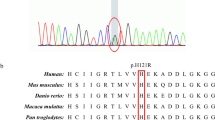
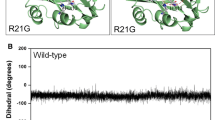
Abstract
Our objective was to investigate the frequency of KIF5A variants in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and the clinical characteristics of familial ALS (FALS) associated with variants in KIF5A. Whole-exome sequence analysis was performed for a Japanese series of 43 families with FALS and 444 patients with sporadic ALS (SALS), in whom causative variants had not been identified. We compared the frequencies of rare variants (MAF < 0.01) in KIF5A, including missense and loss of function (LoF) variants, between ALS and control subjects (n = 1163). Clinical characteristics of patients with FALS carrying pathogenic variants in KIF5A were also described. LoF variants were identified only in the probands of two families with FALS, both of which were 3′ splice-site variants leading to exon skipping and an altered C-terminal domain, located in the mutational hotspot causing FALS, and were considered to be pathogenic for FALS. Rare missense variants in KIF5A were identified in five patients with SALS (1.13%) and 11 control subjects (0.95%, carrier frequency), which were not significantly different. Consequently, the pathogenic LoF variants in KIF5A accounted for 2.1% of all FALS families in this study. These patients suffered from ALS characteristically associated with the predominant involvement of upper motor neuron. In conclusion, we identified two pathogenic splice-site variants in KIF5A in the probands in two Japanese families with FALS, which altered the C-terminal region of KIF5A. Our findings broaden the phenotype spectrum of ALS associated with variants in KIF5A in the Japanese series.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor JP, Brown RH Jr, Cleveland DW (2016) Decoding ALS: from genes to mechanism. Nature 539(7628):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20413
Leblond CS, Kaneb HM, Dion PA, Rouleau GA (2014) Dissection of genetic factors associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 262 Pt B:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.04.013
White MA, Sreedharan J (2016) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: recent genetic highlights. Curr Opin Neurol 29(5):557–564. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000367
Naruse H, Ishiura H, Mitsui J, Date H, Takahashi Y, Matsukawa T, Tanaka M, Ishii A, Tamaoka A, Hokkoku K, Sonoo M, Segawa M, Ugawa Y, Doi K, Yoshimura J, Morishita S, Goto J, Tsuji S (2018) Molecular epidemiological study of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Japanese population by whole-exome sequencing and identification of novel HNRNPA1 mutation. Neurobiol Aging 61:255.e259–255.e216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.08.030
Naruse H, Ishiura H, Mitsui J, Takahashi Y, Matsukawa T, Tanaka M, Doi K, Yoshimura J, Morishita S, Goto J, Toda T, Tsuji S (2019) Burden of rare variants in causative genes for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) accelerates age at onset of ALS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(5):537–542. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-318568
Takahashi Y, Seki N, Ishiura H, Mitsui J, Matsukawa T, Kishino A, Onodera O, Aoki M, Shimozawa N, Murayama S, Itoyama Y, Suzuki Y, Sobue G, Nishizawa M, Goto J, Tsuji S (2008) Development of a high-throughput microarray-based resequencing system for neurological disorders and its application to molecular genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 65(10):1326–1332. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.65.10.1326
Takahashi Y, Fukuda Y, Yoshimura J, Toyoda A, Kurppa K, Moritoyo H, Belzil VV, Dion PA, Higasa K, Doi K, Ishiura H, Mitsui J, Date H, Ahsan B, Matsukawa T, Ichikawa Y, Moritoyo T, Ikoma M, Hashimoto T, Kimura F, Murayama S, Onodera O, Nishizawa M, Yoshida M, Atsuta N, Sobue G, JaCals FJA, Williams KL, Blair IP, Nicholson GA, Gonzalez-Perez P, Brown RH Jr, Nomoto M, Elenius K, Rouleau GA, Fujiyama A, Morishita S, Goto J, Tsuji S (2013) ERBB4 mutations that disrupt the neuregulin-ErbB4 pathway cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 19. Am J Hum Genet 93(5):900–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.008
Naruse H, Iwata A, Takahashi Y, Ichihara K, Kamei S, Yamatoku M, Hirayama T, Suzuki N, Aoki M, Miyagawa T, Shimizu J, Tsuji S, Goto J (2013) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with novel A4D SOD1 mutation with late age at onset and rapid progressive course. Neurol Clin Neurosci 1(1):45–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/ncn3.8
Segawa M, Hoshi A, Naruse H, Kuroda M, Bujo H, Ugawa Y (2015) A patient with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with a new valosin-containing protein (VCP) gene mutation. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 55(12):914–920. https://doi.org/10.5692/clinicalneurol.cn-000765
Ishiura H, Takahashi Y, Mitsui J, Yoshida S, Kihira T, Kokubo Y, Kuzuhara S, Ranum LP, Tamaoki T, Ichikawa Y, Date H, Goto J, Tsuji S (2012) C9ORF72 repeat expansion in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the Kii peninsula of Japan. Arch Neurol 69(9):1154–1158. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2012.1219
Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simon-Sanchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Schymick JC, Laaksovirta H, van Swieten JC, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Mok K, Ryten M, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister JB, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita VM, Kaivorinne AL, Holtta-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chio A, Restagno G, Borghero G, Sabatelli M, Consortium I, Heckerman D, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rothstein JD, Sendtner M, Drepper C, Eichler EE, Alkan C, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Dutra A, Pak E, Hardy J, Singleton A, Williams NM, Heutink P, Pickering-Brown S, Morris HR, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ (2011) A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 72(2):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.010
Reid E, Kloos M, Ashley-Koch A, Hughes L, Bevan S, Svenson IK, Graham FL, Gaskell PC, Dearlove A, Pericak-Vance MA, Rubinsztein DC, Marchuk DA (2002) A kinesin heavy chain (KIF5A) mutation in hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG10). Am J Hum Genet 71(5):1189–1194. https://doi.org/10.1086/344210
Liu YT, Laura M, Hersheson J, Horga A, Jaunmuktane Z, Brandner S, Pittman A, Hughes D, Polke JM, Sweeney MG, Proukakis C, Janssen JC, Auer-Grumbach M, Zuchner S, Shields KG, Reilly MM, Houlden H (2014) Extended phenotypic spectrum of KIF5A mutations: from spastic paraplegia to axonal neuropathy. Neurology 83(7):612–619. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000000691
Kaji S, Kawarai T, Miyamoto R, Nodera H, Pedace L, Orlacchio A, Izumi Y, Takahashi R, Kaji R (2016) Late-onset spastic paraplegia type 10 (SPG10) family presenting with bulbar symptoms and fasciculations mimicking amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 364:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.03.001
Duis J, Dean S, Applegate C, Harper A, Xiao R, He W, Dollar JD, Sun LR, Waberski MB, Crawford TO, Hamosh A, Stafstrom CE (2016) KIF5A mutations cause an infantile onset phenotype including severe myoclonus with evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction. Ann Neurol 80(4):633–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24744
Nicolas A, Kenna KP, Renton AE, Ticozzi N, Faghri F, Chia R, Dominov JA, Kenna BJ, Nalls MA, Keagle P, Rivera AM, van Rheenen W, Murphy NA, van Vugt J, Geiger JT, Van der Spek RA, Pliner HA, Shankaracharya SBN, Marangi G, Topp SD, Abramzon Y, Gkazi AS, Eicher JD, Kenna A, Mora G, Calvo A, Mazzini L, Riva N, Mandrioli J, Caponnetto C, Battistini S, Volanti P, La Bella V, Conforti FL, Borghero G, Messina S, Simone IL, Trojsi F, Salvi F, Logullo FO, D’Alfonso S, Corrado L, Capasso M, Ferrucci L, Moreno CAM, Kamalakaran S, Goldstein DB, Gitler AD, Harris T, Myers RM, Phatnani H, Musunuri RL, Evani US, Abhyankar A, Zody MC, Kaye J, Finkbeiner S, Wyman SK, LeNail A, Lima L, Fraenkel E, Svendsen CN, Thompson LM, Van Eyk JE, Berry JD, Miller TM, Kolb SJ, Cudkowicz M, Baxi E, Benatar M, Taylor JP, Rampersaud E, Wu G, Wuu J, Lauria G, Verde F, Fogh I, Tiloca C, Comi GP, Soraru G, Cereda C, Corcia P, Laaksovirta H, Myllykangas L, Jansson L, Valori M, Ealing J, Hamdalla H, Rollinson S, Pickering-Brown S, Orrell RW, Sidle KC, Malaspina A, Hardy J, Singleton AB, Johnson JO, Arepalli S, Sapp PC, McKenna-Yasek D, Polak M, Asress S, Al-Sarraj S, King A, Troakes C, Vance C, de Belleroche J, Baas F, Ten Asbroek A, Munoz-Blanco JL, Hernandez DG, Ding J, Gibbs JR, Scholz SW, Floeter MK, Campbell RH, Landi F, Bowser R, Pulst SM, Ravits JM, MacGowan DJL, Kirby J, Pioro EP, Pamphlett R, Broach J, Gerhard G, Dunckley TL, Brady CB, Kowall NW, Troncoso JC, Le Ber I, Mouzat K, Lumbroso S, Heiman-Patterson TD, Kamel F, Van Den Bosch L, Baloh RH, Strom TM, Meitinger T, Shatunov A, Van Eijk KR, de Carvalho M, Kooyman M, Middelkoop B, Moisse M, McLaughlin RL, Van Es MA, Weber M, Boylan KB, Van Blitterswijk M, Rademakers R, Morrison KE, Basak AN, Mora JS, Drory VE, Shaw PJ, Turner MR, Talbot K, Hardiman O, Williams KL, Fifita JA, Nicholson GA, Blair IP, Rouleau GA, Esteban-Perez J, Garcia-Redondo A, Al-Chalabi A, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Ostrow LW, Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD, Simmons Z, Cooper-Knock J, Brice A, Goutman SA, Feldman EL, Gibson SB, Taroni F, Ratti A, Gellera C, Van Damme P, Robberecht W, Fratta P, Sabatelli M, Lunetta C, Ludolph AC, Andersen PM, Weishaupt JH, Camu W, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Brown RH Jr, van den Berg LH, Veldink JH, Harms MB, Glass JD, Stone DJ, Tienari P, Silani V, Chio A, Shaw CE, Traynor BJ, Landers JE (2018) Genome-wide analyses identify KIF5A as a novel ALS gene. Neuron 97(6):1268–1283.e1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.02.027
Brenner D, Yilmaz R, Müller K, Grehl T, Petri S, Meyer T, Grosskreutz J, Weydt P, Ruf W, Neuwirth C, Weber M, Pinto S, Claeys KG, Schrank B, Jordan B, Knehr A, Günther K, Hübers A, Zeller D, Kubisch C, Jablonka S, Sendtner M, Klopstock T, de Carvalho M, Sperfeld A, Borck G, Volk AE, Dorst J, Weis J, Otto M, Schuster J, Del Tredici K, Braak H, Danzer KM, Freischmidt A, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Ludolph AC, Andersen PM, Weishaupt JH (2018) Hot-spot KIF5A mutations cause familial ALS. Brain 141(3):688–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx370
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(5):293–299
Krawczak M, Thomas NS, Hundrieser B, Mort M, Wittig M, Hampe J, Cooper DN (2007) Single base-pair substitutions in exon-intron junctions of human genes: nature, distribution, and consequences for mRNA splicing. Hum Mutat 28(2):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20400
Crimella C, Baschirotto C, Arnoldi A, Tonelli A, Tenderini E, Airoldi G, Martinuzzi A, Trabacca A, Losito L, Scarlato M, Benedetti S, Scarpini E, Spinicci G, Bresolin N, Bassi MT (2012) Mutations in the motor and stalk domains of KIF5A in spastic paraplegia type 10 and in axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2. Clin Genet 82(2):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01717.x
Jennings S, Chenevert M, Liu L, Mottamal M, Wojcik EJ, Huckaba TM (2017) Characterization of kinesin switch I mutations that cause hereditary spastic paraplegia. PLoS One 12(7):e0180353. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180353
Faruq M, Kumar D, Wadhwa S, Shamim U, Mathur A, Parveen S, Garg A, Srivastava AK (2019) Intrafamilial variable spastic paraplegia/ataxia/ALS phenotype linked to a novel KIF5A mutation. Clin Genet 96(3):271–273. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13585
Campbell PD, Shen K, Sapio MR, Glenn TD, Talbot WS, Marlow FL (2014) Unique function of Kinesin Kif5A in localization of mitochondria in axons. J Neurosci 34(44):14717–14732. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2770-14.2014
Hares K, Redondo J, Kemp K, Rice C, Scolding N, Wilkins A (2017) Axonal motor protein KIF5A and associated cargo deficits in multiple sclerosis lesional and normal-appearing white matter. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 43(3):227–241. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12305
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients for participating in this study. We also thank all the neurologists who provided samples for this study.
Funding
This work was supported in part by KAKENHI (Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas Nos. 22129001 and 22129002) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and Grants-in-Aid [H23-Jitsuyoka (Nanbyo)-Ippan-004 and H26-Jitsuyoka (Nanbyo)-Ippan-080] from the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Labour, Japan, and grants (Nos. 15ek0109065h0002, 16kk0205001h001, 17kk0205001h0002, and 17ek0109279h0001) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) to S.T. This work was also supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows) Grant Number JP19J01720.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naruse, H., Ishiura, H., Mitsui, J. et al. Splice-site mutations in KIF5A in the Japanese case series of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurogenetics 22, 11–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-020-00626-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-020-00626-1