Abstract
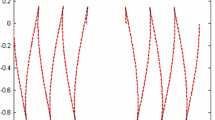
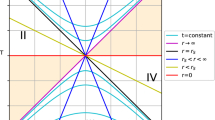
Timelike geodesics on a hyperplane orthogonal to the symmetry axis of the Gödel spacetime appear to be elliptic-like if standard coordinates naturally adapted to the cylindrical symmetry are used. The orbit can then be suitably described through an eccentricity-semi-latus rectum parametrization, familiar from the Newtonian dynamics of a two-body system. However, changing coordinates such planar geodesics all become explicitly circular, as exhibited by Kundt’s form of the Gödel metric. We derive here a one-to-one correspondence between the constants of the motion along these geodesics as well as between the parameter spaces of elliptic-like versus circular geodesics. We also show how to connect the two equivalent descriptions of particle motion by introducing a pair of complex coordinates in the 2-planes orthogonal to the symmetry axis, which brings the metric into a form which is invariant under Möbius transformations preserving the symmetries of the orbit, i.e., taking circles to circles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gödel, K.: An Example of a new type of cosmological solutions of Einstein’s field equations of gravitation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 21, 447 (1949). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.21.447
Kundt, W.: Trägheitsbahnen in einem von Gödel angegebenen kosmologischen Modell. Z. Phys. 145, 611 (1956)
Chandrasekhar, S., Wright, J.P.: The Geodesics in Gödel’s Universe. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 47, 341 (1961)
Novello, M., Svaiter, N.F., Guimaraes, M.E.X.: Synchronized frames for Godel’s universe”. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 25, 137 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00758823
Obukhov, Y.N.: On physical foundations and observational effects of cosmic rotation, Published in Colloquium on Cosmic Rotation: Proceedings. Edited by Scherfner, M., Chrobok, T., Shefaat, M. (Wissenschaft und Technik Verlag: Berlin, 2000) pp. 23–96 [astro-ph/0008106]
Grave, F., Buser, M., Muller, T., Wunner, G., Schleich, W.P.: The Gödel universe: Exact geometrical optics and analytical investigations on motion”. Phys. Rev. D 80, 103002 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.80.103002
D. Bini, A. Geralico and R. T. Jantzen, Separable geodesic action slicing in stationary spacetimes,” Gen. Rel. Grav. 44, 603 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-011-1295-2[arXiv:1408.5259 [gr-qc]]
Hawking, S.W., Ellis, G.F.R.: The Large Scale Structure of Spacetime. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (1973)
Novello, M., Soares, I.D., Tiomno, J.: Geodesic Motion And Confinement In Gödel’s Universe. Phys. Rev. D 27, 779 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.27.779
Bini, D., Geralico, A., Jantzen, R.T., Plastino, W.: Gödel spacetime: Planar geodesics and gyroscope precession, Phys. Rev. D 100, no. 8, 084051 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.100.084051[arXiv:1905.04917 [gr-qc]]
Oblak, B.: From the Lorentz Group to the Celestial Sphere, arXiv:1508.00920 [math-ph]
Bengtsson, I.: Spherical symmetry and black holes, http://3dhouse.se/ingemar/sfar.pdf
Reboucas, M.J., Tiomno, J.: On the homogeneity of riemannian space-times of godel type. Phys. Rev. D 28, 1251–1264 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.28.1251
Barrow, J.D., Dabrowski, M.P.: Godel universes in string theory, Phys. Rev. D 58, 103502 (1998) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.58.103502[arXiv:gr-qc/9803048 [gr-qc]]
Gleiser, R.J., Gurses, M., Karasu, A., Sarioglu, O.: Closed timelike curves and geodesics of Gödel-type metrics. Class. Quant. Grav. 23, 2653 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/0264-9381/23/7/025
Calvao, M.O., Soares, I.D., Tiomno, J.: Geodesics in Gödel-type space-times. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 22, 683 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00755988
Silk, J.: Local Irregularities in a Godel Universe. Astrophys. J. 143, 689 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1086/148551
Silk, J.: The instability of a rotating universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 147, 13 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/147.1.13
Barrow, J.D., Tsagas, C.G.: Dynamics and stability of the Godel universe. Class. Quant. Grav. 21, 1773–1790 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/0264-9381/21/7/005. [arXiv:gr-qc/0308067 [gr-qc]]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bini, D., Geralico, A., Jantzen, R.T. et al. Gödel spacetime, planar geodesics and the Möbius map. Gen Relativ Gravit 52, 73 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-020-02731-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-020-02731-w