Abstract
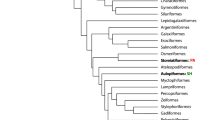
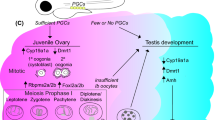
Monosex breeding technology has received enormous attention for the Scylla paramamosain, an economic crustacean species with distinctive sexual dimorphism. However, the molecular mechanism of gonadal development and sexual differentiation still remain inconclusive. In this study, we reported the cloning, characterization of a FoxL2-like gene with male-biased expression in the mud crab (SpFoxL2). The SpFoxL2 encoded a putative forkhead-box protein with 352 amino acids. Phylogenetic tree revealed the SpFoxL2 was clustered with the invertebrates FoxL2 homologues, most closed to E. sinensis. By quantitative real-time PCR, it was shown that the SpFoxL2 was expressed in intestine, ovary and testis, with the highest expression level in testis. During gonadal development, the expression level of SpFoxL2 in ovary was lower than that in testis at all stages. The expression level of SpFoxL2 constantly declined from stage I to stage V in ovary. While, there is a rising tendency from stage I to stage IV in testis. Notably, this male-biased expression pattern could be detected as early as the juvenile crab stage I (CI stage) before morphological sexual differentiation in the mud crab. By fluorescence in-situ hybridization, SpFoxL2 mRNA was found located in both somatic and germ cells in gonads. In testis, it was most strongly localized in the meiosis germ cells (spermatocytes). While in ovary, the signal became weaker in the meiosis germ cells (oocytes). The results imply that the SpFoxl2 may play an important role in male differentiation and development, laying a foundation for future research on sexual differentiation of the species.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Alam MA, Kobayashi Y, Horiguchi R, Hirai T, Nakamura M (2008) Molecular cloning and quantitative expression of sexually dimorphic markers Dmrt1 and Foxl2 during female-to-male sex change in Epinephelus merra. Gen Comp Endocrinol 157:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.03.018
Baron D, Cocquet J, Xia X, Fellous M, Guiguen Y, Veitia RA (2004) An evolutionary and functional analysis of FoxL2 in rainbow trout gonad differentiation. J Mol Endocrinol 33:705–715. https://doi.org/10.1677/jme.1.01566
Carlsson P, Mahlapuu M (2002) Forkhead transcription factors: key players in development and metabolism. Dev Biol 250:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.2002.0780
Cocquet J, Pailhoux E, Jaubert F, Servel N, Xia X, Pannetier M, De Baere E, Messiaen L, Cotinot C, Fellous M, Veitia RA (2002) Evolution and expression of FOXL2. J Med Genet 39:916–921. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.39.12.916
Cocquet J, Pannetier M, Fellous M, Veitia RA (2005) Sense and antisense Foxl2 transcripts in mouse. Genomics 85:531–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.01.007
Crisponi L, Deiana M, Loi A, Chiappe F, Uda M, Amati P, Bisceglia L, Zelante L, Nagaraja R, Porcu S, Ristaldi MS, Marzella R, Rocchi M, Nicolino M, LienhardtRoussie A, Nivelon A, Verloes A, Schlessinger D, Gasparini P, Bonneau D, Cao A, Pilia G (2001) The putative forkhead transcription factor FOXL2 is mutated in blepharophimosis/ptosis/epicanthus inversus syndrome. Nat Genet 27:159–166 https://www.nature.com/articles/ng0201_159
De Baere E, Beysen D, Oley C, Lorenz B, Cocquet J, De Sutter P, Devriendt K, Dixon M, Fellous M, Fryns JP (2003) FOXL2 and BPES: mutational hotspots, phenotypic variability, and revision of the genotype–phenotype correlation. Am J Hum Genet 72:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1086/346118
Govoroun MS, Pannetier M, Pailhoux E, Cocquet J, Brillard JP, Couty I, Batellier F, Cotinot C (2004) Isolation of chicken homolog of the FOXL2 gene and comparison of its expression patterns with those of aromatase during ovarian development. Dev Dyn 231:859–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.20189
Islam MS, Kodama K, Kurokura H (2010) Ovarian development of the mud crab Scylla paramamosain in a tropical mangrove swamps, Thailand. J Sci Res 2:380–389 https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/JSR/article/view/3543
Jin SB, Fu HT, Jiang SF, Xiong YW, Sun SM, Qiao H, Zhang WY, Gong YS, Wu Y (2018) Molecular cloning, expression, and in situ hybridization analysis of Forkhead box protein L2 during development in Macrobrachium nipponense. J World Aquacult Soc 49:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12510
Lakshmi P (2017) Structural analysis of FOXL2 gene and its role in kidney failure. Bioinformatics Review 3:16–26 https://bioinformaticsreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/BiR-LP-3-7-3-OA.pdf?x73134
Lin JL, Shi X, Fang SB, Zhang Y, You CH, Ma HY, Lin F (2019) Comparative transcriptome analysis combining SMRT and NGS sequencing provides novel insights into sexual differentiation and development in mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Aquaculture 512:734447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734447
Liu XL, Zhang ZF, Shao MY, Liu JG, Muhammad F (2012) Sexually dimorphic expression of foxl2 during gametogenesis in scallop Chlamys farreri, conserved with vertebrates. Dev Genes Evol 222:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-012-0410-z
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loffler KA, Zarkower D, Koopman P (2003) Etiology of ovarian failure in blepharophimosis ptosis epicanthus inversus syndrome: FOXL2 is a conserved, early-acting gene in vertebrate ovarian development. Endocrinology 144:3237–3243. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-0095
Ma LB, Zhang FY, Ma CY, Qiao ZG (2006) Scylla paramamosain (Estampador) the most common mud crab (genus Scylla) in China: evidence from mtDNA. Aquac Res 37:1694–1698. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2006.01603.x
Ma HY, Ma CY, Li SJ, Jiang W, Li XC, Liu YX, Ma LB (2014) Transcriptome analysis of the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) by 454 deep sequencing: assembly, annotation, and marker discovery. PLoS One 9:e102668. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102668
Miki T, Marongiu F, Dorko K, Ellis ECS, Strom SC (2010) In situ hybridization to identify gut stem cells. Current Protocols in Stem Cell Biology 12:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470151808.sc02f01s12
Naimi A, Martinez AS, Specq ML, Diss B, Mathieu M, Sourdaine P (2009) Molecular cloning and gene expression of Cg-Foxl2 during the development and the adult gametogenetic cycle in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 154:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2009.05.011
Nakamoto M, Matsuda M, Wang DS, Nagahama Y, Shibata N (2006) Molecular cloning and analysis of gonadal expression of Foxl2 in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344:353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.137
Ottolenghi C, Omari S, Garcia Ortiz JE, Uda M, Crisponi L, Forabosco A, Pilia G, Schlessinger D (2005) Foxl2 is required for commitment to ovary differentiation. Hum Mol Genet 14:2053–2062. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddi210
Ottolenghi C, Pelosi E, Tran J, Colombino M, Douglass E, Nedorezov T, Cao A, Forabosco A, Schlessinger D (2007) Loss of Wnt4 and Foxl2 leads to female-to-male sex reversal extending to germ cells. Hum Mol Genet 16:2795–2804. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm235
Shi X, Waiho K, Li XC, Ikhwanuddin M, Miao GD, Lin F, Zhang YL, Li SK, Zheng HP, Liu WH, Aweya JJ, Azmie G, Baylon JC, Quinitio ET, Ma HY (2018) Female-specifific SNP markers provide insights into a WZ/ZZ sex determination system for mud crabs Scylla paramamosain, S. tranquebarica and S. serrata with a rapid method for genetic sex identifification. BMC Genomics 19:981 https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12864-018-5380-8.pdf
Uda M, Ottolenghi C, Crisponi L, Garcia JE, Deiana M, Kimber W, Forabosco A, Cao A, Schlessinger D, Pilia G (2004) Foxl2 disruption causes mouse ovarian failure by pervasive blockage of follicle development. Hum Mol Genet 13:1171–1181. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh124
Uhlenhaut NH, Jakob S, Anlag K, Eisenberger T, Sekido R, Kress J, Treier AC (2009) Somatic sex reprogramming of adult ovaries to testes by FOXL2 ablation. Cell 139:1130–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.021
Verdin H, De Baere E (2012) FOXL2 impairment in human disease. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 77:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1159/000335236
Wang DS, Kobayashi T, Zhou LY, Nagahama Y (2004) Molecular cloning and gene expression of Foxl2 in the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:83–89 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006291X04010095
Wang Y, Chen Y, Han K, Zou Z, Zhang Z (2012) A vasa gene from green mud crab Scyllaparamamosain and its expression during gonadal development and gametogenesis. Mol Biol Rep 39:4327–4335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.133
Weigel D, Jӓckle H (1990) The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors. Cell 63:455–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-L
Weigel D, Jürgens G, Küttner F, Seifert E, Jӓckle H (1989) The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell 57:645–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5
Yang YJ, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhou L, Gui JF (2017) Sequential, divergent, and cooperative requirements of Foxl2a and Foxl2b in ovary development and maintenance of Zebrafish. Genetics 205:1551–1572. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.199133
Yang XL, Ikhwanuddin M, Li XC, Lin F, Wu QY, Zhang YL, You CH, Liu WH, Cheng YW, Shi X, Wang SQ, Ma HY (2018) Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insights into differentially expressed genes and long non-coding RNAs between ovary and testis of the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Mar Biotechnol 20:20–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-017-9784-2
Ye HH, Li SJ, Huang HY, Wang GZ (2002) Histological studies on testes development of the mud crab, Scylla serrate. Zool Res 23:141–144 http://www.zoores.ac.cn/en/article/id/846?viewType=HTML
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the STU Scientific Research Foundation for Talents (No. NTF17014) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81702764).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Lin, J., Tan, X. et al. Identification and Sexually Dimorphic Expression of a FoxL2-like Gene in Mud Crab (Scylla paramamosain): Potential Roles in Male Differentiation and Development. Thalassas 37, 131–140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-020-00249-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-020-00249-1