Abstract
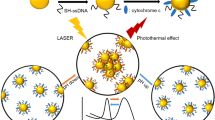
The ideal photothermal therapy agent should exhibit a high energy conversion capacity, but it should not induce any cytotoxic effects unless it is exposed to electromagnetic radiation. We present data on biocompatibility and photothermal conversion capacity of colloidal gold nanoparticle assemblies (NPAs), obtained by hydroxylamine hydrochloride reduction at room temperature. The cytotoxic profile of NPAs with a mean diameter of 20 and 120 nm, respectively, was assessed using 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, demonstrating tolerable cytotoxic effect on A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line at gold concentrations up to 150 μg gold/mL. Insights regarding the oxidative stress were gained using peroxide-sensitive fluorescent probes, which showed no additional oxidative stress due to NPA exposure. Using infrared thermal imaging, the photothermal conversion was evidenced, the effect being more prominent for the 120-nm diameter NPAs irradiated with the 785-nm laser. The photothermal capabilities of NPAs were highlighted also by Raman imaging studies, showing intracellular carbon by-products due to the thermal damage. Intracellular carbon deposits overlapping with the nanoparticle-rich sites were identified. These results highlight that NPAs are a versatile platform with possible applications in nanoparticle-based photothermal therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skitzki JJ, Repasky EA, Evans SS (2009) Hyperthermia as an immunotherapy strategy for cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs (London, England: 2000) 10(6):550–558
Verma J, Lal S, Van Noorden CJ (2014) Nanoparticles for hyperthermic therapy: synthesis strategies and applications in glioblastoma. Int J Nanomed 9:2863–2877. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s57501
Chapman S, Dobrovolskaia M, Farahani K, Goodwin A, Joshi A, Lee H, Meade T, Pomper M, Ptak K, Rao J, Singh R, Sridhar S, Stern S, Wang A, Weaver JB, Woloschak G, Yang L (2013) Nanoparticles for cancer imaging: the good, the bad, and the promise. Nano Today 8(5):454–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2013.06.001
Giljohann DA, Seferos DS, Daniel WL, Massich MD, Patel PC, Mirkin CA (2010) Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(19):3280–3294. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200904359
Dykman LA, Khlebtsov NG (2011) Gold nanoparticles in biology and medicine: recent advances and prospects. Acta Nat 3(2):34–55
Boitor RA, Tódor IS, Leopold LF, Leopold N (2015) Room temperature synthesis of highly monodisperse and Sers-active glucose-reduced gold nanoparticles. J Appl Spectrosc 82(3):415–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-015-0122-z
Marisca OT, Kantner K, Pfeiffer C, Zhang Q, Pelaz B, Leopold N, Parak WJ, Rejman J (2015) Comparison of the in vitro uptake and toxicity of collagen- and synthetic polymer-coated gold nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 5(3):1418–1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031418
Khalili Fard J, Jafari S, Eghbal MA (2015) A review of molecular mechanisms involved in toxicity of nanoparticles. Adv Pharm Bull 5(4):447–454. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2015.061
Misawa M, Takahashi J (2011) Generation of reactive oxygen species induced by gold nanoparticles under x-ray and UV irradiations. Nanomedicine 7(5):604–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.01.014
Fu PP, Xia Q, Hwang HM, Ray PC, Yu H (2014) Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: generation of reactive oxygen species. J Food Drug Anal 22(1):64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.005
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24(10):R453–R462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Liou G-Y, Storz P (2010) Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic Res 44(5). https://doi.org/10.3109/10715761003667554
Tódor IS, Szabó L, Marişca OT, Chiş V, Leopold N (2014) Gold nanoparticle assemblies of controllable size obtained by hydroxylamine reduction at room temperature. J Nanopart Res 16(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2740-4
Diaconeasa Z, Rugină D, Coman C, Socaciu C, Leopold L, Vulpoi A, Tăbăran F, Suciu M, Mesaros A, Mirea Popa L, Pop O, Simon S, Pintea A (2017) New insights regarding the selectivity and the uptake potential of nanoceria by human cells. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.05.081
Rugina D, Diaconeasa Z, Coman C, Bunea A, Socaciu C, Pintea A (2015) Chokeberry anthocyanin extract as pancreatic β-cell protectors in two models of induced oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:10–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/429075
Hampe J, Franke A, Rosenstiel P, Till A, Teuber M, Huse K, Albrecht M, Mayr G, De La Vega FM, Briggs J, Gunther S, Prescott NJ, Onnie CM, Hasler R, Sipos B, Folsch UR, Lengauer T, Platzer M, Mathew CG, Krawczak M, Schreiber S (2007) A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat Genet 39(2):207–211. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1954
Alkilany AM, Murphy CJ (2010) Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far? J Nanopart Res 12(7):2313–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9911-8
Sohaebuddin SK, Thevenot PT, Baker D, Eaton JW, Tang L (2010) Nanomaterial cytotoxicity is composition, size, and cell type dependent. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-7-22
Hudson DE, Hudson DO, Wininger JM, Richardson BD (2013) Penetration of laser light at 808 and 980 nm in bovine tissue samples. Photomed Laser Surg 31(4):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2012.3284
Downes A, Mouras R, Bagnaninchi P, Elfick A (2011) Raman spectroscopy and CARS microscopy of stem cells and their derivatives(). J Raman Spectrosc 42(10):1864–1870. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2975
Fu D, Zhou J, Zhu WS, Manley PW, Wang YK, Hood T, Wylie A, Xie XS (2014) Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering. Nat Chem 6(7):614–622. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1961
Gregas MK, Yan F, Scaffidi J, Wang H-N, Vo-Dinh T (2011) Characterization of nanoprobe uptake in single cells: spatial and temporal tracking via SERS labeling and modulation of surface charge. Nanomedicine 7(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2010.07.009
Yosef HK, Mavarani L, Maghnouj A, Hahn S, El-Mashtoly SF, Gerwert K (2015) In vitro prediction of the efficacy of molecularly targeted cancer therapy by Raman spectral imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(27):8321–8331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8875-z
Brauchle E, Thude S, Brucker SY, Schenke-Layland K (2014) Cell death stages in single apoptotic and necrotic cells monitored by Raman microspectroscopy. Sci Rep 4:4698. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04698
Boitor R, Sinjab F, Strohbuecker S, Sottile V, Notingher I (2016) Towards quantitative molecular mapping of cells by Raman microscopy: using AFM for decoupling molecular concentration and cell topography. Faraday Discuss 187:199–212. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fd00172b
Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Van Treuren W, Ren B, Schwager E, Knights D, Song SJ, Yassour M, Morgan XC, Kostic AD, Luo C, Gonzalez A, McDonald D, Haberman Y, Walters T, Baker S, Rosh J, Stephens M, Heyman M, Markowitz J, Baldassano R, Griffiths A, Sylvester F, Mack D, Kim S, Crandall W, Hyams J, Huttenhower C, Knight R, Xavier RJ (2014) The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 15(3):382–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.005
Jawhari T, Roid A, Casado J (1995) Raman spectroscopic characterization of some commercially available carbon black materials. Carbon 33(11):1561–1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(95)00117-V
Kamada N, Hisamatsu T, Okamoto S, Chinen H, Kobayashi T, Sato T, Sakuraba A, Kitazume MT, Sugita A, Koganei K, Akagawa KS, Hibi T (2008) Unique CD14 intestinal macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of Crohn disease via IL-23/IFN-gamma axis. J Clin Invest 118(6):2269–2280. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci34610
Hart AL, Al-Hassi HO, Rigby RJ, Bell SJ, Emmanuel AV, Knight SC, Kamm MA, Stagg AJ (2005) Characteristics of intestinal dendritic cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 129(1):50–65
Smith AM, Rahman FZ, Hayee BH, Graham SJ, Marks DJB, Sewell GW, Palmer CD, Wilde J, Foxwell BMJ, Gloger IS, Sweeting T, Marsh M, Walker AP, Bloom SL, Segal AW (2009) Disordered macrophage cytokine secretion underlies impaired acute inflammation and bacterial clearance in Crohn’s disease. J Exp Med 206(10):2301–2301. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20091233090209c
Day ES, Thompson PA, Zhang L, Lewinski NA, Ahmed N, Drezek RA, Blaney SM, West JL (2011) Nanoshell-mediated photothermal therapy improves survival in a murine glioma model. J Neuro-Oncol 104(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0470-8
Fay BL, Melamed JR, Day ES (2015) Nanoshell-mediated photothermal therapy can enhance chemotherapy in inflammatory breast cancer cells. Int J Nanomed 10:6931–6941. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S93031
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Competitiveness Operational Programme 2014-2020 POC-A1-A1.1.4-E-2015, financed under the European Regional Development Fund, project number P37_245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6050 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tódor, I.S., Marişca, O.T., Rugină, D. et al. Photothermal property assessment of gold nanoparticle assemblies obtained by hydroxylamine reduction. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1369–1377 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04721-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04721-5