Abstract
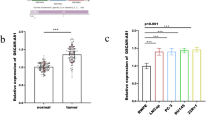
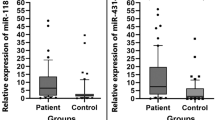
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is a common malignancy of urinary system cancers, accounting for about 1/3 of all newly diagnosed bladder cancer cases. Due to its strong metastasis, the 5-year survival of MIBC is less than 50%, and in serious cases, the overall survival of metastatic bladder cancer patients is about 1.3 years. LncRNAs, a type of non-coding RNAs defined as the transcripts exceeding 200 nucleotides in length, are frequently aberrant in multiple cancers including cervical, ovarian, breast and bladder cancers. Recently, LUCAT1 (short for lung cancer-associated transcript 1), a lncRNA first reported to be involved in smoking-related lung cancer, has been observed to exhibit crucial roles in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration and invasion processes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and colorectal cancer. However, whether it involves in the pathogenesis of MIBC remains underexplored. In the present study, LUCAT1 was up-regulated in the serum samples of MIBC patients and bladder cancer cell lines, as assessed using real-time PCR. Our in vitro data (including wound healing and trans-well assays) showed that LUCAT1 was required for the proliferation, EMT, migration and invasion processes of T24 cells. Moreover, LUCAT1 directly targeted miR-199a-5p and miR-199b-5p, as affirmed using the luciferase reporter assay, and manipulation of LUCAT1 significantly suppressed miR-199a-5p and miR-199b-5p. Collectively, our findings highlight an axis of LUCAT1/miR-199a/b-5p in MIBC pathogenesis. Therefore, LUCAT1 may possibly be a promising candidate for diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target of MIBC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abufaraj M et al (2018) The role of surgery in metastatic bladder cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol 73:543–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.030
Alfred Witjes J et al (2017) Updated 2016 EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. Eur Urol 71:462–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.020
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F (2017) Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol 71:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010
Aranda JF, Canfran-Duque A, Goedeke L, Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C (2015) The miR-199-dynamin regulatory axis controls receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Sci 128:3197–3209. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.165233
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Callegari E et al (2013) Anti-tumor activity of a miR-199-dependent oncolytic adenovirus. PLoS ONE 8:e73964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073964
Cao YP et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA expression profiles for the characterization of different bladder cancer grade. Cell Physiol Biochem 50:1154–1163. https://doi.org/10.1159/000494542
Chi Q et al (2019) Tumor-suppressor microRNA-139-5p restrains bladder cancer cell line ECV-304 properties via targeting Connexin 43. Chin Med J (Engl) 132:2354–2361. https://doi.org/10.1097/cm9.0000000000000455
Cui X, Guo Y, Wang Q, Li X (2019) MiR-199-3p-Dnmt3a-STAT3 signalling pathway in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis. Exp Physiol 104:1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1113/ep087751
Ecke TH et al (2017) miR-199a-3p and miR-214-3p improve the overall survival prediction of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy. Cancer Med 6:2252–2262. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1161
Han Z, Shi L (2018) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via miR-200c/ABCB1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.121
Kapranov P et al (2007) RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316:1484–1488. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1138341
Kiefer JC (2007) Epigenetics in development. Dev Dyn 236:1144–1156. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21094
Knowles MA, Hurst CD (2015) Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer 15:25–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3817
Koshizuka K et al (2017) Regulation of ITGA3 by the anti-tumor miR-199 family inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci 108:1681–1692. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13298
Lou Y et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 promotes tumourigenesis by inhibiting ANXA2 phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 23:1873–1884. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14088
Lukiw WJ, Handley P, Wong L, Crapper McLachlan DR (1992) BC200 RNA in normal human neocortex, non-Alzheimer dementia (NAD), and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (AD). Neurochem Res 17:591–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00968788
Luzon-Toro B, Fernandez RM, Martos-Martinez JM, Rubio-Manzanares-Dorado M, Antinolo G, Borrego S (2019) LncRNA LUCAT1 as a novel prognostic biomarker for patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Sci Rep 9:14374. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50913-7
Ma L et al (2019) LncBook: a curated knowledgebase of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D128–D134. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky960
Monastyrskaya K, Sanchez-Freire V, Hashemi Gheinani A, Klumpp DJ, Babiychuk EB, Draeger A, Burkhard FC (2013) miR-199a-5p regulates urothelial permeability and may play a role in bladder pain syndrome. Am J Pathol 182:431–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.10.020
Mou E, Wang H (2019) LncRNA LUCAT1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through modulating miR-5702. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20190489
Perkel JM (2013) Visiting "noncodarnia". Biotechniques 54:301. https://doi.org/10.2144/000114037
Rafiee A, Riazi-Rad F, Havaskary M, Nuri F (2018) Long noncoding RNAs: regulation, function and cancer. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 34:153–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/02648725.2018.1471566
Rinn JL et al (2007) Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 129:1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022
Rouprêt M et al (2018) European Association of Urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2017 update. Eur Urol 73:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.036
Sahu A, Singhal U, Chinnaiyan AM (2015) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: from function to translation. Trends Cancer 1:93–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2015.08.010
Sanchez-Elsner T, Gou D, Kremmer E, Sauer F (2006) Noncoding RNAs of trithorax response elements recruit Drosophila Ash1 to Ultrabithorax. Science 311:1118–1123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1117705
Song T, Zhang X, Yang G, Song Y, Cai W (2015) Decrement of miR-199a-5p contributes to the tumorigenesis of bladder urothelial carcinoma by regulating MLK3/NF-κB pathway. Am J Transl Res 7:2786–2794
Sun Y et al (2017) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 is associated with poor prognosis in human non-small lung cancer and regulates cell proliferation via epigenetically repressing p21 and p57 expression. Oncotarget 8:28297–28311. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16044
von Hardenberg J et al (2014) Expression and predictive value of lymph-specific markers in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Oncol 32(54):e9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.08.031
Wang AH, Zhao JM, Du J, Pang QX, Wang MQ (2019a) Long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation and invasion by upregulating MTA1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:6824–6829. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201908_18721
Wang Y, Li Z, Li W, Zhou L, Jiang Y (2019b) Prognostic significance of long non-coding RNAs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98:e17276. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000017276
Yang C et al (2018) Circular RNA circ-ITCH inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and regulating p21, PTEN expression. Mol Cancer 17:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0771-7
Yu H, Xu Y, Zhang D, Liu G (2018) Long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 promotes malignancy of ovarian cancer through regulation of miR-612/HOXA13 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2095–2100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.165
Zhang HY, Li CH, Wang XC, Luo YQ, Cao XD, Chen JJ (2019a) MiR-199 inhibits EMT and invasion of hepatoma cells through inhibition of Snail expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:7884–7891. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201909_18998
Zhang L, Liu SK, Song L, Yao HR (2019b) SP1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer by sponging miR-181a. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:556–564. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1575840
Zheng ZG et al (2016) The essential role of H19 contributing to cisplatin resistance by regulating glutathione metabolism in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Sci Rep 6:26093. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26093
Zheng R et al (2018a) Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA PTENP1 suppresses bladder cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17:143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0880-3
Zheng Z et al (2018b) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation and invasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:891–904. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491957
Zheng A, Song X, Zhang L, Zhao L, Mao X, Wei M, Jin F (2019) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1/miR-5582-3p/TCF7L2 axis regulates breast cancer stemness via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:305. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1315-8
Zhou Q, Hou Z, Zuo S, Zhou X, Feng Y, Sun Y, Yuan X (2019) LUCAT1 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis by targeting the ribosomal protein L40-MDM2-p53 pathway through binding with UBA52. Cancer Sci 110:1194–1207. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13951
Zhu KR, Sun QF, Zhang YQ (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINP1 induces tumorigenesis of Wilms' tumor by affecting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:5691–5698. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201907_18306
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [YZ]. The experiments were performed by [XS] and [XL]. Data collection and analysis were conducted by [HL] and [YP]. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained for experimentation with human subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Song, X., Li, X. et al. Serum LUCAT1 implicates the pathogenesis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer via targeting miR-199a-5p and miR-199b-5p. J Mol Hist 51, 583–591 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09907-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09907-3