Abstract
River basins often extend over several regions connected by both water flows and socioeconomic factors. Therefore, water policy and diverse hydrological scenarios can affect socioeconomic variables in other parts of a river basin. This paper proposes a tool combining hydro-economic and input–output models to analyze the socioeconomic impacts of different hydrologic scenarios from a multiregional standpoint. To this end, we have built a monthly-basis hydro-economic model to fit a multiregional input–output table to estimate direct and indirect impacts on value added and employment, bringing together data on water flow and regional demand, sector-based economic analysis and macroeconomic impacts. In a given hydrological scenario, the hydro-economic model determines the output of irrigated farmland in each region and the value added generated by each crop. These data are then processed using the multiregional input–output model to determine socio-economic impacts in each of the regions forming the river basin. This methodology allows evaluation of different water policies, providing a tool for policymakers to estimate socio-economic impacts. Finally, we apply this methodology in two scenarios reflecting the opportunity costs of diverse hydrological scenarios in terms of value added and employment terms to demonstrate its excellent analytic capacity.
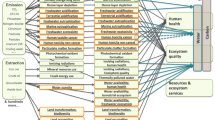
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acreman MC, Ferguson AJD (2010) Environmental flows and the European Water Framework Directive. Freshw Biol 55:32–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02181.x
Akter S, Grafton RQ, Merritt WS (2014) Integrated hydro-ecological and economic modeling of environmental flows: Macquarie Marshes, Australia. Agric Water Manag 145:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2013.12.005
Almazán-Gómez MA, Sánchez-Chóliz J (2016) The Mequinenza Reservoir: its contribution to the Ebro Delta and its potential for economic development—El embalse de Mequinenza: Su aportación al delta del Ebro y su potencialidad para el desarrollo económico (In Spanish). Reg Sect Econ Stud 16:147–166
Almazán-Gómez MA, Sánchez-Chóliz J, Sarasa C (2018) Environmental flow management: an analysis applied to the Ebro River basin. J Clean Prod 182:838–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.207
Almazán-Gómez MA, Duarte R, Langarita R, Sánchez-Chóliz J (2019) Effects of water re-allocation in the Ebro river basin: A multiregional input–output and geographical analysis. J Environ Manag 241:645–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.042
Antonelli M, Roson R, Sartori M (2012) Systemic input–output computation of green and blue virtual water ‘flows’ with an illustration for the Mediterranean region. Water Resour Manag 26:4133–4146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0135-9
Arthington AH, Bhaduri A, Bunn SE et al (2018) The Brisbane declaration and global action agenda on environmental flows (2018). Front Environ Sci 6:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00045
Ballester A, Mott Lacroix KE (2016) Public participation in water planning in the Ebro River basin (Spain) and Tucson basin (U.S., Arizona): impact on water policy and adaptive capacity building. Water 8:273. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8070273
Bonsch M, Popp A, Biewald A et al (2015) Environmental flow provision: implications for agricultural water and land-use at the global scale. Glob Environ Chang 30:113–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.10.015
Cai B, Wang C, Zhang B (2017) Worse than imagined: unidentified virtual water flows in China. J Environ Manag 196:681–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.062
Cazcarro I, Duarte R, Sánchez-Chóliz J (2016) Downscaling the grey water footprints of production and consumption. J Clean Prod 132:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.113
Cazcarro I, Duarte R, Sánchez Chóliz J, Sarasa C (2019) Water and production reallocation in the Spanish agri-food system. Econ Syst Res 5314:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/09535314.2019.1693982
Crespo D, Albiac J, Kahil T et al (2019) Tradeoffs between water uses and environmental flows: a hydroeconomic analysis in the Ebro basin. Water Resour Manag 33:2301–2317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02254-3
Dietzenbacher E (2005) More on multipliers*. J Reg Sci 45:421–426. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-4146.2005.00377.x
Duarte R, Langarita R, Sánchez-Chóliz J (2017) The electricity industry in Spain: a structural analysis using a disaggregated input-output model. Energy 141:2640–2651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.08.088
George B, Malano H, Davidson B et al (2011) An integrated hydro-economic modelling framework to evaluate water allocation strategies I: model development. Agric Water Manag 98:733–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.12.004
Hai R, Shi H, Zhang B et al (2015) An ecological information analysis-based approach for assessing the sustainability of water use systems: a case study of the Huaihe River Basin, China. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:2197–2211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-0944-7
Harou JJ, Pulido-Velázquez M, Rosenberg DE et al (2009) Hydro-economic models: concepts, design, applications, and future prospects. J Hydrol 375:627–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.037
Hašková S (2017) Holistic assessment and ethical disputation on a new trend in solid biofuels. Sci Eng Ethics 23:509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-016-9790-1
Hoa NT, Aviso KB, Kojima N, Tokai A (2018) Structural analysis of the interrelationship between economic activities and water pollution in Vietnam in the period of 2000–2011. Clean Technol Environ Policy 20:621–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1492-8
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Jacob D, Taylor M, et al (2018) Impacts of 1.5°C global warming on natural and human systems. In: Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pörtner H-O, et al (eds) Global warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change,. pp 175–311
Kahil MT, Dinar A, Albiac J (2015) Modeling water scarcity and droughts for policy adaptation to climate change in arid and semiarid regions. J Hydrol 522:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.12.042
Kahil MT, Ward FA, Albiac J et al (2016) Hydro-economic modeling with aquifer–river interactions to guide sustainable basin management. J Hydrol 539:510–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.057
López-Díaz DC, Lira-Barragán LF, Rubio-Castro E et al (2018) Optimization of biofuels production via a water–energy–food nexus framework. Clean Technol Environ Policy 20:1443–1466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1395-0
Maneta MP, Torres MDO, Wallender WW et al (2009) A spatially distributed hydroeconomic model to assess the effects of drought on land use, farm profits, and agricultural employment. Water Resour Res 45:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007534
Mardoyan A, Braun P (2015) Analysis of Czech subsidies for solid biofuels. Int J Green Energy 12:405–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2013.841163
Maroušek J (2014) Novel technique to enhance the disintegration effect of the pressure waves on oilseeds. Ind Crops Prod 53:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.048
Maroušek J, Stehel V, Vochozka M et al (2019) Ferrous sludge from water clarification: changes in waste management practices advisable. J Clean Prod 218:459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.037
Milano M, Ruelland D, Dezetter A et al (2013) Modeling the current and future capacity of water resources to meet water demands in the Ebro basin. J Hydrol 500:114–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.07.010
Moriondo M, Bindi M, Kundzewicz ZW et al (2010) Impact and adaptation opportunities for European agriculture in response to climatic change and variability. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Change 15:657–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-010-9219-0
Perni Á, Martínez-Paz J, Martínez-Carrasco F (2012) Social preferences and economic valuation for water quality and river restoration: the Segura River, Spain. Water Environ J 26:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-6593.2011.00286.x
Pulido-Velázquez M, Andreu J, Sahuquillo A, Pulido-Velazquez D (2008) Hydro-economic river basin modelling: the application of a holistic surface–groundwater model to assess opportunity costs of water use in Spain. Ecol Econ 66:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.12.016
Tan RR, Foo DCY (2018) Integrated multi-scale water management as a climate change adaptation strategy. Clean Technol Environ Policy 20:1123–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1551-1
White DJ, Feng K, Sun L, Hubacek K (2015) A hydro-economic MRIO analysis of the Haihe River Basin’s water footprint and water stress. Ecol Model 318:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.01.017
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude for the partial funding received from the Spanish Government under the project ECO 2016-74940-P, from the Aragonese Regional Government and FEDER Funds via the S40_17R reference group of the Aragon Government, and Grant FPU14/ 01694. The authors would also like to thank the editor of CTEP and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, which have helped to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almazán-Gómez, M.A., Duarte, R., Langarita, R. et al. Water and socioeconomic dependencies: a multiregional model. Clean Techn Environ Policy 23, 783–796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01915-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01915-x