Abstract
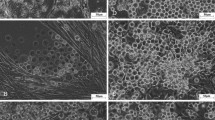
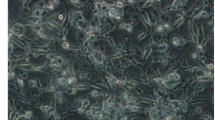
Here, a new cell line, Ha168, was established from Helicoverpa armigera eggs and has been stably subcultured for over 30 passages in TNM-FH medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. The cell line consists of round and spindle-shaped cells and several giant cells. The round cells, with a cell diameter of 14.30 ± 2.804 μm, account for 77% of the cells. DNA amplification fingerprinting, random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis, and analysis of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene confirmed that the Ha168 cells were derived from H. armigera. Karyotype analysis revealed the average chromosome number of Ha168 cells to be 71. Growth curves at passage 25 were determined and demonstrated that the cell population doubling time is 56.8 h. No mycoplasma contamination was detected in the cell line. Ha168 cells can be infected by recombinant baculovirus AcMNPV-EGFP, and exogenous protein expression level in this cell line is 70% of that in the Sf9 cell line.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis TR, Wickham TJ, McKenna KA, Granados RR, Shuler ML, Wood HA (1993) Comparative recombinant protein production of eight insect cell lines. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 29a:388–390
Drexler HG, Uphoff CC (2002) Mycoplasma contamination of cell cultures: incidence, sources, effects, detection, elimination, prevention. Exp Cell Res 39:75–90
Eibl R, Steiger N, Wellnitz S, Vicente T, John C, Eibl D (2013) Fast single-use VLP vaccine productions based on insect cells and the Baculovirus expression vector system: influenza as case study. In: Eibl D, Eibl R (eds) Disposable bioreactors II. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Heidelberg, pp 99–125
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Grace TD (1962) Establishment of four strains of cells from insect tissues grown in vitro. Nature 195:788–789
Hayflick L (1973) Chapter 3 - Subculturing human diploid fibroblast cultures. In: Kruse PF, Patterson MK (eds) Tissue culture. Academic Press, New York and London, pp 220–223
Javier GO, Sudawan C, Barbara LC, Motoko I, Michihiro K (2008) Susceptibility of newly established cell lines from Helicoverpa armigera to homologous and heterologous nucleopolyhedroviruses. J Insect Biotechnol Sericol 77:25–34
Jeyarani S (2012) Establishment of cell line from Helivoverpa armigera (Hubner) embryo: effect of temperature on its susceptiblility to baculoviruses. Madras Agric J 99(1–3):121–124
Kawai Y, Mitsuhashi J (1997) An insect cell line discrimination method by RAPD-PCR. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:512–515
Lery X, LaRue B, Cossette J, Charpentier G (2003) Characterization and authentication of insect cell lines using RAPD markers. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:1035–1041
Li J, He F, Yang Y, Xiao Y, Peng R, Yao H, Li X, Peng J, Hong H, Liu K (2015) Establishment and characterization of a novel cell line from midgut tissue of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 51:562–571
Ling T, Li YU, Bai MQ (2014) Research progress and application of insect cell-baculovirus expression vector system. Progress Microbiol Immunol 42:70–78
Lynn DE (2001) Novel techniques to establish new insect cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:319–321
McIntosh AH, Christian PD, Grasela JJ (1999) The establishment of heliothine cell lines and their susceptibility to two baculoviruses. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 35:94–97
McIntosh AH, Grasela JJ, Matteri RL (1996) Identification of insect cell lines by DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF). Insect Mol Biol 5:187–195
McIntosh AH, Ignoefo CM, Quhou C, Pappas M (1983) Establishment of a cell line from Heliothis armigera (Hbn.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro 19(8):589–590
Mena JA, Kamen AA (2011) Insect cell technology is a versatile and robust vaccine manufacturing platform. Expert Rev Vaccines 10:1063–1081
Mirzaei M, Jardin B, Elias CB, Prakash S (2008) Expression and production of human interleukin-7 in insect cells using baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151:93–103
Murhammer DW (2007) Baculovirus and insect cell expression protocols, second edn. Humana Press, Totowa
Olejnik A, Grajek W (2003) Biotechnology of insect cell tissue culture. Biotechnologia 1:176–192
Palomares LA, Realpe M, Ramírez OT (2015) An overview of cell culture engineering for the insect cell-Baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS). In: Al-Rubeai M (ed) Animal Cell Culture. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 501–519
Patankar AG, Giri AP, Harsulkar AM, Sainani MN, Deshpande VV, Ranjekar PK, Gupta SV (2001) Complexity in specificities and expression of Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases explains polyphagous nature of the insect pest. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:453–464
Ravi KC, Mohan KS, Manjunath TM, Head G, Patil BV, Angeline GDP, Premalatha K, Peter J, Rao NGV (2005) Relative abundance of Helicoverpa armigera (lepidoptera: noctuidae) on different host crops in india and the role of these crops as natural refuge for bacillus thuringiensis cotton. Environ Entomol 34:59–69
Shao HL, Zheng WW, Liu PC, Wang Q, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2003) Establishment of a new cell line from lepidopteran epidermis and hormonal regulation on the genes. PLoS One 3(9):e3127
Smagghe G, Goodman CL, Stanley D (2009) Insect cell culture and applications to research and pest management. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:93–105
Su R, Zheng GL, Wan FH, Li CY (2016) Establishment and characterization of three embryonic cell lines of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Cytotechnology 68:1223–1232
Sudeep AB, Shouche YS, Mourya DT, Pant U (2002) New Helicoverpa armigera Hbn cell line from larval hemocyte for baculovirus studies. Indian J Exp Biol 40:69–73
Uphoff CC, Drexler HG (2005) Detection of mycoplasma contaminations. In: Helgason CD, Miller CL (eds) Basic cell culture protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 13–23
Van Oers MM (2011) Opportunities and challenges for the baculovirus expression system. J Invertebr Pathol 107(Suppl):S3–S15
Wu CY, Wang CH (2006) New cell lines from Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae): characterization and susceptibility to baculoviruses. J Invertebr Pathol 93:186–191
Zhang H, Zhang YA, Qin Q, Wang Y, Li X, Miao L, Yin Z, Zhang A, Qu L, Ding C (2006) A new cell line from larval fat bodies of the bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 42:290–293
Zhang X, Feng Y, Ding WF, Chen XM, Wang CY, Ma T (2011) Establishment and characterization of an embryonic cell line from Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:327–332
Zhang X, Feng Y, Ding WF, Ma T, Ma Y (2018) The chromosome analysis of 7 insect cell lines from Lepidoptera. For Res 21(4):493–499
Zheng GL, Li CY, Zhou HX, Li SW, Li GX, Xue M (2010) Establishment of two new cell lines from the embryonic tissue of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and their responses to baculovirus infection. Acta Entomol Sin 53:167–174
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31872290 and 31572329) and the National Key R&D Program of China (grant 2019YFD1002102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Li, Y., Wang, H. et al. Establishment and characterization of a new embryonic cell line from Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 56, 559–566 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00473-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00473-2