Abstract
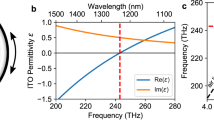
Indium tin oxide (ITO) has become a very useful plasmonic and nonlinear optical material because of its highly tunable electrical and optical properties and strong optical nonlinearity. In this work, the authors conducted detailed fabrication process studies by using high-temperature reactive sputtering to finely tune the optical properties of ITO thin films, particularly the epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) wavelength in the near and mid-IR spectrum. Sputtered ITO thin films are characterized by using spectroscopic ellipsometry, surface profilometry, Hall measurements, and 4-point probe testing. Additionally, the effect of post-deposition annealing of ITO films is also investigated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Shrestha, Y. Wang, A.C. Overvig, M. Lu, A. Stein, L. Dal Negro, and N. Yu: Indium tin oxide broadband metasurface absorber. ACS Photonics 5, 3526–3533 (2018).
F. Yi, E. Shim, A.Y. Zhu, H. Zhu, J.C. Reed, and E. Cubukcu: Voltage tuning of plasmonic absorbers by indium tin oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 221102 (2013).
J.R. Hendrickson, S. Vangala, C. Dass, R. Gibson, J. Goldsmith, K. Leedy, D.E. Walker, Jr, J.W. Cleary, W. Kim, and J. Guo: Coupling of epsilon-near-zero mode to gap plasmon mode for flat-top wideband perfect light absorption. ACS Photonics 5, 776–781 (2018).
J. Chen, E.M. Smith, J.W. Cleary, C. Dass, A. Reed, S. Vangala, J.R. Hendrickson, and J. Guo: Wideband absorbing nonlinear optical metamaterials using coupled epsilon-near-zero mode. META 2019 Conference Proceeding, Lisbon, Portugal, 2019; pp. 1637–1638.
J. Yoon, M. Zhou, M.A. Badsha, T.Y. Kim, Y.C. Jun, and C.K. Hwangbo: Broadband epsilon-near-zero perfect absorption in the near-infrared. Sci. Rep. 5, 12788 (2015).
X. Liu, K. Zang, J.H. Kang, J. Park, J.S. Harris, P.G. Kik, and M.L. Brongersma: Epsilon-near-zero Si slot-waveguide modulator. ACS Photonics 5, 4484–4490 (2018).
G.K. Shirmanesh, R. Sokhoyan, R.A. Pala, and H.A. Atwater: Dual-gated active metasurface at 1550 nm with wide (>300°) phase tunability. Nano Lett. 18, 2957–2963 (2018).
M. Kelley, A. Lee, M. Mozumdar, K. Dajani, and A. Ahmed: Design and modeling of sub-picosecond all-optical modulation using the nonlinear response of indium tin oxide. JOSA B 36, F149–F153 (2019).
C. Liu, K. Pang, K. Manukyan, O. Reshef, Y. Zhou, J. Patrow, A. Pennathur, H. Song, Z. Zhao, R. Zhang, F. Alishahi, A. Fallahpour, Y. Cao, A. Almaiman, J.M. Dawlaty, N.A. Chaitanya, I. De Leon, M.Z. Alam, R.W. Boyd, M. Tur, and A.E. Wilner: Resonance splitting and enhanced optical nonlinearities in ITO-based epsilon-near-zero metasurface with cross-shaped nanoantennas. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, OSA Technical Digest, Optical Society of America, 2019; Paper FW4B.5.
M. Alam, I. De Leon, and R. Boyd: Large optical nonlinearity of indium tin oxide in its epsilon-near-zero region. Science 352, 795–797 (2016).
C.K. Dass, H. Kwon, S. Vangala, E.M. Smith, J.W. Cleary, J. Guo, A. Alu, and J.R. Hendrickson: Gap plasmon enhanced second harmonic generation in epsilon-near-zero nanolayers. ACS Photonics 7, 174–179 (2020).
A. Capretti, Y. Wang, N. Engheta, and L. Dal Negro: Comparative study of second-harmonic generation from epsilon-near-zero indium tin oxide and titanium nitride nanolayers excited in the near-infrared spectral range. ACS Photonics 2, 1584–1591 (2015).
Y. Wang, A.C. Overvig, S. Shrestha, R. Zhang, R. Wang, N. Yu, and L. Dal Negro: Tunability of indium tin oxide materials for mid-infrared plasmonic applications. Opt. Mater. Express 7, 2727–2739 (2017).
Y. Gui, M. Miscuglio, Z. Ma, M. Tahersima, S. Sun, R. Amin, H. Dalir, and V. Sorger: Towards integrated metatronics: a holistic approach on precise optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide. Sci. Rep. 9, 11279 (2019).
J.W. Cleary, E.M. Smith, K.D. Leedy, G. Grzybowski, and J. Guo: Optical and electrical properties of ultra-thin indium tin oxide nanofilms on silicon for infrared photonics. Opt. Mater. Express 8, 1231–1245 (2018).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Program Manager Dr. Gernot Pomrenke) under award number FA9550-19RYCOR048 and FA9550-20RYCOR059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, E.M., Hendrickson, J.R., Cleary, J.W. et al. Tunable indium tin oxide for metamaterial perfect absorbers and nonlinear devices. MRS Communications 10, 573–578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2020.62
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2020.62