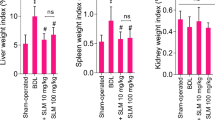
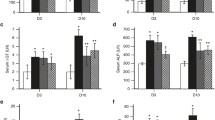
Abstract
Cholestasis-associated renal injury, known as cholemic nephropathy (CN), is a severe clinical complication. CN could lead to acute kidney injury. However, there is no specific pharmacological intervention for cholestasis-induced renal injury. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial impairment seem to play a role in the pathogenesis of CN. Betaine (3-methyl glycine; BET) is an amino acid derivative with a wide range of pharmacological actions. Several studies mentioned the effects of BET on oxidative stress in different experimental models. It has also been found that BET positively affected mitochondrial function. The current study aimed to evaluate the effects of BET supplementation on CN in the bile duct ligation (BDL) model of cholestasis. BET (0.25% and 1% w: v in drinking water) was administered to BDL animals for seven consecutive days. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and mitochondrial indices were evaluated in cholestatic animals. Significant elevation in reactive oxygen species formation, lipid peroxidation, and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) was evident in BDL rats. Moreover, reduced glutathione (GSH) levels and renal antioxidant capacity were decreased in cholestatic animals. Mitochondrial depolarization, mitochondrial permeabilization, decreased mitochondrial dehydrogenases activity, and lipid peroxidation was also detected in the kidney of BDL rats. Tubular atrophy, interstitial inflammation, and renal fibrosis were also detected in BDL rats. BET alleviated biomarkers of oxidative stress, improved mitochondrial indices, and decreased renal histopathological alterations in BDL animals. The antioxidant effects and the positive effects of BET on cellular mitochondria seem to play a fundamental role in its nephroprotective role during cholestasis.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ΔΨ:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- ATP:
-
Adenosine tri-phosphate
- BDL:
-
Bile duct ligation
- BET:
-
Betaine
- CN:
-
Cholemic nephropathy
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
References
Ahmadian E, Babaei H, Mohajjel Nayebi A, Eftekhari A, Eghbal MA (2017) Mechanistic approach for toxic effects of bupropion in primary rat hepatocytes. Drug Res 67:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-123034
Alía M, Horcajo C, Bravo L, Goya L (2003) Effect of grape antioxidant dietary fiber on the total antioxidant capacity and the activity of liver antioxidant enzymes in rats. Nutr Res 23:1251–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0271-5317(03)00131-3
Aniort J, Poyet A, Kemeny J-L, Philipponnet C, Heng A-E (2017) Bile Cast Nephropathy Caused by Obstructive Cholestasis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases: The Official Journal of the National Kidney Foundation 69:143–146. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.08.023
Betjes MGH, Bajema I (2006) The pathology of jaundice-related renal insufficiency: cholemic nephrosis revisited. Journal of Nephrology 19:229–233
Bingül İ, Aydın AF, Başaran-Küçükgergin C, Doğan-Ekici I, Çoban J, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Uysal M (2016) High-fat diet plus carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis is alleviated by betaine treatment in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 39:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.07.028
Brookes PS, Yoon Y, Robotham JL, Anders MW, Sheu S-S (2004) Calcium, ATP, and ROS: a mitochondrial love-hate triangle. Am J Physio-Cell Physiol 287:C817–C833. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2004
Caro AA, Adlong LW, Crocker SJ, Gardner MW, Luikart EF, Gron LU (2012) Effect of garlic-derived organosulfur compounds on mitochondrial function and integrity in isolated mouse liver mitochondria. Toxicol Lett 214:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.08.017
Chávez-Iñiguez JS, Meza-Ríos A, Santos-Garcia A, García-García G, Armendariz-Borunda J (2019) Cholemic nephropathy: Hyperbilirubinemia and its impact on renal function. J Ren Hepatic Disord 3:33–39. https://doi.org/10.15586/jrenhep.2019.52
Chen Y, Xing D, Wang W, Ding Y, Du L (2007) Development of an ion-pair HPLC method for investigation of energy charge changes in cerebral ischemia of mice and hypoxia of Neuro‐2a cell line. Biomed Chromatogr 21:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.798
Copple BL, Jaeschke H, Klaassen CD (2010) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of cholestasis. Semin Liver Dis 30:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1253228
Craig SAS (2004) Betaine in human nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 80:539–549. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/80.3.539
Day CR, Kempson SA (2016) Betaine chemistry, roles, and potential use in liver disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860:1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.02.001
Duffjr MR, Howell EE (2015) Chemical interactions of betaine with folate and other biomolecules. Betaine: Chemistry, Analysis, Function and Effects:62. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781782628446-00062
Erlinger S (2014) Bile acids in cholestasis: bad for the liver, not so good for the kidney. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 38:392–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2014.03.003
Erman F, Balkan J, Çevikbaş U, Koçak-Toker N, Uysal M (2004) Betaine or taurine administration prevents fibrosis and lipid peroxidation induced by rat liver by ethanol plus carbon tetrachloride intoxication. Amino Acids 27:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-004-0105-5
Fan C-Y, Wang M-X, Ge C-X, Wang X, Li J-M, Kong L-D (2014) Betaine supplementation protects against high-fructose-induced renal injury in rats. J Nutr Biochem 25:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.11.010
Fang J et al (2019) Polydatin protects against acute cholestatic liver injury in mice via the inhibition of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. 55:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.02.029
Fernández-Vizarra E, Ferrín G, Pérez-Martos A, Fernández-Silva P, Zeviani M, Enríquez JA (2010) Isolation of mitochondria for biogenetical studies: An update. Mitochondrion 10:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2009.12.148
Fickert P et al (2013) Bile acids trigger cholemic nephropathy in common bile-duct-ligated mice. Hepatology 58:2056–2069. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26599
Forton DM et al (2004) Fatigue and primary biliary cirrhosis: association of globus pallidus magnetisation transfer ratio measurements with fatigue severity and blood manganese levels. Gut 53:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2003.016766
Go EK, Jung KJ, Kim JY, Yu BP, Chung HY (2005) Betaine suppresses proinflammatory signaling during aging: the involvement of nuclear factor-κB via nuclear factor-inducing kinase/IκB kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:1252–1264. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/60.10.1252
Gossard AA, Talwalkar JA (2014) Cholestatic liver disease. Med Clin N Am 98:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2013.09.002
Graf D, Kurz AK, Reinehr R, Fischer R, Kircheis G, Häussinger D (2002) Prevention of bile acid–induced apoptosis by betaine in rat liver. Hepatology 36:829–839. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2002.35536
Grattagliano I, Oliveira PJ, Vergani L, Portincasa P (2017) Oxidative and nitrosative stress in chronic cholestasis. In: Liver Pathophysiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804274-8.00017-5
Gujral JS, Farhood A, Bajt ML, Jaeschke H (2003) Neutrophils aggravate acute liver injury during obstructive cholestasis in bile duct–ligated mice. Hepatology 38:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2003.50341
Gupta R, Dubey DK, Kannan GM, Flora SJS (2007) Concomitant administration of Moringa oleifera seed powder in the remediation of arsenic-induced oxidative stress in mouse. Cell Biol Int 31:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellbi.2006.09.007
Hagar H, Al Malki W (2014) Betaine supplementation protects against renal injury induced by cadmium intoxication in rats: role of oxidative stress and caspase-3. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:803–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.013
Hagar H, El Medany A, Salam R, El Medany G, Nayal OA (2015) Betaine supplementation mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative/nitrosative stress and suppression of inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 67:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2014.11.001
Hamdy N, El-Demerdash E (2012) New therapeutic aspect for carvedilol: Antifibrotic effects of carvedilol in chronic carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.04.012
Heidari R et al (2018e) Betaine treatment protects liver through regulating mitochondrial function and counteracting oxidative stress in acute and chronic animal models of hepatic injury. Biomed Pharmacother 103:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.010
Heidari R (2019) The footprints of mitochondrial impairment and cellular energy crisis in the pathogenesis of xenobiotics-induced nephrotoxicity, serum electrolytes imbalance, and Fanconi’s syndrome: A comprehensive review. Toxicology 423:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2019.05.002
Heidari R et al (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis-associated cholemic nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacother 109:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.104
Heidari R, Niknahad H (2019) The role and study of mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress in cholestasis. In: Vinken M (ed) Experimental Cholestasis Research. Methods in Molecular Biology. Springer New York, New York, pp 117–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9420-5_8
Heidari R, Moezi L, Asadi B, Ommati MM, Azarpira N (2017) Hepatoprotective effect of boldine in a bile duct ligated rat model of cholestasis/cirrhosis. PharmaNutrition 5:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2017.07.001
Heidari R, Ahmadi A, Mohammadi H, Ommati MM, Azarpira N, Niknahad H (2018a) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are involved in the mechanism of methotrexate-induced renal injury and electrolytes imbalance. Biomed Pharmacother 107:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.050
Heidari R, Ghanbarinejad V, Mohammadi H, Ahmadi A, Esfandiari A, Azarpira N, Niknahad H (2018b) Dithiothreitol supplementation mitigates hepatic and renal injury in bile duct ligated mice: Potential application in the treatment of cholestasis-associated complications. Biomed Pharmacother 99:1022–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.018
Heidari R, Ghanbarinejad V, Ommati MM, Jamshidzadeh A, Niknahad H (2018c) Mitochondria protecting amino acids: Application against a wide range of mitochondria-linked complications. PharmaNutrition 6:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2018.09.001
Heidari R, Jafari F, Khodaei F, Shirazi Yeganeh B, Niknahad H (2018d) Mechanism of valproic acid-induced Fanconi syndrome involves mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidney. Nephrology 23:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.13012
Holt S, Marley R, Fernando B, Harry D, Anand R, Goodier D, Moore K (1999) Acute cholestasis-induced renal failure: effects of antioxidants and ligands for the thromboxane A2 receptor. Kidney Int 55:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00252.x
Hossain MA, Piyatida P, da Silva JAT, Fujita M (2012) Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: Central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. Journal of Botany. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/872875
Ishida T, Kotani H, Miyao M, Kawai C, Jemail L, Abiru H, Tamaki K (2016) Renal impairment with sublethal tubular cell injury in a chronic liver disease mouse model. PloS One 11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146871
Ji C, Kaplowitz N (2003) Betaine decreases hyperhomocysteinemia, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and liver injury in alcohol-fed mice. Gastroenterology 124:1488–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00276-2
Katalinic V, Modun D, Music I, Boban M (2005) Gender differences in antioxidant capacity of rat tissues determined by 2,2’-azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonate; ABTS) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assays. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol: CBP 140:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.01.005
Krones E et al (2017) NorUrsodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cholemic nephropathy in bile duct ligated mice. J Hepatol 67:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.019
Krones E, Wagner M, Eller K, Rosenkranz AR, Trauner M, Fickert P (2015) Bile acid-induced cholemic nephropathy. Dig Dis 33:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371689
Krones E, Pollheimer MJ, Rosenkranz AR, Fickert P (2018) Cholemic nephropathy–historical notes and novel perspectives. . Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1864:1356–1366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.028
Krones E, Pollheimer MJ, Rosenkranz AR, Fickert P (2018) Cholemic nephropathy–historical notes and novel perspectives. . Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1864:1356–1366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.028
Lee I (2015) Betaine is a positive regulator of mitochondrial respiration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 456:621–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.005
Mandorfer M, Hecking M (2019) The Renaissance of cholemic nephropathy: A likely underestimated cause of renal dysfunction in liver disease. Hepatology 69:1858–1860. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30558
Martínez-Cecilia D et al (2016) Oxidative stress influence on renal dysfunction in patients with obstructive jaundice: A case and control prospective study. Redox Biol 8:160–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.12.009
Meeks RG, Harrison S (1991) Hepatotoxicology. CRC Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840160532
Ommati MM et al (2019) Carnosine and histidine supplementation blunt lead-induced reproductive toxicity through antioxidative and mitochondria-dependent mechanisms. Biol Trace Elem Res 187:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1358-2
Ommati MM et al (2020) Betaine supplementation mitigates intestinal damage and decreases serum bacterial endotoxin in cirrhotic rats. PharmaNutrition 12:100179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2020.100179
Orellana M, Rodrigo R, Thielemann L, Guajardo V (2000) Bile duct ligation and oxidative stress in the rat: effects in liver and kidney. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 126:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0742-8413(00)00102-X
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 12:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0756-2
Panozzo MP, Basso D, Balint L, Zaninotto M, Bonvicini P, Plebani M (1995) Renal functional alterations in extrahepatic cholestasis: Can oxidative stress be involved? Eur Surg Res 27:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1159/000129417
Patil A, Mayo MJ (2008) Complications of cholestasis. In: Md KDL, Md JAT (eds) Cholestatic Liver Disease. Clinical Gastroenterology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 155–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-118-5_9
Preedy V (2015) Betaine: Chemistry, analysis, function and effects. Royal Society of Chemistry, London
Rasheed R, Ashraf MA, Hussain I, Haider MZ, Kanwal U, Iqbal M (2014) Exogenous proline and glycinebetaine mitigate cadmium stress in two genetically different spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Braz J Bot 37:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-014-0089-7
Rodríguez-Garay EA (2003) Cholestasis: human disease and experimental animal models. Ann Hepatol 2:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-2681(19)32126-X
Ross AB, Zangger A, Guiraud SP (2014) Cereal foods are the major source of betaine in the Western diet–analysis of betaine and free choline in cereal foods and updated assessments of betaine intake. Food Chem 145:859–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.122
Sheen J-M, Huang L-T, Hsieh C-S, Chen C-C, Wang J-Y, Tain Y-L (2010) Bile duct ligation in developing rats: temporal progression of liver, kidney, and brain damage. J Pediatr Surg 45:1650–1658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.12.019
Sidransky H, Farber E (1960) Liver choline oxidase activity in man and in several species of animals. Arch Biochem Biophys 87:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(60)90133-8
Smid V et al (2016) Changes in liver ganglioside metabolism in obstructive cholestasis-the role of oxidative stress. Folia Biol 62:148
Socci DJ, Bjugstad KB, Jones HC, Pattisapu JV, Arendash GW (1999) Evidence that oxidative stress is associated with the pathophysiology of inherited hydrocephalus in the H-Tx rat model. Exp Neurol 155:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1998.6969
Tag CG, Sauer-Lehnen S, Weiskirchen S, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Tolba RH, Tacke F, Weiskirchen R (2015) Bile duct ligation in mice: induction of inflammatory liver injury and fibrosis by obstructive cholestasis. J Visualized Exp: JoVE. https://doi.org/10.3791/52438
Tag CG, Weiskirchen S, Hittatiya K, Tacke F, Tolba RH, Weiskirchen R (2015b) Induction of experimental obstructive cholestasis in mice. Lab Anim 49:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677214567748
Truong DH, Eghbal MA, Hindmarsh W, Roth SH, O’Brien PJ (2006) Molecular mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 38:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602530600959607
Woolbright BL, Jaeschke H (2012) Novel insight into mechanisms of cholestatic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 18:4985–4993. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.4985
Wright G et al (2007) Endotoxemia produces coma and brain swelling in bile duct ligated rats. Hepatology 45:1517–1526. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21599
Yi E-Y, Kim Y-J (2012) Betaine inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through suppression of the NF-κB and Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 41:1879–1885. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1616
Zeisel SH, Mar M-H, Howe JC, Holden JM (2003) Concentrations of choline-containing compounds and betaine in common foods. J Nutr 133:1302–1307. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.5.1302
Zhou Y, Kempson SA, Danbolt NC (2015) CHAPTER 6: Betaine Uptake with a Focus on the Betaine/GABA Transporter. In: Betaine. pp 76–89. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781782628446-00076
Acknowledgements
This investigation was financially supported by the Vice-Chancellor of Research Affairs of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (Grant No.: 98-01-36-19445), Shiraz, Iran, by the last author (Dr. Reza Heidari); and Shanxi Agricultural University (SXAU, Grant No.: 2018YJ33 (National Natural Science Foundation) and K271999031 (Outstanding Doctors Volunteering to Work in Shanxi Province), Shanxi, China, by the first author (Dr. Mohammad Mehdi Ommati). Authors thank the Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Center (PSRC) of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences and Life Sciences Department of SXAU for providing technical facilities to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None to be declared.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ommati, M.M., Farshad, O., Azarpira, N. et al. Betaine alleviates cholestasis-associated renal injury by mitigating oxidative stress and enhancing mitochondrial function. Biologia 76, 351–365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00576-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00576-x