Abstract
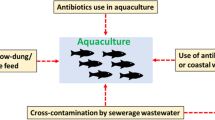
Viral disease outbreaks are the major concern in aquaculture sector, affecting the development of crustacean aquaculture. Since the emergence of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp farms, this caused huge economic loss and societal impact in aquaculture industry. Several strategies include controlled environmental conditions; vaccines and immunostimulants were proposed for disease management. However, there are no effective treatment methods available for viral infections in shrimp; the search for alternative approach is the need of the hour. Recently, natural products from medicinal plants, marine algae, and their derivatives gained importance in the control of disease conditions in shrimps. In this review, we focused on the importance and role of seaweed polysaccharides on the effective management of WSSV in aquaculture animals. In addition, the review emphasizes the mechanisms of anti-WSSV activity of seaweed polysaccharides and their potential therapeutic strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi A, Zorofchian Moghadamtousi S, Abubakar S, Zandi K (2015) Antiviral potential of algae polysaccharides isolated from marine sources: a review. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/825203
Bondad-Reantaso MG, Subasinghe RP, Josupeit H, Cai J, Zhou X (2012) The role of crustacean fisheries and aquaculture in global food security: past, present and future. J Invertebr Pathol 110:158–165
Chen YY, Kitikiew S, Yeh ST, Chen JC (2016) White shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei that have received fucoidan exhibit a defense against Vibrio alginolyticus and WSSV despite their recovery of immune parameters to background levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol 59:414–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.10.050
Dey BK, Dugassa GH, Hinzano SM, Bossier P (2019) Causative agent, diagnosis and management of white spot disease in shrimp: a review. Rev Aquac 12:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12352
Durand S, Lightner DV, Redman RM, Bonami JR (1997) Ultrastructure and morphogenesis of white spot syndrome baculovirus (WSSV). Dis Aquat Org 29:205–211. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao029205
Escobedo-Bonilla CM, Alday-Sanz V, Wille M, Sorgeloos P, Pensaert MB, Nauwynck HJ (2008) A review on the morphology, molecular characterization, morphogenesis and pathogenesis of white spot syndrome virus. J Fish Dis 31:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00877.x
FAO (2016) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2016: Contributing to food security and nutrition for all, FAO. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5555e.pdf. Accessed 10 Apr 2020
Govindaraju K, Prerna DI, Veeramani V, Ashok Kumar T, Tamilselvan S (2019) Application of nanotechnology in diagnosis and disease management of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in aquaculture. J Clust Sci 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01724-3
Haq BAB, Vignesh R, Srinivasan M (2012) Deep insight into white spot syndrome virus vaccines: a review. Asian Pacific J Trop Dis 2:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(12)60018-8
Huynh TG, Yeh ST, Lin YC, Shyu JF, Chen LL, Chen JC (2011) White shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei immersed in seawater containing Sargassum hemiphyllum var. chinense powder and its extract showed increased immunity and resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.05.014
Immanuel G, Sivagnanavelmurugan M, Balasubramanian V, Palavesam A (2010) Effect of hot water extracts of brown seaweeds Sargassum spp. on growth and resistance to white spot syndrome virus in shrimp Penaeus monodon postlarvae. Aquac Res 41:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02526.x
Immanuel G, Sivagnanavelmurugan M, Balasubramanian V, Palavesam A (2012a) Sodium alginate from Sargassum wightii retards mortalities in Penaeus monodon postlarvae challenged with white spot syndrome virus. Dis Aquat Org 99:187–196. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02466
Immanuel G, Sivagnanavelmurugan M, Marudhupandi T, Radhakrishnan S, Palavesam A (2012b) The effect of fucoidan from brown seaweed Sargassum wightii on WSSV resistance and immune activity in shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fab). Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:551–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.01.003
Klongklaew N, Praiboon J, Tamtin M, Srisapoome P (2020) Antibacterial and antiviral activities of local Thai green macroalgae crude extracts in pacific white shrimp (litopenaeus vannamei). Mar Drugs 18:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18030140
Li Y, Sun S, Pu X et al (2018) Evaluation of antimicrobial activities of seaweed resources from Zhejiang Coast, China. Sustain 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072158
Li C, Weng S, He J (2019) WSSV–host interaction: host response and immune evasion. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:558–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.043
Meenakshi S, Saravanan R, Balasubramanian T, Palavesam A (2019) In vivo administration of fucoidan from Turbinaria decurrens protects shrimps from white spot syndrome virus. Indian J Geo-Marine Sci 48:212–216
Mohan K, Ravichandran S, Muralisankar T, Uthayakumar V, Chandirasekar R, Seedevi P, Abirami RG, Rajan DK (2019) Application of marine-derived polysaccharides as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review of current knowledge and further perspectives. Fish Shellfish Immunol 86:1177–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.12.072
Ojerio VT, Corre VL, Toledo NA et al (2018) Alginic acid as immunostimulant: effects of dose and frequency on growth performance, immune responses, and white spot syndrome virus resistance in tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fabricius, 1798). Aquac Int 26:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0212-4
Pereira L (2018) Biological and therapeutic properties of the seaweed polysaccharides. Int Biol Rev 2. https://doi.org/10.18103/ibr.v2i2.1762
Raguraman V, MubarakAli D, Narendrakumar G et al (2018) Unraveling rapid extraction of fucoxanthin from Padina tetrastromatica: purification, characterization and biomedical application. Process Biochem 73:211–219
Raguraman V, Jyotsna J, Palaniappan S et al (2019) Sulfated polysaccharide from Sargassum tenerrimum attenuates oxidative stress induced reactive oxygen species production in in vitro and in zebrafish model. Carbohydr Polym 203:441–449
Rudtanatip T, Asuvapongpatana S, Withyachumnarnkul B, Wongprasert K (2014) Sulfated galactans isolated from the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri target the envelope proteins of white spot syndrome virus and protect against viral infection in shrimp haemocytes. J Gen Virol 95:1126–1134. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.062919-0
Salunke M, Kalyankar A, Khedkar CD, Shingare M, Khedkar GD (2020) A review on shrimp aquaculture in India: historical perspective, constraints, status and future implications for impacts on aquatic ecosystem and biodiversity. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 28:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2020.1723058
Schleder DD, Peruch LGB, Poli MA, Ferreira TH, Silva CP, Andreatta ER, Hayashi L, do Nascimento Vieira F (2018) Effect of brown seaweeds on Pacific white shrimp growth performance, gut morphology, digestive enzymes activity and resistance to white spot virus. Aquaculture 495:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.06.020
Schleder DD, Blank M, Peruch LGB, Poli MA, Gonçalves P, Rosa KV, Fracalossi DM, Vieira FN, Andreatta ER, Hayashi L (2020) Impact of combinations of brown seaweeds on shrimp gut microbiota and response to thermal shock and white spot disease. Aquaculture 519:734779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734779
Shekhar MS, Ponniah AG (2015) Recent insights into host-pathogen interaction in white spot syndrome virus infected penaeid shrimp. J Fish Dis 38:599–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12279
Sivagnanavelmurugan M, Marudhupandi T, Palavesam A, Immanuel G (2012) Antiviral effect of fucoidan extracted from the brown seaweed, Sargassum wightii, on shrimp Penaeus monodon postlarvae against white spot syndrome virus. J World Aquac Soc 43:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2012.00596.x
Sivagnanavelmurugan, M, Radhakrishnan, S, Palavesam, A, Arul, V, Immanuel G (2018) Characterization of alginic acid extracted from Sargassum wightii and determination of its antiviral activity on shrimp Penaeus monodon postlarvae against white spot syndrome virus. Int J Curr Res Life Sci 07:1863–1872
Sotanon N, Saleeart A, Rattanarojpong T, Thanh Dong H, Senapin S, Wongprasert K, Sarikavanij S, Khunrae P (2018) C-terminal domain of WSSV VP37 is responsible for shrimp haemocytes binding which can be inhibited by sulfated galactan. Fish Shellfish Immunol 77:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.03.043
Vasantharaja R, Stanley Abraham L, Gopinath V, Hariharan D, Smita KM (2018) Attenuation of oxidative stress induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cytotoxicity in fibroblast cells by sulfated polysaccharide from Padina gymnospora. Int J Biol Macromol 124:50–59
Velmurugan S, Jerin N, Michael Babu M, Bindhu F, Albin Dhas S, Citarasu T (2014) Screening and characterization of antiviral compounds from Enteromorpha flexuosa against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) and its in vivo influence on Indian white shrimp Fenneropenaeus indicus. Aquac Int 23:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-014-9798-y
Verbruggen B, Bickley LK, van Aerle R, Bateman K, Stentiford G, Santos E, Tyler C (2016) Molecular mechanisms of white spot syndrome virus infection and perspectives on treatments. Viruses 8:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8010023
Vo TS, Ngo DH, Kang KH, Jung WK, Kim SK (2015) The beneficial properties of marine polysaccharides in alleviation of allergic responses. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201400412
Wang W, Wang SX, Guan HS (2012) The antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides: an overview. Mar Drugs 10:2795–2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10122795
Wijesinghe WAJP, Jeon Y-J (2012) Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: a review. Carbohydr Polym 88:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.029
Wongprasert K, Rudtanatip T, Praiboon J (2014) Immunostimulatory activity of sulfated galactans isolated from the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri and development of resistance against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.10.010
Yudiati E, Isnansetyo A, Murwantoko et al (2019) Alginate from Sargassum siliquosum simultaneously stimulates innate immunity, upregulates immune genes, and enhances resistance of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). Mar Biotechnol 21:503–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-019-09898-7
Zhou Q, Xu L, Li H, Qi YP, Yang F (2009) Four major envelope proteins of white spot syndrome virus bind to form a complex. J Virol 83:4709–4712. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02360-08
Acknowledgments
We thank the management of Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology (SIST) for its strong support to carry out research activities.
Funding
The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)-Earth Science and Technology Cell (ESTC), Government of India provided financial assistance (MoES/11-MRDFIESTC-MEB (SU)/2/2014 PCIII).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raguraman, V., Ravindran, N., Selvaraju, K. et al. Seaweed polysaccharides as potential therapeutic agents against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV): a mini review. Aquacult Int 28, 2333–2343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00587-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00587-0