Abstract
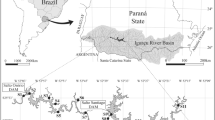
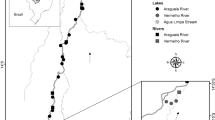
Environmental heterogeneity and productivity are factors driving beta diversity of freshwater communities. Further, characteristics as spatial extent and connectivity, as well as land use and cover, can determine local biodiversity patterns. We evaluated the correlates of within-lake beta diversity of phytoplankton communities in 25 coastal shallow lakes in southern Brazil. We hypothesize that within-lake beta diversity is positively related to environmental heterogeneity, productivity, spatial extent and connectivity. We also searched for correlates between beta diversity and land cover, once the studied lakes are mostly surrounded by natural landscapes. We measured beta diversity using four dissimilarity coefficients that provide a gradient of emphasis on compositional and abundance changes. We found that beta diversity differed among lakes, indicating changes in both species’ composition and abundance, but how it correlated with predictors differed depending on how beta diversity was measured. Beta diversity based on changes in species incidence and in two measures of abundance (modified Gower based on log10 and log2) was positively related to percentage of wetland cover and negatively related to percentage of grassland. Further, environmental heterogeneity was related to abundance-based (modified Gower log2) beta diversity. Our hypotheses were partly corroborated, indicating that factors modulating beta diversity patterns are complex and not easy to detect. We show that phytoplankton beta diversity in shallow coastal lakes is promoted by factors acting at both local and landscape scales. Finally, we emphasize that investigating beta diversity patterns should thoughtfully consider the use of dissimilarity coefficients measuring both changes in species composition and abundance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaensen F, Chardon JP, De Blust G, Swinen E, Villalba S, Gulinck H, Matthysen E (2003) The application of ‘lest-cost’ modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc Urban Plan 64:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2046(02)00242-6
Akasaka M, Takamura N (2012) Hydrologic connection between ponds positively affects macrophyte α and γ diversity but negatively affects β diversity. Ecology 93:967–973. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0879.1
Almeida-Gomes M, Valente-Neto F, Pacheco EO, Ganci CC, Leibold MA, Melo AS, Provete DB (2020) How does the landscape affect metacommunity structure? A quantitative review for lentic environments. Curr Landsc Ecol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40823-020-00049-6
Alvares CA, Stape JL, Sentelhas PC, Gonçalves JLM, Sparovek G (2014) Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol Z 22:711–728. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0507
Alves-de-Souza C, Benevides T, Santos JBO, Dassow PV, Guillou L, Menezes M (2017) Does environmental heterogeneity explain temporal β diversity of small eukaryotic phytoplankton? Example from a tropical eutrophic coastal lagoon. J Plankton Res 39:698714. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbx026
American Public Health Association (2012) Standard methods for examination of water and waste water, 22nd edn. Byrd Prepress, Springfield
Anderson MJ (2006) Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 62:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-0420.2005.00440.x
Anderson MJ, Ellingsen KE, McArdle BH (2006) Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol Lett 9:683–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00926.x
Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF, Harrison SP, Kraft NJB, Stegen JC, Swenson NG (2011) Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol Lett 14:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01552.x
Astorga A, Death R, Death F, Paavola R, Chakraborty M, Muotka T (2014) Habitat heterogeneity drives the geographical distribution of beta diversity: the case of New Zealand stream invertebrates. Ecol Evol 4:2693–2702. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1124
Bini LM, Landeiro VL, Padial AA, Siqueira T, Heino J (2014) Nutrient enrichment is related to two facets of beta diversity for stream invertebrates across the United States. Ecology 95:1569–1578. https://doi.org/10.1890/13-0656.1
Bohnenberger JE, Schneck F, Crossetti LO, Lima MS, Motta-Marques D (2018) Taxonomic and functional nestedness patterns of phytoplankton communities among coastal shallow lakes in southern Brazil. J Plankton Res 40:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fby032
Cardoso LS, Motta-Marques DM (2009) Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake. Aquat Ecol 43:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-007-9151-x
Carrizo SF, Jähnig SC, Bremerich V, Freyhof J, Harrison I, He F, Langhans SD, Tockner K, Zarfl C, Darwall W (2017) Freshwater megafauna: flagships for freshwater biodiversity under threat. Bioscience 67:919–927. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/bix099
Ceschin F, Bini LM, Padial AA (2018) Correlates of fish and aquatic macrophyte beta diversity in the Upper Paraná River floodplain. Hydrobiologia 805:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3325-x
Chase JM (2007) Drought mediates the importance of stochastic community assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:17430–17434. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704350104
Chase JM (2010) Stochastic community assembly causes higher biodiversity in more productive environments. Science 328:1388–1391. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1187820
Cook SC, Housley L, Back JA, King RS (2018) Freshwater eutrophication drives sharp reductions in temporal beta diversity. Ecology 99:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2069
Crawley MJ (2007) The R book. Wiley, London
Crossetti LO, Bicudo DC, Bicudo CEM, Bini LM (2008) Phytoplankton biodiversity changes in a shallow tropical reservoir during the hypertrophication process. Braz J Biol 6:1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842008000500013
Dudgeon D, Arthngton AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévequê C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81:163–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1464793105006950
ESRI (2010) ArcGIS desktop: release 10. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands
Finlay BJ (2002) Global dispersal of free-living microbial eukaryote species. Science 296:1061–1063. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1070710
Fox J, Weisberg S (2011) An R companion to applied regression, 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Guimarães TFR (2013) Influência de variáveis de paisagem sobre a riqueza e composição de assembléias de peixes em lagoas costeiras no Sul do Brasil. Dissertação, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul
Guimarães TFR, Hartz SM, Becker FG (2014) Lake connectivity and fish species richness in southern Brazilian coastal lakes. Hydrobiologia 740:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1954-x
Heino J, Melo AS, Bini LM (2015a) Reconceptualising the beta diversity-environmental heterogeneity relationship in running water systems. Freshw Biol 60:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12502
Heino J, Melo AS, Siqueira T, Soininen J, Valanko S, Bini LM (2015b) Metacommunity organization, spatial extent and dispersal in aquatic systems: patterns, processes and prospects. Freshw Biol 60:845–869. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12533
Heino J, Bini LM, Andersson J, Bergsten J, Bjelke U, Johansson F (2017) Unravelling the correlates of species richness and ecological uniqueness in a metacommunity of urban pond insects. Ecol Indic 73:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.006
Hillebrand H, Dürselen D, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520403.x
Jackson DA (1993) Stopping rules in principal component analysis: a comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology 74:2204–2214. https://doi.org/10.2307/1939574
Jespersen AM, Christoffersen K (1987) Measurements of chlorophyll a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Arch Hydrobiol 109:445–454
Johnson RK, Angeler DG (2014) Effects of agricultural land use on stream assemblages: taxon specific responses of alpha and beta diversity. Ecol Indic 45(386):393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.04.028
Laurance WF, Sayer J, Cassman KG (2014) Agricultural expansion and its impacts on tropical nature. Trends Ecol Evol 29:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2013.12.001
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Law R, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol Lett 7:601–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00608.x
Loitzenbauer E, Mendes CAB (2012) Salinity dynamics as a tool for water resources management in coastal zones: an application in the Tramandaí River basin, southern Brazil. Ocean Coast Manag 55:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2011.10.011
Lopes PM, Bini LM, Declerck SAJ, Farjalla VF, Vieira LCG, Bonecker CC, Lansac-Toha FA, Esteves FA, Bozelli RL (2014) Correlates of zooplankton beta diversity in tropical lake systems. PLoS ONE 9:e109581. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109581
Lopes VG, Branco CWC, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B, Bini LM (2019) Zooplankton temporal beta diversity along the longitudinal axis of a tropical reservoir. Limnology 20(121):130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-018-0558-y
Lougheed VL, Mcintosh MD, Parker CA, Stevenson RJ (2008) Wetland degradation leads to homogenization of the biota at local and landscape scales. Freshw Biol 53:2402–2413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02064.x
Lund JWG, Kipling C, LeCren ED (1958) The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimations by counting. Hydrobiologia 11:143–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007865
Martiny BH, Eisen JA, Penn K, Allison SD, Horner-Devine MC (2011) Drivers of bacterial b-diversity depend on spatial scale. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:78507854. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1016308108
Mikulyuk A, Sharma S, Egeren SJV, Erdmann ES, Nault ME, Hauxwell J (2011) The relative role of environmental, spatial, and land-use patterns in explaining aquatic macrophyte community composition. Can J of Fish Aquat Sci 68:1778–1789. https://doi.org/10.1139/f2011-095
Mori AS, Isbell F, Seidl R (2018) β-Diversity, community assembly and ecosystem functioning. Trends Ecol Evol 33:549–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2018.04.012
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.027
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P,Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2018) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.5-1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.com
Padial AA, Ceschin F, Declerck SAJ, De Meester L, Bonecker CC, Lansac-Tôha FA, Rodrigues L, Rodrigues LC, Train S, Velho LFM, Bini LM (2014) Dispersal ability determines the role of environmental, spatial and temporal drivers of metacommunity structure. PLoS ONE 9:e111227. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111227
Pineda A, Iatskiu P, Jati S, Paula ACM, Zanco BF, Bonecker CC, Moresco GA, Ortega LA, Souza YR, Rodrigues LC (2020) Damming reduced the functional richness and caused the shift to a new functional state of the phytoplankton in a subtropical region. Hydrobiologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04311-0
Pinese OP, Pinese JF, Claro KD (2015) Structure and biodiversity of zooplankton communities in freshwater habitats of a Vereda Wetland Region, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Acta Limnol Bras 27:275–288. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X0415
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Reid AJ, Carlson AK, Creed IF, Eliason EJ, Gell PA, Johnson PT, Kidd KA, MacCormack TJ, Olden JD, Ormerod SJ, Smol JP, Taylor WW, Tockner K, Vermaire JC, Dudgeon D, Cooke SJ (2019) Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol Rev 94:849–873. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12480
Reynolds CS (2006) Ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Reynolds CS, Dokulil M, Padisák J (2000) Understanding the assembly of phytoplankton in relation to the trophic spectrum: where are we now? Hydrobiologia 424:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3488-2_14
Schäfer A, Lanzer R, Scur L (2017) Atlas socioambiental do município de Osório. Editora da Universidade de Caxias do Sul, Caxias do Sul
Schneck F, Schwarzbold A, Rodrigues SC, Melo AS (2011) Environmental variability drives phytoplankton assemblage persistence in a subtropical reservoir. Aust Ecol 36:839–848. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.2010.02224.x
Schwarzbold A, Schäfer A (1984) Gênese e morfologia das lagoas costeiras do Rio Grande do Sul—Brasil. Amazoniana 9:87–104
Shurin JB, Cottenie K, Hillebrand H (2009) Spatial autocorrelation and dispersal limitation in freshwater organisms. Oecologia 159:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1174-z
Siqueira T, Lacerda CG, Saito VS (2015) How does landscape modification induce biological homogenization in tropical stream communities? Biotropica 47:509–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12224
Soininen J, Bartels P, Heino J, Luoto M, Hillebrand H (2015) Toward more integrated ecosystem research in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Bioscience 65:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biu216
Tomazelli LJ, Willwock JA (1991) Geologia do Sistema lagunar holocênico do litoral norte do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Pesquisas em Geociências 18:13–24. https://doi.org/10.22456/1807-9806.21358
Utermöhl H (1958) Zurvervolkomnung der quantitative Phytoplankton-methodik. MitteilungInternationale Vereinigungfür Theoretische und Angewandte. Limnologie 9:1–38
Van den Hoek C, Mann DG, Jahns HM (1995) Alage: an introduction to phycology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou montains, Oregon and California. Ecol Monogr 30:279–338
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Winegardner AK, Legendre P, Beisner BE, Gregory-Eaves I (2017) Diatom diversity patterns over the past c. 150 years across the conterminous United Stated of America: identifying mechanisms behind beta diversity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 26:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12640
Zorzal-Almeida S, Bini LM, Bicudo DC (2017) Beta diversity of diatoms is driven by environmental heterogeneity, spatial extent and productivity. Hydrobiologia 800:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3117-3
Zorzal-Almeida S, Salim A, Andrade MRM, Nascimento MN, Bini LM, Bicudo DC (2018) Effects of land use and spatial processes in water and surface sediment of tropical reservoir at local and regional scales. Sci Total Environ 644:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.361
Zuur A, Ieno EN, Walker N, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the technicians of the Instituto de Pesquisas Hidráulicas and Centro de Estudos Costeiros, Limnológicos e Marinhos (UFRGS) for their support with sampling and laboratory analyses. We also thank the two anonymous reviewers which suggestions greatly improved the manuscript. This study was partially funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, process No. 474279/2013-8). APTC and JEB were supported by student fellowships by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. MSL and JEB were supported by student fellowships by CNPq (Nos. 141228/2012-1 and 142139/2015-7, respectively). SMH is supported by research grants from CNPq (No. 305549/2018-9). LUH is supported by research grants from CNPq (Nos. 421632/2016-0 and 305203/2017-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Télesphore Sime-Ngando.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, A.P.T., Crossetti, L.O., Hartz, S.M. et al. Land cover is the main correlate of phytoplankton beta diversity in subtropical coastal shallow lakes. Aquat Ecol 54, 1015–1028 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-020-09790-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-020-09790-w