jolin-Dahel KS, Schock PC et al (2010) Striatal interneurons in dissociated cell culture. Histochem Cell Biol 134:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0707-9
Sharma G, Vijayaraghavan S (2003) Modulation of presynaptic store calcium induces release of glutamate and postsynaptic firing. Neuron 38:929–939
Takács VT, Cserép C, Schlingloff D et al (2018) Co-transmission of acetylcholine and GABA regulates hippocampal states. Nat Commun 9:2848. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05136-1
Wong TP, Debeir T, Duff K, Cuello AC (1999) Reorganization of cholinergic terminals in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in transgenic mice carrying mutated Presenilin-1 and amyloid precursor protein transgenes. J Neurosci 19(7):2706–2716
Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (2011) Cholinergic systems mediate action from movement to higher consciousness. Behav Brain Res 221:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.12.046
Zoli M (2000) Distribution of cholinergic neurons in the mammalian brain with special reference to their relationship with neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 13–30
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Georgetown Microscopy & Imaging Shared Resource which is partially supported by NIH/NCI grant P30-CA051008.
Funding
This work was supported by grants to DTSP: National Institutes of Health (RF1 AG056603-01) and SD: National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (TL1TR001431).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, SD and DTSP; Methodology SD, CRR and DTSP; Experiments, SD and CRR; Data Analysis, SD, CRR, MAG, and AKS; Writing, all authors; Funding Acquisition, DTSP and SD; Supervision, DTSP and SD.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All animals used in experimental procedures were approved (IACUC protocol #: 15-026-100232) and performed in accordance with the Georgetown University Animal Care and Use Committee (GUACUC).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djemil, S., Ressel, C.R., Abdel-Ghani, M. et al. Central Cholinergic Synapse Formation in Optimized Primary Septal-Hippocampal Co-cultures. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 1787–1799 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00948-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00948-6