Abstract
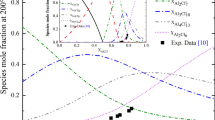
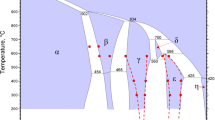
V2O5/CaO diffusion couples were prepared to investigate the reaction characteristics between V2O5 and CaO at 1073 K to 1273 K in air. The distribution, species, and number of phases generated in the proximity of the V2O5/CaO interface were characterized by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), Fourier transform–infrared (FT–IR) spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD) that was capable of selecting the scanning location. The results show that CaV2O6 was quickly generated to become the matrix all over the V-rich layer at a relatively low temperature (1073 K to 1223 K); Ca2V2O7 was then formed in the vicinity of the CaV2O6/CaO interface. The presence of Ca2V2O7 near the CaV2O6/air interface was unexpected and indicated that the diffusion of oxygen from the air into the V-rich layer had promoted its formation. Upon increasing the annealing temperature, CaV2O6 disappeared gradually at 1223 K, Ca2V2O7 became the matrix at 1223 K, and Ca3(VO4)2 appeared near the Ca2V2O7/CaO interface at 1173 K. Average interdiffusion coefficients in Ca3(VO4)2 at 1173 K, 1223 K, and 1273 K were 1.66 × 10−10, 3.45 × 10−10, and 17.5 × 10−10 cm2 s−1, respectively. The diffusion activation energy calculated using the Arrhenius equation was 290.15 ± 32.29 kJ/mol. With increasing annealing time, the amount of the phases (Ca2V2O7 at 1073 K to 1123 K and Ca3(VO4)2 at 1173 K to 1273 K) in the vicinity of the V-rich layer/CaO interface increased. At 1173 K, the diffusion thickness of Ca3(VO4)2 increased with increasing annealing time with a square root of time dependency, which suggested that the formation of Ca3(VO4)2 in the Ca2V2O7 mixture was governed by the solid–solid diffusion process.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
Abbreviations
- D :
-
Interdiffusion coefficient
- D 0 :
-
Pre-exponential factor
- E D :
-
Diffusion activation energy
- R:
-
Gas constant
- T :
-
Absolute temperature
References
1.C.F. Yang: Iron and Steel, 2013, vol. 48 (4), pp. 1–11.
2.C. Yang and Y. Zhang: Iron and Steel, 2002, vol. 37 (11), pp. 42–47.
3.R.J. Van Thyne: JOM, 1963, vol. 15, pp. 642–44.
4.R.R. Moskalyk and A.M. Alfantazi: Miner. Eng., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 793–805.
5.J.H. Zhang, W. Zhang, L. Zhang, and S.Q. Gu: Int. J. Miner. Process., 2015, vol. 138, pp. 20–29.
6.T.Y. Wang, L.J. Xu, C.L. Liu, and Z.D. Zhang: Chin. J. Geochem., 2014, vol. 33, pp. 163–67.
7.A.N. Morozov: Metallurgy, 1938, vol. 13, pp. 21–28.
8.Y. Yuan: Steel Res. Int., 1991, vol. 62, pp. 60–65.
9.Z. Cao, N. Wang, W. Xie, Z. Qiao, and I. Jung: Calphad, 2017, vol. 56, pp. 72–79.
10.J.C. Bouloux, J. Galy, and P. Hagenmuller: Rev. Chem. Min., 1974, vol. 11, pp. 48–70.
11.R. Li, P. Niu, S. Deng, T. Yuan, and G. Liu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 6–10.
12.G. Xu, Y. Liu, and Z. Kang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 3126–31.
13.C.S. Liu, K.H. Kim, S.J. Kim, J.S. Li, S. Ueda, X. Gao, H. Shibata, and S. Kitamura: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1875–84.
14.Z.S Ren, X.J. Hu, X.X. Xue, and K.C. Chou: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 580, pp. 182–86.
15.Z.S Ren, X.J. Hu, S.Y. Li, X.X. Xue, and K.C. Chou: Int. J. Min. Met. Mater., 2013, vol. 20, pp. 273–78.
16.H. Fukuyama, K. Hossain, and K. Nagata: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 257–64.
Y.I. Boyko, V.I. Biletskyi, V.V. Bogdanov, R.V. Vovk, G.Y. Khadzhai, I.L. Goulatis, A. Chroneos (2018) J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29:4743–48.
18.B. Xu, W.P. Tong, C.Z. Liu, H. Zhang, L. Zuo, and J.C. He: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 27 (9), pp. 856–60.
19.K. Matsuura, Y. Itoh, and T. Narita: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 583–87.
20.U.G. Nielsen, H.J. Jakobsen, and J. Skibsted: J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, vol. 105, pp. 420–29.
V.B. Taxak, S. Dayawati, S.P. Khatkar (2013) Curr. Appl. Phys. vol. 13, pp. 594–98.
22.D.L. Chen, Z.S. Liu, B.B. Fan, J. Li, W.B. Cao, H.L. Wang, H.X. Lu, and H.L. Xu: Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2014, vol. 11, pp. 946–53.
23.N.Y. Mostafa, E.A. Kishar, and S.A. Abo-El-Enein: J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 473, pp. 538–42.
H. Ye, X. Liu, and H. Hong: J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2009, vol. 20, pp. 843–50.
25.L. Chen, Y. Kaneko, N. Ayuzawa, and T. Suzuki: J. Ion Exchange, 1999, vol. 10, pp. 2–7.
26.V. Dimitrov: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1995, vols. 192–193, pp. 183–86.
27.P. Parhi, V. Manivannan, S. Kohli, and P. Mccurdy: Bull. Mater. Sci., 2008, vol. 31, pp. 885–90.
H.R. Yue and X.X. Xue: J. Hazard. Mater. (2020), vol. 393, p. 122368.
29.P. Zhang, T. DebRoy, and S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 2105–14.
30.J. Zheng, X. Hu, Z. Ren, X. Xue, and K Chou: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1762–66.
31.T. Takenaka, S. Kano, M. Kajihara, N. Kurokawa, and K. Sakamoto: Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct., 2005, vol. 396, pp. 115–23.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51674084 and U1502273) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 182503035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted February 20, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, HR., Xue, XX. Evolution of Generated Calcium Vanadates at Different Locations in the Vicinity of the V2O5/CaO Interface with Annealing Parameters. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2358–2370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01919-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01919-4