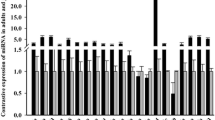
Abstract
Nrf2 is an important transcription factor involved in the antioxidant response and is widely expressed in animal tissues. The function of Nrf2 is regulated by its negative regulator Keap1 by inducing its cytoplasmic degradation. Recent studies have suggested that Nrf2 is also regulated post-transcriptionally via miRNAs. However, to date, how miRNAs regulate Nrf2 in fish skeletal muscles is unknown. In this study, the full-length cDNAs with 2398 bp of the Nrf2 was firstly cloned by SMART RACE amplification tools from Chinese perch. The Nrf2 gene structure and its 3’-UTR region for possible miRNA binding sites, as well as its spatial expression profile were assayed. Then, we employed TargetScan Fish tool MiRNAnome to predict putative sites for five miRNAs including miR-181a-5p, MiR-194a, MiR-216a, miR-459-5p, and miR-724. Using qRT-PCR assay, we found that Nrf2 mRNA levels have negative correlation with all five miRNAs expression in muscle of nutritionally deprived fish, and that ectopic expression of miR-181a-5p alone reduces Nrf2 mRNA levels. Luciferase reporter assay in a heterologous cell system revealed that each of the five miRNAs reduced Nrf2 expression, suggesting a direct regulatory mechanism. Moreover, the miR-181a-5p suppression using specific antagomir led to a significant increase in Nrf2 expression in vivo. At the same time, the expression levels of the antioxidant enzymes CAT, ZnSOD, GPx, GSTA, and GSTA genes increased significantly after injecting miR-181a-5p antagomir. Taken together, these findings provide evidence that miRNAs are involved in the Nrf2 signaling networks in regulation of oxidative stress in fish, at least in Chinese perch muscle.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel, D.P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Barve A, Khor TO, Nair S, Reuhl K, Suh N, Reddy B, Newmark H, Kong AN (2009) γ-Tocopherol-enriched mixed tocopherol diet inhibits prostate carcinogenesis in TRAMP mice. Int J Cancer 124:1693–1699
Cho, W.C. (2010). MicroRNAs in cancer—from research to therapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer. 1805:209–217
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P (2002) Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99:11908–11913
Dong X, Zhang Y, Shang X, Zeng Y (2019) Effects of miR-101 on the proliferation and apoptosis of gastric mucosal epithelial cells via Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:5187–5194
Fields WR, Morrow CS, Doehmer J, Townsend AJ (1999) Expression of stably transfected murine glutathione S-transferase A3-3 protects against nucleic acid alkylation and cytotoxicity by aflatoxin B1 in hamster V79 cells expressing rat cytochrome P450-2B1. Carcinogenesis 20:1121–1125
Guo X, Connick MC, Vanderhoof J, Ishak M-A, Hartley RS (2015) MicroRNA-16 modulates HuR regulation of cyclin E1 in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 16:7112–7132
Harvey C, Thimmulappa R, Singh A, Blake D, Ling G, Wakabayashi N, Fujii J, Myers A, Biswal S (2009) Nrf2-regulated glutathione recycling independent of biosynthesis is critical for cell survival during oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 46:443–453
He X, Chen MG, Lin GX, Ma Q (2006) Arsenic induces NAD (P) H-quinone oxidoreductase I by disrupting the Nrf2· Keap1· Cul3 complex and recruiting Nrf2· Maf to the antioxidant response element enhancer. J Biol Chem 281:23620–23631
He X, Kan H, Cai L, Ma Q (2009) Nrf2 is critical in defense against high glucose-induced oxidative damage in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:47–58
Hsieh T-C, Elangovan S, Wu JM (2010) Differential suppression of proliferation in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells exposed to α-, γ-and δ-tocotrienols is accompanied by altered expression of oxidative stress modulatory enzymes. Anticancer Res 30:4169–4176
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I (1997) An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236:313–322
Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf2 signaling in coordinated activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1199–1207
Jiang W-D, Liu Y, Hu K, Jiang J, Li S-H, Feng L, Zhou X-Q (2014) Copper exposure induces oxidative injury, disturbs the antioxidant system and changes the Nrf2/ARE (CuZnSOD) signaling in the fish brain: protective effects of myo-inositol. Aquat Toxicol 155:301–313
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:89–116
Kobayashi A, Kang M-I, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K, Yamamoto M (2004) Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 24:7130–7139
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M (2005) Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:385–394
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M (2006) Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzym Regul 46:113–140
Kusik BW, Carvan Iii MJ, Udvadia AJ (2008) Detection of mercury in aquatic environments using EPRE reporter zebrafish. Mar Biotechnol 10:750–757
Kwak MK, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2002) Enhanced expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 by cancer chemopreventive agents: role of antioxidant response element-like sequences in the nrf2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol 22:2883–2892
Lima RT, Busacca S, Almeida GM, Gaudino G, Fennell DA, Vasconcelos MH (2011) MicroRNA regulation of core apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur J Cancer 47:163–174
Lin Y-H (2019) MicroRNA networks modulate oxidative stress in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 20:4497
Liu Y, Zhang L, Liang J (2015) Activation of the Nrf2 defense pathway contributes to neuroprotective effects of phloretin on oxidative stress injury after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Neurol Sci 351:88–92
Ma Q (2008) Xenobiotic-activated receptors: from transcription to drug metabolism to disease. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1651–1671
Ma Q, Kinneer K, Bi Y, Chan JY, Kan YW (2004) Induction of murine NAD (P) H: quinone oxidoreductase by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin requires the CNC (cap n collar) basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2): cross-interaction between AhR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) and Nrf2 signal transduction. Biochem J 377:205–213
Mateescu B, Batista L, Cardon M, Gruosso T, De Feraudy Y, Mariani O, Nicolas A, Meyniel J-P, Cottu P, Sastre-Garau X (2011) miR-141 and miR-200a act on ovarian tumorigenesis by controlling oxidative stress response. Nat Med 17:1627
Miao W, Hu L, Scrivens PJ, Batist G (2005) Transcriptional regulation of NF-E2 p45-related factor (NRF2) expression by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-xenobiotic response element signaling pathway direct cross-talk between phase I And II drug-metabolizing enzymes. J Biol Chem 280:20340–20348
Muthusamy VR, Kannan S, Sadhaasivam K, Gounder SS, Davidson CJ, Boeheme C, Hoidal JR, Wang L, Rajasekaran NS (2012) Acute exercise stress activates Nrf2/ARE signaling and promotes antioxidant mechanisms in the myocardium. Free Radic Biol Med 52:366–376
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2003) Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:233–260
Niture SK, Kaspar JW, Shen J, Jaiswal AK (2010) Nrf2 signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:37–42
Padgett KA, Lan RY, Leung PC, Lleo A, Dawson K, Pfeiff J, Mao TK, Coppel RL, Ansari AA, Gershwin ME (2009) Primary biliary cirrhosis is associated with altered hepatic microRNA expression. J Autoimmun 32:246–253
Sajadimajd S, Khazaei M (2018) Oxidative stress and cancer: the role of Nrf2. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 18:538–557
Sangokoya C, Telen MJ, Chi J-T (2010) microRNA miR-144 modulates oxidative stress tolerance and associates with anemia severity in sickle cell disease. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 116:4338–4348
Sun L, Li Z, Xue H, Ma T, Ren C, Li M, Lu Y, Sun H, Zhang K (2019) MiR-26a promotes fracture healing of nonunion rats possibly by targeting SOSTDC1 and further activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 460:165–173
Wakabayashi N, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Kang M-I, Kobayashi A, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Talalay P (2004) Protection against electrophile and oxidant stress by induction of the phase 2 response: fate of cysteines of the Keap1 sensor modified by inducers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101:2040–2045
Waki T, Lee SY, Niikura T, Iwakura T, Dogaki Y, Okumachi E, Oe K, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2016) Profiling microRNA expression during fracture healing. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:83
Wang K, Zhang T, Dong Q, Nice EC, Huang C, Wei Y (2013) Redox homeostasis: the linchpin in stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Death Dis 4:e537–e537
Wang L, Gallagher EP (2013) Role of Nrf2 antioxidant defense in mitigating cadmium-induced oxidative stress in the olfactory system of zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266:177–186
Wang N, Wang W, Sadiq FA, Wang S, Caiqin L, Jianchang J (2020) Involvement of Nrf2 and Keap1 in the activation of antioxidant responsive element (ARE) by chemopreventive agent peptides from soft-shelled turtle. Process Biochem 92:174–181
Wang X-J, Zhang DD (2009) Ectodermal-neural cortex 1 down-regulates Nrf2 at the translational level. PLoS One 4
Wen L-M, Jiang W-D, Liu Y, Wu P, Zhao J, Jiang J, Kuang S-Y, Tang L, Tang W-N, Zhang Y-A (2015) Evaluation the effect of thiamin deficiency on intestinal immunity of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol 46:501–515
Wu P, Wang A, Cheng J, Chen L, Pan Y, Li H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Chu W, Zhang J (2020) Effects of starvation on antioxidant-related signaling molecules, oxidative stress, and autophagy in juvenile Chinese perch skeletal muscle. Mar Biotechnol 22:81–93
Wu P, Zheng X, Zhou X-Q, Jiang W-D, Liu Y, Jiang J, Kuang S-Y, Tang L, Zhang Y-A, Feng L (2018) Deficiency of dietary pyridoxine disturbed the intestinal physical barrier function of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:459–473
Yang M, Yao Y, Eades G, Zhang Y, Zhou Q (2011) MiR-28 regulates Nrf2 expression through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129:983–991
Yu S, Khor TO, Cheung K-L, Li W., Wu T-Y, Huang Y, Foste, BA, Kan YW, Kong A-N (2010) Nrf2 expression is regulated by epigenetic mechanisms in prostate cancer of TRAMP mice. PloS One 5
Yu S, Kong A-N (2007) Targeting carcinogen metabolism by dietary cancer preventive compounds. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7:416–424
Zhang H, Davies KJ, Forman HJ (2015) Oxidative stress response and Nrf2 signaling in aging. Free Radic Biol Med 88:314–336
Zhao H-F, Feng L, Jiang W-D, Liu Y, Jiang J, Wu P, Zhao J, Kuang S-Y, Tang L, Tang W-N (2015). Flesh shear force, cooking loss, muscle antioxidant status and relative expression of signaling molecules (Nrf2, Keap1, TOR, and CK2) and their target genes in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) muscle fed with graded levels of choline. PloS One 10
Zhu X, Li Y-L, Chen D-X, Wu P, Yi T, Chen T, Zhang J-S, Chu W-Y (2015) Selection of reference genes for microRNA quantitative expression analysis in Chinese perch, Siniperca chuatsi. Int J Mol Sci 16:8310–8323
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. NilliZmora in the University of Maryland reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31820103016 and 31230076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was conducted following the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health of Hunan University, China. All procedures for fish handling were performed after fish were anesthetized using MS-222 (3-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester methane sulfonate).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Chen, L., Cheng, J. et al. MiRNAs-Modulation of Nrf2 Signaling Networks in Regulation Oxidative Stress of Chinese Perch Skeletal Muscle After Fasting Treatment. Mar Biotechnol 22, 620–630 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-020-09982-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-020-09982-3