Abstract
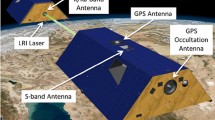
The gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on (GRACE-FO) satellites, launched in May of 2018, are equipped with geodetic quality GPS receivers for precise orbit determination (POD) and gravity recovery. The primary objective of the GRACE-FO mission is to map the time-variable and mean gravity field of the Earth. To achieve this goal, both GRACE-FO satellites are additionally equipped with a K-band ranging (KBR) system, accelerometers and star trackers. Data processing strategies, data weighting approaches and impacts of observation types and rates are investigated in order to determine the most efficient approach for processing GRACE-FO multi-type data for precise orbit determination and gravity recovery. Two GPS observation types, un-differenced (UD) and double-differenced (DD) observations in general can be used for GPS-based POD and gravity recovery. The GRACE-FO KBR observations are mainly used for gravity recovery, but they can be also used for POD to improve the relative orbit accuracy. The main purpose of this paper is to study the impacts of the DD, UD and KBR observations on GRACE-FO POD and gravity recovery. The precise orbit accuracy is assessed using several tests, which include analysis of orbital fits, satellite laser ranging residuals, KBR range residuals and orbit comparisons. The gravity recovery is validated by comparing different gravity solutions through coefficient-wise comparison, degree difference variances and water height variations over the whole Earth and selected area and river basins.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The synthetic datasets generated and analyzed during the study are available on request from the corresponding author. The GNSS datasets used for this study are available at https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive. The GRACE-FO data can be found at https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/GRACE_L1B_GRAV_JPL_RL02.
References
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Métivier L, Collilieux X (2016) ITRF2014: a new release of the international reference frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J. Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013098
Barlier F, Berger C, Falin J, Kockarts G, Thuillier G (1978) Atmospheric model based on satellite drag data. Ann Geophys 34:9–24
Bertiger W, Bar-Server Y, Christensen E, Davis J, Haines B, Ibanez-meier R, Jee J, Lichten S, Melbourne W, Muellerschon R, Munson T, Vihue Y, Wu S, Yunck T, Schutz B, Abusali P, Rim H, Watwins W, Wills P (1994) GPS precise tracking of TOPEX/Poseidon: results and implications. J Geophys Res Oceans TOPEX/Poseidon Special Issue 99C12: 24449-24464
Bertiger W, Bar-Sever Y, Bettadpur B, Desai S, Dunn C, Haines B, Kruizinga G, Kuna D, Nandi S, Romans L, Watkins M, Wu S (2002) GRACE millimeters and microns in orbit. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 2002, Portland OR, USA
Bertiger W, Desai S, Dorsey A, Haines B, Harvey N, Kuang D, Sibthorpe A, Weiss J (2010) Sub-centimeter precision orbit determination with GPS for ocean altimetry. Mar Geodesy 33(S1):363–378
Bettadpur S (2012) GRACE product specification documents, CSR-GR-03-02, v4.6. Center for Space Research, the University Texas at Austin
Bettadpur S, McCullough C (2017) The classical variational approach. In: Naeimi M, Flury J (eds) Global gravity field modelling from satellite-to-satellite tracking data. Lecture notes in Earth system science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49941-3_3
Boomkamp H, Koenig R (2005) Bigger, better, faster POD. I:, 2004 Berne workshop & symposium. Astronomical Institute, University of Bern
Capitaine N, Gambis D, McCarthy D, Petit G, Ray J, Richter B, Rothacher M, Standish M, Vondrak J (eds.) (2002) IERS Technical Note 29 Proceedings of the IERS workshop on the implementation of the new IAU resolutions 2002. Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodasie, Frankfurt am Main
Chambers D, Bonin J (2012) Evaluation of release-05 GRACE time-variable gravity coefficients over the ocean. Ocean Sci 8(5):859–868
Debslaw H, Bergmann-Wolf I, Dill R, Poroput L, Flechtner F (2017) AOD1B product description document. GRACE 327–750. https://podaac-tools.jpl.nasa.gov/drive/files/allData/gracefo/docs/AOD1B_PDD_RL06_v6.1.pdf
Flechtner F, Morton P, Wattkins M, Webb F (2015) Status of the GRACE following-on mission. In: Proceedings of the international association of geodesy symposia gravity, geoid and height system (2012, Vemice, Italy), IAGS-D-12-00141
Gambis D (2004) Monitoring earth orientation using space-geodetic techniques: state-of-the-art and prospective. J Geod 78:295–303
Gunter B (2004) Computational methods and processing strategies for estimating Earth’s gravity field. Dissertation, Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, The University of Texas at Austin
Jaeggi A, Huggentobler U, Bock H, Beutler G (2007) Precise orbit determination for GRACE using undifferenced or double differenced GPS data. Adv Space Res 39:1612–1619
Kang Z (1998) Praezise Bahnbestimmung niedrigfliegender Satelliten mittels GPS und die Nutzung fuer die globale Scwerefeldmodellierung. Thesis, Scientific Technical Report; 98/25
Kang Z, Schwintzer P, Reigber Ch, Zhu SY (1995) Precise orbit determination for TOPEX/POSEIDON using GPS-SST data. Adv Sp Res 16(12):59
Kang Z, Tapley B, Bettadpur S, Rim H, Nagel P (2002) Precise orbit determination for CHAMP using accelerometer data. Adv Astronaut Sci 112:1405–1410
Kang Z, Tapley B, Bettadpur S, Ries J, Nagel P, Pastor R (2006) Precise orbit determination for the GRACE mission using only GPS data. J Geod 80:322–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-006-0073-5
Knocke P, Ries J, Tapley B (1988) Earth radiation pressure effects on satellites. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS astrodynamics coference, Am. Inst. Aeron. Astronaut, Washington, D. C, pp 577–587
Kornfeld R, Arnold B, Gross M, Dahys N, Klipstein W, Gath P, Bettadpur S (2019) GRACE-FO: the gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on mission. J Spacecr Rockets 56(3):931–951
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using International GNSS Service (IGS) products. https://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf
Landerer F, Flechtner F, Webb F, Watkins M, Save H, Bettadpur S, Gaston R (2019) GRACE following-on: mission status and first mass change observations. IUGG July 8–18, 2019, Montreal Canada
Mao X, Visser P, Van den IJssel J (2019) Absolute and relative orbit determination for the CHAMP/GRACE constellation. Adv Sp Res 63:3796–3816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.02.030
Mathews PM, Herring TA, Buffet B (2002) Modeling of nutation-precession: new nutation series for nonrigid Earth, and insights into the Earth’s interior. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001jb000390
McCullough C, Harvey N, Save H (2019) Description of calibrated GRACE-FO accelerometer data products. JPL D-103863. https://podaac-tools.jpl.nasa.gov/drive/files/allData/gracefo/docs/GFO.ACT.JPL-D-103863.20190520.pdf
Meyer U, Jaeggi A, Jean Y, Beutler G (2016) AIUB-RL02: an improved time series of monthly gravity fields from GRACE data. Geophys J Int 205:1196–1207
Petit G, Luzum B (2010) IERS conventions 2010. IERS Technical Note No. 36
Ray R (1999) A global ocean tide model from TOPEX/POSEIDON altimetry: GOT99.2, Rep. NASA/TM-1999-209478, 58 pp. Goddard Space Flight Cent., Greenbelt, Md
Reigber C (1989) Theory of satellite geodesy and gravity field determination. Lecture notes in earth sciences, vol 25. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0010546
Ries J, Bettadpur S, Eanes R, Kang Z, Ko U, McCullough C, Nagel P, Pie N, Poole S, Richter T, Save H, Tapley B (2016) Development and evaluation of the global gravity model GGM05, CSR-16-02. The University of Texas at Austin
Rim H (1992) TOPEX orbit determination using GPS Tracking system. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, The University of Texas at Austin
Save H (2019), GRACE-FO CSR Level-2 processing standards document, CSR GRFO-19-01
Standish EM (1998) JPL planetary and lunar ephemerides DE405/LE405, JPL IOM 312.F-98-048
Švehla D, Rothacher M (2005) Kinematic positioning of LEO and GPS satellites and IGS stations on the ground. Adv Sp Res 36:376–381
Tapley B, Shutz B, Born G (2004) Statistical orbit determination. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Tapley B, Ries J, Bettapur S, Chambers D, Cheng M, Condi F, Guenter B, Kang Z, Nagel P, Pastor R, Pekker T, Poole S, Wang F (2005) GGM02—an improved Earth gravity field model from GRACE. J Geod 79:467–478
Yuan D (1991) The determination and error assessment of the Earth’s gravity field model, Report CSR-91-01. Center for Space Research, the University of Texas at Austin
Zhu S, Reigber C, Koenig R (2004) Integrated adjustment of CHAMP, GRACE and GPS data. JoG 78(1-2):103–108
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the International Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Service (IGS) for providing the GPS ground station data and GPS satellite orbit products and the International Laser Range Service (ILRS) for the SLR data. High performance computing resources were provided by the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at the University of Texas at Austin. This research was supported by JPL contract 1604489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZK and SB designed the research. The software modification for this study was performed by ZK with support from PN. ZK made the precise orbit determination and gravity recovery using GPS UD and KBR data; PN made them using GPS DD and KBR data. ZK wrote the manuscript with corrections and comments from SB, PN and SP. All authors were involved in result discussions throughout the development.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Z., Bettadpur, S., Nagel, P. et al. GRACE-FO precise orbit determination and gravity recovery. J Geod 94, 85 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01414-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01414-3