Abstract
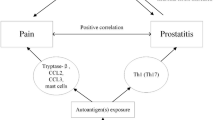
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndromes (CP/CPPS) is a clinical tricky problem due to its enigmatic etiology, low cure rate, and high recurrence rate. The research on its pathogenesis has never stopped. In this experimental autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) model, male C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously immunized with prostate extracts in an adequate adjuvant. For mice in the antibody intervention group, anti-T2 polyclonal antibodies were intraperitoneally injected during the induction of EAP. Animals were periodically monitored for pelvic pain. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used to assess prostate inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels in serum were measured by ELISA kits. The immunized animals developed prostatitis as a consequence of the immune response against prostate antigens. Pelvic pain thresholds were gradually decreased and TNF-α expression significantly increased. T2 plays an important role in the disease since polyclonal antibodies to T2 greatly ameliorated symptoms in animals induced for EAP. T2 peptide may represent the major autoantigen epitope in EAP, which could serve for a better understanding of the etiology of CP/CPPS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stein, A., T. May, and Y. Dekel. 2014. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a clinical enigma. Postgraduate Medicine 126 (4): 115–123. https://doi.org/10.3810/pgm.2014.07.2789.
Smith, Christopher P. 2016. Male chronic pelvic pain: an update. Indian journal of urology : IJU : journal of the Urological Society of India 32 (1): 34–39. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-1591.173105.
Clemens, J.Q., C. Mullins, A.L. Ackerman, T. Bavendam, A. van Bokhoven, B.M. Ellingson, S.E. Harte, et al. 2019. Urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: insights from the MAPP research network. Nature Reviews Urology 16 (3): 187–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-018-0135-5.
Liao, Chun-Hou, Herng-Ching Lin, and Chao-Yuan Huang. 2016. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is associated with irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based study. Scientific Reports 6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26939, 6.
Polackwich, A.S., and D.A. Shoskes. 2016. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A review of evaluation and therapy. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases 19 (2): 132–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2016.8.
Aaron, Leslie A., Richard Herrell, Suzanne Ashton, Megan Belcourt, Karen Schmaling, Jack Goldberg, and Dedra Buchwald. 2001. Comorbid clinical conditions in chronic fatigue. Journal of General Internal Medicine 16 (1): 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2001.03419.x.
Farmer, Melissa A., Mona L. Chanda, Elle L. Parks, Marwan N. Baliki, A. Vania Apkarian, and Anthony J. Schaeffer. 2011. Brain functional and anatomical changes in chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The Journal of Urology 186 (1): 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.027.
Clemens, J.Q., S.O. Brown, and E.A. Calhoun. 2008. Mental health diagnoses in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a case/control study. Journal of Urology 180 (4): 1378–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.06.032.
Batstone, G.R., A. Doble, and J.S. Gaston. 2002. Autoimmune T cell responses to seminal plasma in chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). Clinical and Experimental Immunology 128 (2): 302–307.
Tomaskovic, I., B. Ruzic, D. Trnski, and O. Kraus. 2009. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males may be an autoimmune disease, potentially responsive to corticosteroid therapy. Medical Hypotheses 72 (3): 261–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2008.10.020.
Ihsan, Awais Ullah, Farhan Ullah Khan, Waqas Nawaz, Muhammad Zahid Khan, Mengqi Yang, and Xiaohui Zhou. 2017. Establishment of a rat model of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) induced by immunization with a novel peptide T2. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 91: 687–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.004.
Khan, Farhan Ullah, Awais Ullah Ihsan, Waqas Nawaz, Muhammad Zahid Khan, Mengqi Yang, Gang Wang, Xiaoqian Liao, Lei Han, and Xiaohui Zhou. 2017. A novel mouse model of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome induced by immunization of special peptide fragment with aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. Immunology Letters 187: 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.05.008.
Zhang, L., A.U. Ihsan, Y. Cao, Y. Cheng, and X. Zhou. 2018. Establishment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis model by T-2 peptide in aluminium hydroxide adjuvant. Andrologia 50 (3). https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12922.
Barnes, D.A., J. Tse, M. Kaufhold, M. Owen, J. Hesselgesser, R. Strieter, R. Horuk, and H.D. Perez. 1998. Polyclonal antibody directed against human RANTES ameliorates disease in the Lewis rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model. Journal of Clinical Investigation 101 (12): 2910–2919. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci2172.
Wang, Xiaoqian, Zhang Yu, Zhiding Wang, Xiaoling Liu, Gaizhi Zhu, Gencheng Han, Guojiang Chen, et al. 2018. Anti-IL-39 (IL-23p19/Ebi3) polyclonal antibodies ameliorate autoimmune symptoms in lupus-like mice. Molecular Medicine Reports 17 (1): 1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8048.
Chaplan, S.R., F.W. Bach, J.W. Pogrel, J.M. Chung, and T.L. Yaksh. 1994. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 53 (1): 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9.
Liu, Yuqian, Reyaj Mikrani, Dianyou Xie, Junaid Wazir, Sajan Shrestha, Rahat Ullah, Mirza Muhammad Faran Ashraf Baig, et al. 2020. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and prostate cancer: study of immune cells and cytokines. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology 34 (2): 160–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12517.
Wang, Wenlu, Muhammad Naveed, Fatima Majeed, Xingxing Cui, Awais Ullah Ihsan, Ziwei Liu, Hafiz Muhammad Zubair, Meng Tang, Muhammad Sohail, and Zhou Xiaohui. 2019. Morphological reseach on expression of inflammatory mediators in murine models of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) induced by T2 antigen. Andrologia 51 (11): e13435.
Keetch, D.W., P. Humphrey, and T.L. Ratliff. 1994. Development of a mouse model for nonbacterial prostatitis. Journal of Urology 152 (1): 247–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)32871-9.
Qi, X., L. Han, X. Liu, J. Zhi, B. Zhao, D. Chen, F. Yu, and X. Zhou. 2012. Prostate extract with aluminum hydroxide injection as a novel animal model for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology 80 (6):1389.e1389-1315. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.07.030.
Maccioni, M., V.E. Rivero, and C.M. Riera. 1998. Prostatein (or rat prostatic steroid binding protein) is a major autoantigen in experimental autoimmune prostatitis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 112 (2): 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00588.x.
Penna, G., B. Fibbi, M. Maggi, and L. Adorini. 2009. Prostate autoimmunity: from experimental models to clinical counterparts. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology 5 (5): 577–586. https://doi.org/10.1586/eci.09.37.
Tsavaler, L., M.H. Shapero, S. Morkowski, and R. Laus. 2001. Trp-p8, a novel prostate-specific gene, is up-regulated in prostate cancer and other malignancies and shares high homology with transient receptor potential calcium channel proteins. Cancer Research 61 (9): 3760–3769.
Liu, Yuqian, Reyaj Mikrani, Yanjun He, Mirza Muhammad Faran Asraf Baig, Muhammad Abbas, Muhammad Naveed, Meng Tang, Qin Zhang, Cuican Li, and Xiaohui Zhou. 2020. TRPM8 channels: a review of distribution and clinical role. European Journal of Pharmacology: 173312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173312.
McKemy, D.D., W.M. Neuhausser, and D. Julius. 2002. Identification of a cold receptor reveals a general role for TRP channels in thermosensation. Nature 416 (6876): 52–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature719.
Stein, R.J., S. Santos, J. Nagatomi, Y. Hayashi, B.S. Minnery, M. Xavier, A.S. Patel, et al. 2004. Cool (TRPM8) and hot (TRPV1) receptors in the bladder and male genital tract. Journal of Urology 172 (3): 1175–1178. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000134880.55119.cf.
Hedelin, Hans, and Karin Jonsson. 2007. Chronic abacterial prostatitis and cold exposure: an explorative study. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 41 (5): 430–435. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365590701365123.
Cao, Yanfang, Yijie Cheng, Awais Ullah Ihsan, Farhan Ullah Khan, Dianyou Xie, Xingxing Cui, Wenlu Wang, and Xiaohui Zhou. 2019. A nanoparticle-coupled T2 peptide induces immune tolerance and ameliorates chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) in mice model. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology 33 (3): 267–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12438.
Cheng, Yijie, Yanfang Cao, Awais Ullah Ihsan, Farhan Ullah Khan, Li Xue, Dianyou Xie, Xingxing Cui, Wenlu Wang, Ziwei Liu, and Cunyu Li. 2019. Novel treatment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis by nanoparticle-conjugated autoantigen peptide T2. Inflammation 42 (3): 1071–1081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00968-5.
Tang, Meng, Rahat Ullah, Junaid Wazir, Farhan Ullah Khan, Awais Ullah Ihsan, Xingxing Cui, Wenlu Wang, Min Hu, Yuqian Liu, and Xiaohui Zhou. 2019. Effect of oral T2 antigen on chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in mice model. Inflammation 42: 2086–2094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01072-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Tang, M., Zhang, Q. et al. T2 Peptide Represents a Major Autoantigen Epitope in Experimental Autoimmune Prostatitis. Inflammation 44, 243–248 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01326-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01326-6