Abstract
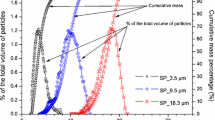
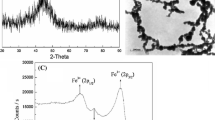
The deposition characteristics of lead ions (Pb2+) in the presence of silicon powders (i.e., suspended particles, SPs) were investigated in water seepage in a long one-dimensional sand column experiment. The injected SPs possess a very wide particle-size distribution (PSD). The concentrations of deposited Pb2+ and SPs and the migration distance along the water flow direction were measured by sampling. The PSDs of the deposited SPs in different sections were obtained by laser diffraction after transport test completion, and microstructure photographs were also acquired through metallographic microscopy. The test results show that the presence of SPs may promote or inhibit Pb2+ migration, which is closely related to the concentration of the injected Pb2+, particle size and concentration of the injected SPs, seepage velocity, and change in the absolute zeta potential of the surface charge. The median diameter of the deposited SPs near the injection end is larger than that of the injected SPs and gradually decreases with increasing distance. Overall, the transport of SPs represents a clear particle-separation characteristic and significantly influences the migration progress of pollutants such as heavy metal ions such as Pb2+ due to their coupling effects.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbar, B., Alem, A., Pantet, A., Nasre-Dine, Ahfir, Marcotte, S., Wang, H., Duchemin, B.: Effect of natural geotextile on the cotransport of heavy metals (Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) and kaolinite particles. Environ. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1637463
Agbozu, I.E., Bassey, U.: Kinetic modeling for removal of Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cr ions from petrochemical effluent using termite soil. Int. J. Sci. 5(2), 77–82 (2016)
Ahfir, N.D., Hammadi, A., Alem, A., Wang, H.Q., Bras, G.L., Ouahbi, T.: Porous media grain size distribution and hydrodynamic forces effects on transport and deposition of suspended particles. J. Environ. Sci. 53(3), 161–172 (2017)
Alem, A., Ahfir, N.D., Elkawafi, A., Wang, H.: Hydraulic operating conditions and particle concentration effects on physical clogging of a porous medium. Transp Porous Media 106, 303–321 (2015)
Bai, B., Long, F., Rao, D., Xu, T.: The effect of temperature on the seepage transport of suspended particles in a porous medium. Hydrol. Process. 31(2), 382–393 (2017)
Bai, B., Rao, D., Chang, T., Guo, Z.: A nonlinear attachment-detachment model with adsorption hysteresis for suspension-colloidal transport in porous media. J. Hydrol. 578, 124080 (2019a)
Bai, B., Zhai, Z., Rao, D.: The seepage transport of heavy metal Pb2+ through sand column in the presence of silicon powders. J Hydrol Hydromech 67, 349–358 (2019b)
Bai, B., Xu, T., Nie, Q., Li, P.: Temperature-driven migration of heavy metal Pb2+ along with moisture movement in unsaturated soils. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 153, 119573 (2020)
Bedrikovetsky, P., You, Z., Badalyan, A., Osipov, Y., Kuzmina, L.: Analytical model for straining- dominant large-retention depth filtration. Chem. Eng. J. 330, 1148–1159 (2017)
Bennacer, L., Ahfir, N.D., Alem, A., Wang, H.Q.: Coupled effects of ionic strength, particle size, and flow velocity on transport and deposition of suspended particles in saturated porous media. Transp. Porous Media 118(3), 251–269 (2017)
Bradford, S.A., Kim, H.N., Haznedaroglu, B.Z., Torkzaban, S., Walker, S.L.: Coupled factors influencing concentration-dependent colloid transport and retention in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(18), 6996–7002 (2009)
Chen, X., Wu, Z., Qipeng, C., Cao, W.: Effect of ultrasonic stimulation on particle transport and fate over different lengths of porous media. J. Hydrol. 559, 972–983 (2018)
Chrysikopoulos, C.V., Katzourakis, V.E.: Colloid particle size-dependent dispersivity. Water Resour. Res. 51, 4668–4683 (2015)
Chrysikopoulos, C.V., Sotirelis, N.P., Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.G.: Cotransport of graphene oxide nanoparticles and kaolinite colloids in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 119, 181–204 (2017)
Cui, X., Liu, Q., Zhang, C.: Detachment characteristics of deposited particles in porous medium: experimentation and modeling. Transp. Porous Media 119, 633–647 (2017)
Fangueiro, D., Bermond, A., Santos, E., Carapuca, H., Duarte, A.: Heavy metal mobility assessment in sediments based on a kinetic approach of the EDTA extraction: search for optimal experimental conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta 459(2), 245–256 (2002)
Hudcova, B., Veselska, V., Filip, J., Cihalova, S., Komarek, M.: Highly effective Zn(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solutions using Mg-Fe layered double hydroxides: comprehensive adsorption modeling coupled with solid state analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 171, 944–953 (2018)
Johnson, W.P., Pazmino, E., Ma, H.: Direct observations of colloid retention in granular media in the presence of energy barriers, and implications for inferred mechanisms from indirect observations. Water Res. 44, 1158–1169 (2010)
Karathanasis, A.D.: Subsurface migration of copper and zinc mediated by soil colloids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 63(4), 830–838 (1999)
Katzourakis, V.E., Chrysikopoulos, C.V.: Two-site colloid transport with reversible and irreversible attachment: analytical solutions. Adv. Water Resour. 130, 29–36 (2019)
Kim, H.N., Walker, S.L.: Escherichia coli transport in porous media: influence of cell strain, solution chemistry, and temperature. Colloids Surf. B 71(1), 160–167 (2009)
Kumpiene, J.: Management with willow short rotation coppice increase the functional gene diversity and functional activity of a heavy metal polluted soil. Chemosphere 138, 469–477 (2015)
Lee, S., Ko, I.W., Yoon, I.H., Kim, D.W., Kim, K.W.: Colloid mobilization and heavy metal transport in the sampling of soil solution from Duckum soil in South Korea. Environ. Geochem. Health 41, 469–480 (2019)
Li, Y., Ahmadi, A., Aziz, O., Pu, H.: Three-dimensional microscale simulation of colloidal particle transport and deposition in model porous media with converging/diverging geometries. Colloids Surfaces A 544, 179–186 (2018)
Ma, J., Guo, H., Lei, M., Wan, X., Zhang, H., Feng, X., Wei, R., Tian, L., Han, X.: Blocking effect of colloids on arsenate adsorption during co-transport through saturated sand columns. Environ. Pollut. 213, 638–647 (2016)
Malkovsky, V.I., Petrov, V.A., Dikov, Y.P., Alexandrova, E.V., Bychkova, Y.V., Shulik, L.S.: Colloid-facilitated transport of uranium by groundwater at the U-Mo ore field in eastern Transbaikalia. Environ. Earth Sci. 73(10), 1–8 (2015)
Nie, Q., Li, Y., Wang, G., Bai, B.: Physicochemical and microstructural properties of red muds under acidic and alkaline conditions. Appl. Sci. 10(9), 2993 (2020)
Qiao, J., Sun, H., Luo, X., Zhang, W., Mathews, S., Yin, X.: EDTA-assisted leaching of Pb and Cd from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 167, 422–428 (2017)
Raikova, S., Piccini, M., Surman, M.K., Allen, M.J., Chuck, C.J.: Making light work of heavy metal contamination: the potential for coupling bioremediation with bioenergy production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6133
Rao, D., Bai, B.: Study of the factors influencing diffusive tortuosity based on pore–scale SPH simulation of granular soil. Transp. Porous Media 132, 333–353 (2020)
Russell, T., Bedrikovetsky, P.: Colloidal-suspension flows with delayed fines detachment: analytical model and laboratory study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 190, 98–109 (2018)
Sugimoto, T., Kobayashi, M., Adachi, Y.: The effect of double layer repulsion on the rate of turbulent and Brownian aggregation: experimental consideration. Colloids Surf. A 443(4), 418–424 (2014)
Syngouna, V.I., Chrysikopoulos, C.V.: Cotransport of clay colloids and viruses through water-saturated vertically oriented columns packed with glass beads: gravity effects. Sci. Total Environ. 545–546, 210–218 (2016)
Tang, J., Zhu, W., Kookana, R., Katayama, A.: Characteristics of biochar and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 116(6), 653–659 (2013)
Tansel, B., Rafiuddin, S.: Heavy metal content in relation to particle size and organic content of surficial sediments in Miami River and transport potential. Int. J. Sedim. Res. 31, 324–329 (2016)
Valsala, R., Govindarajan, S.K.: Co-colloidal BTEX and microbial transport in a saturated porous system: numerical modeling and sensitivity analysis. Transp. Porous Media 127, 269–294 (2019)
Wang, C., Bobba, A.D., Attinti, R., Shen, C., Lazouskaya, V., Wang, L., Jin, Y.: Retention and transport of silica nanoparticles in saturated porous media: effect of concentration and particle size. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 7151–7158 (2012)
Wang, X., Xu, X., Dang, W., Tang, Z., Hu, C., Wei, B.: Interception characteristics and pollution mechanism of the filter medium in polymer-flooding produced water filtration process. Processes 7, 927 (2019)
Wu, G., Li, L.Y.: Modeling of heavy metal migration in sand/bentonite and the leachate pH effect. J. Contam. Hydrol. 33, 313–336 (1998)
Xu, S., Gao, B., Saiers, J.E.: Straining of colloidal particles in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 42(12), 731–741 (2006)
Zhang, P., Bai, B., Jiang, S., Wang, P., Li, H.: Transport and deposition of suspended particles in saturated porous media: effect of the hydrodynamic forces and pore structure. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 16(4), 951–960 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51678043; 51878035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, B., Zhang, J., Liu, L. et al. The Deposition Characteristics of Coupled Lead Ions and Suspended Silicon Powders Along the Migration Distance in Water Seepage. Transp Porous Med 134, 707–724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01464-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01464-3