Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative condition characterized by motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, resting tremor, and rigidity. PD diagnosis is based on medical history, review of signs, symptoms, neurological and physical examinations. Unfortunately, by the time the disease is diagnosed, dopamine (DA) neuronal loss is often extended, thereby resulting in ineffective therapies. Recent evidence suggests that neuroinflammation may be pivotal during PD onset and progression. However, suitable cellular models and biomarkers to detect early signs of neuroinflammation are still missing. In this study, we developed a well-differentiated DAergic neuronal cell line where we triggered a neuroinflammatory response to assess the temporal expression of the tissue- and urokinase plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA) and their endogenous inhibitor (PAI-1) along with that of pro-inflammatory mediators and the neuronal marker nNOS. Human neuroblastoma cells SH-SY5Y were differentiated into DAergic neuronal-like cells using a combination of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and serum depletion. Terminally-differentiated neurons were then exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for short (up to 24 h) or long term (up to 10 days) to mimic acute or chronic inflammation. Results demonstrated that uPA protein expression was stably upregulated during chronic inflammation, whereas the expression of nNOS protein better reflected the cellular response to acute inflammation. Additional studies revealed that the temporal induction of uPA was associated with increased AKT phosphorylation, but did not seem to involve cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) activation, nor the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. In conclusion, our in vitro data suggests that nNOS and uPA may serve as viable candidate biomarkers of acute and chronic neuroinflammation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen AD, Binzer M, Stenager E, Gramsbergen JB (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease–a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand 135:34–56
Aquilano K, Vigilanza P, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2006) Mitochondrial damage due to SOD1 deficiency in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: a rationale for the redundancy of SOD1. FASEB J 20:1683–1685
Avwenagha O, Campbell G, Bird MM (2003) Distribution of GAP-43, β-III tubulin and F-actin in developing and regenerating axons and their growth cones in vitro, following neurotrophin treatment. J Neurocytol 32:1077–1089
Baldelli S, Aquilano K, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2011) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase interacts with Sp1 through the PDZ domain inhibiting Sp1-mediated copper-zinc superoxide dismutase expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:163–169
Baranes D, Lederfein D, Huang Y-Y, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER (1998) Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the late phase of LTP and to synaptic growth in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway. Neuron. 21:813–825
Bennur S, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Pawlak R, Strickland S, McEwen BS, Chattarji S (2007) Stress-induced spine loss in the medial amygdala is mediated by tissue-plasminogen activator. Neuroscience. 144:8–16
Biosa A, De Lazzari F, Masato A, Filograna R, Plotegher N, Beltramini M, Bubacco L, Bisaglia M (2019) Superoxide dismutases SOD1 and SOD2 rescue the toxic effect of dopamine-derived products in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Neurotox Res 36:746–755
Brown D, Tamas A, Reglodi D, Tizabi Y (2014) PACAP protects against inflammatory-mediated toxicity in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells: implication for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 26:230–239
Brzozowski MJ, Alcantara SL, Iravani MM, Rose S, Jenner P (2011) The effect of nNOS inhibitors on toxin-induced cell death in dopaminergic cell lines depends on the extent of enzyme expression. Brain Res 1404:21–30
Bucolo C, Leggio GM, Maltese A, Castorina A, D’gata V, Drago F (2012) Dopamine-(3) receptor modulates intraocular pressure: implications for glaucoma. Biochem Pharmacol 83:680–686
Bugge TH, Flick MJ, Danton MJ, Daugherty CC, Romer J, Dano K, Carmeliet P, Collen D, Degen JL (1996) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is effective in fibrin clearance in the absence of its receptor or tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:5899–5904
Bukhari N, Torres L, Robinson JK, Tsirka SE (2011) Axonal regrowth after spinal cord injury via chondroitinase and the tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)/plasmin system. J Neurosci 31:14931–14943
Cai L, Tu L, Li T, Yang X, Ren Y, Gu R, Zhang Q, Yao H, Qu X, Wang Q, Tian J (2019) Downregulation of lncRNA UCA1 ameliorates the damage of dopaminergic neurons, reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease through the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 75:105734
Calabrese V, Santoro A, Monti D, Crupi R, Di Paola R, Latteri S, Cuzzocrea S, Zappia M, Giordano J, Calabrese EJ, Franceschi C (2018) Aging and Parkinson’s disease: inflammaging, neuroinflammation and biological remodeling as key factors in pathogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 115:80–91
Castorina A, Leggio GM, Giunta S, Magro G, Scapagnini G, Drago F, D'Agata V (2011) Neurofibromin and amyloid precursor protein expression in dopamine D3 receptor knock-out mice brains. Neurochem Res 36:426–434
Castorina A, D’Amico AG, Scuderi S, Leggio GM, Drago F, D'Agata V (2013) Dopamine D3 receptor deletion increases tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) activity in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 250:546–556
Castorina A, Waschek JA, Marzagalli R, Cardile V, Drago F (2015) PACAP interacts with PAC1 receptors to induce tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) expression and activity in Schwann cell-like cultures. PLoS One 10:e0117799
Castorina A, Vogiatzis M, Kang JWM, Keay KA (2019) PACAP and VIP expression in the periaqueductal grey of the rat following sciatic nerve constriction injury. Neuropeptides. 74:60–69
Chahine LM, Stern MB, Chen-Plotkin A (2014) Blood-based biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:S99–S103
Cheng Z, Teo G, Krueger S, Rock TM, Koh HW, Choi H, Vogel C (2016) Differential dynamics of the mammalian mRNA and protein expression response to misfolding stress. Mol Syst Biol 12:855
Costa M, Shen Y, Maurer F, Medcalf RL (1998) Transcriptional regulation of the tissue-type plasminogen-activator gene in human endothelial cells: identification of nuclear factors that recognise functional elements in the tissue-type plasminogen-activator gene promoter. Eur J Biochem 258:123–131
Cunningham O, Campion S, Perry VH, Murray C, Sidenius N, Docagne F, Cunningham C (2009) Microglia and the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor/uPA system in innate brain inflammation. Glia. 57:1802–1814
de Pedro-Cuesta J, Rábano A, Martínez-Martín P, Ruiz-Tovar M, Alcalde-Cabero E, Almazán-Isla J, Avellanal F, Calero M (2015) Comparative incidence of conformational, neurodegenerative disorders. PLoS One 10:e0137342
Feng P, Ohlsson M, Ny T (1990) The structure of the TATA-less rat tissue-type plasminogen activator gene. Species-specific sequence divergences in the promoter predict differences in regulation of gene expression. J Biol Chem 265:2022–2027
Filograna R, Civiero L, Ferrari V, Codolo G, Greggio E, Bubacco L, Beltramini M, Bisaglia M (2015) Analysis of the catecholaminergic phenotype in human SH-SY5Y and BE (2)-M17 neuroblastoma cell lines upon differentiation. PLoS One 10:e0136769
Forster JI, Koglsberger S, Trefois C, Boyd O, Baumuratov AS, Buck L, Balling R, Antony PM (2016) Characterization of differentiated SH-SY5Y as neuronal screening model reveals increased oxidative vulnerability. J Biomol Screen 21:496–509
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C (2003) PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene. 22:8983–8998
Gitler, A.D., Dhillon, P., Shorter, J., 2017. Neurodegenerative disease: models, mechanisms, and a new hope. Vol., eds. The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Giunta S, Castorina A, Adorno A, Mazzone V, Carnazza ML, D'Agata V (2010) PACAP and VIP affect NF1 expression in rat malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) cells. Neuropeptides. 44:45–51
González H, Pacheco R (2014) T-cell-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation involved in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroinflammation 11:201
Gur-Wahnon D, Mizrachi T, Maaravi-Pinto F-Y, Lourbopoulos A, Grigoriadis N, Brenner T (2013) The plasminogen activator system: involvement in central nervous system inflammation and a potential site for therapeutic intervention. J Neuroinflammation 10:891
Hong H, Kim BS, Im H-I (2016) Pathophysiological role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders. International Neurourology Journal 20:S2
Jin X, Yamashita T (2016) Microglia in central nervous system repair after injury. J Biochem 159:491–496
Justin A, Mandal S, Prabitha P, Dhivya S, Yuvaraj S, Kabadi P, Sekhar SJ, Sandhya CH, Wadhwani AD, Divakar S, Bharathi JJ, Durai P, Prashantha Kumar BR (2020) Rational design, synthesis, and in vitro neuroprotective evaluation of novel glitazones for PGC-1α activation via PPAR-γ: a new therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotox Res 37:508–524
Kavya R, Saluja R, Singh S, Dikshit M (2006) Nitric oxide synthase regulation and diversity: implications in Parkinson’s disease. Nitric Oxide 15:280–294
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2015) Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol 89:867–882
Kovalevich, J., Langford, D., 2013. Considerations for the use of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in neurobiology. In Neuronal cell culture. Vol., ed.^eds. Springer, pp. 9-21
Lawrimore CJ, Crews FT (2017) Ethanol, TLR3, and TLR4 agonists have unique innate immune responses in neuron-like SH-SY5Y and microglia-like BV2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 41:939–954
Lin YC, Uang HW, Lin RJ, Chen IJ, Lo YC (2007) Neuroprotective effects of glyceryl nonivamide against microglia-like cells and 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:877–887
Liu Y, Beyer A, Aebersold R (2016) On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell. 165:535–550
Lo YC, Liu Y, Lin YC, Shih YT, Liu CM, Burka LT (2008) Neuronal effects of 4-t-butylcatechol: a model for catechol-containing antioxidants. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 228:247–255
López-Carballo G, Moreno L, Masiá S, Pérez P, Barettino D (2002) Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by retinoic acid is required for neural differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 277:25297–25304
Ma X-H, Duan W-J, Mo Y-S, Chen J-L, Li S, Zhao W, Yang L, Mi S-Q, Mao X-L, Wang H (2018) Neuroprotective effect of paeoniflorin on okadaic acid-induced tau hyperphosphorylation via calpain/Akt/GSK-3β pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res 1690:1–11
Mehra A, Ali C, Parcq J, Vivien D, Docagne F (2016) The plasminogen activation system in neuroinflammation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease 1862:395–402
Melchor JP, Strickland S (2005) Tissue plasminogen activator in central nervous system physiology and pathology. Thromb Haemost 93:655–660
Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2015) Biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease: present and future. Metabolism. 64:S40–S46
Monaghan T, Mackenzie C, Plevin R, Lutz E (2008) PACAP-38 induces neuronal differentiation of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via cAMP-mediated activation of ERK and p38 MAP kinases 1. J Neurochem 104:74–88
Nakano N, Matsuda S, Ichimura M, Minami A, Ogino M, Murai T, Kitagishi Y (2017) PI3K/AKT signaling mediated by G protein coupled receptors is involved in neurodegenerative Parkinson’s disease (review). Int J Mol Med 39:253–260
Ohlsson M, Leonardsson G, Jia XC, Feng P, Ny T (1993) Transcriptional regulation of the rat tissue type plasminogen activator gene: localization of DNA elements and nuclear factors mediating constitutive and cyclic AMP-induced expression. Mol Cell Biol 13:266–275
Pang PT, Teng HK, Zaitsev E, Woo NT, Sakata K, Zhen S, Teng KK, Yung WH, Hempstead BL, Lu B (2004) Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science. 306:487–491
Pawlak R, Rao BS, Melchor JP, Chattarji S, McEwen B, Strickland S (2005) Tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen mediate stress-induced decline of neuronal and cognitive functions in the mouse hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18201–18206
Pineda D, Ampurdanes C, Medina MG, Serratosa J, Tusell JM, Saura J, Planas AM, Navarro P (2012) Tissue plasminogen activator induces microglial inflammation via a noncatalytic molecular mechanism involving activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and Akt signaling pathways and AnnexinA2 and Galectin-1 receptors. Glia. 60:526–540
Presgraves SP, Ahmed T, Borwege S, Joyce JN (2003) Terminally differentiated SH-SY5Y cells provide a model system for studying neuroprotective effects of dopamine agonists. Neurotox Res 5:579–598
Rogove AD, Siao C, Keyt B, Strickland S, Tsirka SE (1999) Activation of microglia reveals a non-proteolytic cytokine function for tissue plasminogen activator in the central nervous system. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 22):4007–4016
Rommelspacher, H., 2012. Prospects for new treatment options in neurodegenerative diseases. In Isoquinolines and beta-carbolines as neurotoxins and neuroprotectants. Vol., ed.^eds. Springer, pp. 165-171
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Siao C-J, Fernandez SR, Tsirka SE (2003) Cell type-specific roles for tissue plasminogen activator released by neurons or microglia after excitotoxic injury. J Neurosci 23:3234–3242
Son H, Seuk Kim J, Mogg Kim J, Lee SH, Lee YS (2002) Reciprocal actions of NCAM and tPA via a Ras-dependent MAPK activation in rat hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298:262–268
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF (2015) Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 35:600–604
Surmeier DJ, Obeso JA, Halliday GM (2017) Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:101–113
Szepesi Z, Manouchehrian O, Bachiller S, Deierborg T (2018) Bidirectional microglia-neuron communication in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 12:323
Titze-de-Almeida SS, Lustosa CF, Horst CH, Bel ED, Titze-de-Almeida R (2014) Interferon gamma potentiates the injury caused by MPP(+) on SH-SY5Y cells, which is attenuated by the nitric oxide synthases inhibition. Neurochem Res 39:2452–2464
Tjarnlund-Wolf A, Hultman K, Blomstrand F, Nilsson M, Medcalf RL, Jern C (2014) Species-specific regulation of t-PA and PAI-1 gene expression in human and rat astrocytes. Gene Regul Syst Bio 8:113–118
van Horssen J, van Schaik P, Witte M (2017) Inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction: a vicious circle in neurodegenerative disorders? Neurosci Lett
Wu Y, Le W, Jankovic J (2011) Preclinical biomarkers of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 68:22–30
Yan T, Sun Y, Gong G, Li Y, Fan K, Wu B, Bi K, Jia Y (2019) The neuroprotective effect of Schisandrol A on 6-OHDA-induced PD mice may be related to PI3K/AKT and IKK/IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB pathway. Exp Gerontol 128:110743
Zhang HA, Gao M, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Shi L-l, Chen B-n, Wang Y-h, Wang S-b, Du G-H (2012) Salvianolic acid a protects human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against H 2 O 2-induced injury by increasing stress tolerance ability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 421:479–483
Zhang X, Zhu LB, He JH, Zhang HQ, Ji SY, Zhang CN, Hou NN, Huang CP, Zhu JH (2020) Paroxetine suppresses reactive microglia-mediated but not lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in primary astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation 17:50
Acknowledgments
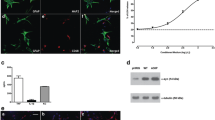
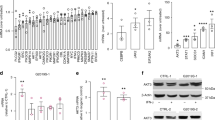
We would like to acknowledge A/Prof. Louise Cole and the UTS Microscopy Imaging Facility (MIF) for the support provided for the acquisition and processing of the immunofluorescent images shown in this study.
Funding
These experiments were supported by the University of Technology Sydney Start-up Research Fund 2018 to Dr. Castorina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niaz, A., Karunia, J., Mandwie, M. et al. Robust Dopaminergic Differentiation and Enhanced LPS-Induced Neuroinflammatory Response in Serum-Deprived Human SH-SY5Y Cells: Implication for Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 71, 565–582 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01678-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01678-6