Abstract
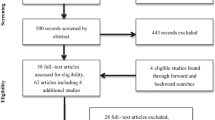
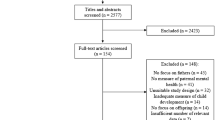
Gender role development occurs in the earliest months and years of a child’s life. Parental attitudes, behaviours and modelling are likely to play a significant role in this process; however, to date no review has been conducted to consolidate knowledge of the effects of differential parenting on child development. This systematic review aimed to investigate the evidence for differential parenting behaviours based on child gender that affect child development, across six areas (vocalisation, socialisation, play, toys, dress and décor). Searches were conducted for English article using four databases: psycINFO, CINAHL, Sociological Abstract, and SCOPUS. The inclusion criteria were biological or adoptive parents, of a typically developing child aged below five, using any parenting behaviour or strategies that differed by child gender. 45 studies were included in this systematic review (14 vocalisation, 21 socialisation, 7 play, 3 toys). A variety of gender-differentiated parenting behaviours and child outcomes were examined. The review found evidence that parents do respond differently to their children. Parents vocalised differently, used different socialising strategies, played differently and provided different toys to their sons and daughters. This differential parenting was associated with some differences in child development across child gender, including differences in child vocalisation, displays of affect, pain responses, compliance, toy play and aggression. However, the overall quality of the evidence, the lack of longitudinal studies and the heterogeneous nature of the outcomes examined suggest the need for a systematic approach to examining the nature and effects of differential parenting on children’s development.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S., Kuebli, J., Boyle, P. A., & Fivush, R. (1995). Gender differences in parent-child conversations about past emotions: A longitudinal investigation. Sex Roles, 33(5–6), 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01954572.
Ahl, R. E., Fausto-Sterling, A., García-Coll, C., & Seifer, R. (2013). Gender and discipline in 5–12-month-old infants: A longitudinal study. Infant Behavior and Development, 36(2), 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2013.01.005.
Alessandri, S. M., & Lewis, M. (1993). Parental evaluation and its relation to shame and pride in young children. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 29(5–6), 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289427.
Archer, J. (1996). Sex differences in social behavior: Are the social role and evolutionary explanations compatible? American Psychologist, 51(9), 909–917. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.51.9.909.
Aznar, A., & Tenenbaum, H. R. (2020). Gender comparisons in mother-child emotion talk: A meta-analysis. Sex Roles, 82(3), 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-019-01042-y.
Bailey, C. S., Denham, S. A., & Curby, T. W. (2013). Questioning as a component of scaffolding in predicting emotion knowledge in preschoolers. Early Child Development and Care, 183(2), 265–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2012.671815.
Baron, A. S., Schmader, T., Cvencek, D., & Meltzoff, A. N. (2013). The gendered self-concept: How implicit gender stereotypes and attitudes shape self-definition. In H. Tenenbaum & P. Leman (Eds.), Gender and development (pp. 109–132). New York: Taylor and Francis.
Bell, C. S., Johnson, J. E., McGillicuddy-DeLisi, A. V., & Sigel, I. E. (1981). The effects of family constellation and child gender on parental use of evaluative feedback. Child Development, 52(2), 701–704. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129192.
Bem, S. L. (1981). Gender schema theory: A cognitive account of sex typing. Psychological Review, 88(4), 354–364.
Bian, L., Leslie, S.-J., & Cimpian, A. (2017). Gender stereotypes about intellectual ability emerge early and influence children’s interests. Science, 355(6323), 389–391. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah6524.
Boe, J. L., & Woods, R. J. (2018). Parents’ influence on infants’ gender-typed toy preferences. Sex Roles, 79(5–6), 358–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-017-0858-4.
Brundin, K., Rödholm, M., & Larsson, K. (1988). Vocal communication between parents and infants. Early Human Development, 16(1), 35–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3782(88)90085-0.
Bussey, K., & Bandura, A. (1984). Influence of gender constancy and social power on sex-linked modeling. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47(6), 1292–1302. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.47.6.1292.
Bussey, K., & Bandura, A. (1999). Social cognitive theory of gender development and differentiation. Psychological Review, 106(4), 676–713. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.106.4.676.
Caldera, Y. M., Huston, A. C., & O'Brien, M. (1989). Social interactions and play patterns of parents and toddlers with feminine, masculine, and neutral toys. Child Development, 60(1), 70–76. https://doi.org/10.2307/1131072.
Callanan, M. A., & Braswell, G. (2006). Parent-child conversations about science and literacy: Links between formal and informal learning. Counterpoints, 249, 123–137.
Cervantes, C. A., & Callanan, M. A. (1998). Labels and explanations in mother–child emotion talk: Age and gender differentiation. Developmental Psychology, 34(1), 88–98. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.34.1.88.
Chaplin, T. M., Cole, P. M., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (2005). Parental socialization of emotion expression: Gender differences and relations to child adjustment. Emotion, 5(1), 80–88. https://doi.org/10.1037/1528-3542.5.1.80.
Clearfield, M. W., & Nelson, N. M. (2006). Sex differences in mothers' speech and play behavior with 6-, 9-, and 14-month-old infants. Sex Roles, 54(1–2), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-005-8874-1.
Collins, W. A., Maccoby, E. E., Steinberg, L., Hetherington, E. M., & Bornstein, M. H. (2000). Contemporary research on parenting: The case for nature and nurture. American Psychologist, 55(2), 218–232. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.2.218.
Connell, R., & Pearse, R. (2015). Gender. In World Perspective (3rd ed.). Cambridge: Polity.
Cox, S. J., Mezulis, A. H., & Hyde, J. S. (2010). The influence of child gender role and maternal feedback to child stress on the emergence of the gender difference in depressive rumination in adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 46(4), 842–852. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019813.
Culp, R. E., Cook, A. S., & Housley, P. C. (1983). A comparison of observed and reported adult-infant interactions: Effects of perceived sex. Sex Roles, 9(4), 475–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289787.
Eisenberg, A. R. (1996). The conflict talk of mothers and children: Patterns related to culture, SES, and gender of child. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 42(3), 438–458.
Eisenberg, N., Wolchik, S. A., Hernandez, R., & Pasternack, J. F. (1985). Parental socialization of young children's play: A short-term longitudinal study. Child Development, 56(6), 1506–1513. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130469.
Endendijk, J. J., Groeneveld, M. G., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Mesman, J. (2016). Gender-differentiated parenting revisited: Meta-analysis reveals very few differences in parental control of boys and girls. PLoS ONE, 11(7), e0159193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159193.
Endendijk, J. J., Groeneveld, M. G., & Mesman, J. (2018). The gendered family process model: An integrative framework of gender in the family. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 47(4), 877–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-018-1185-8.
Endendijk, J. J., Groeneveld, M. G., van Berkel, S. R., Hallers-Haalboom, E. T., Mesman, J., & Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J. (2013). Gender stereotypes in the family context: Mothers, fathers, and siblings. Sex Roles, 68(9), 577–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-013-0265-4.
Endendijk, J. J., Groeneveld, M. G., van der Pol, L. D., van Berkel, S. R., Hallers-Haalboom, E. T., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., et al. (2017). Gender differences in child aggression: Relations with gender-differentiated parenting and parents’ gender-role stereotypes. Child Development, 88(1), 299–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12589.
Endendijk, J. J., Groeneveld, M. G., van der Pol, L. D., van Berkel, S. R., Hallers-Haalboom, E. T., Mesman, J., et al. (2014). Boys don’t play with dolls: Mothers’ and fathers’ gender talk during picture book reading. Parenting, 14(3–4), 141–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2014.972753.
Fagot, B. I. (1974). Sex differences in toddlers' behavior and parental reaction. Developmental Psychology, 10(4), 554–558. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0036600.
Fagot, B. I., & Hagan, R. (1991). Observations of parent reactions to sex-stereotyped behaviors: Age and sex effects. Child Development, 62(3), 617–628. https://doi.org/10.2307/1131135.
Farver, J. A. M., & Wimbarti, S. (1995). Paternal participation in toddlers' pretend play. Social Development, 4(1), 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.1995.tb00048.x.
Fausto-Sterling, A., Coll, C. G., & Lamarre, M. (2012). Sexing the baby: Part 1—What do we really know about sex differentiation in the first three years of life? Social Science & Medicine, 74(11), 1684–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.05.051.
Fiese, B. H., & Skillman, G. (2000). Gender differences in family stories: Moderating influence of parent gender role and child gender. Sex Roles, 43(5–6), 267–283. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026630824421.
Fine, C. (2015). Neuroscience, gender, and “Development To” and “From”: The example of toy preferences. In J. Clausen & N. Levy (Eds.), Handbook of neuroethics (pp. 1737–1755). Dordrecht: Springer.
Fivush, R. (1989). Exploring sex differences in the emotional content of mother-child conversations about the past. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 20(11–12), 675–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00288079.
Fivush, R., Brotman, M. A., Buckner, J. P., & Goodman, S. H. (2000). Gender differences in parent–child emotion narratives. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 42(3–4), 233–253. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007091207068.
Flannagan, D., & Baker-Ward, L. (1996). Relations between mother–child discussions of children's preschool and kindergarten experiences. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 17(3), 423–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0193-3973(96)90035-0.
Freeman, N. K. (2007). Preschoolers' perceptions of gender appropriate toys and their parents' beliefs about genderized behaviors: Miscommunication, mixed messages, or hidden truths? Early Childhood Education Journal, 34(5), 357–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-006-0123-x.
Friedman, C. K., Leaper, C., & Bigler, R. S. (2007). Do mothers' gender-related attitudes or comments predict young children's gender beliefs? Parenting: Science and Practice, 7(4), 357–366. doi: 10.1080/15295190701665656
Garner, P. W., Robertson, S., & Smith, G. (1997). Preschool children's emotional expressions with peers: The roles of gender and emotion socialization. Sex Roles, 36(11–12), 675–691. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1025601104859.
Gelman, S. A. (2008). Learning from others: Children's construction of concepts. Annual Review of Psychology, 60(1), 115–140. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093659.
Gelman, S. A., & Meyer, M. (2011). Child categorization. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 2(1), 95–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.96.
Gelman, S. A., Taylor, M. G., Nguyen, S. P., Leaper, C., & Bigler, R. S. (2004). Mother-child conversations about gender: Understanding the acquisition of essentialist beliefs. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 69(1), i–142.
Goldberg, S., & Lewis, M. (1969). Play behavior in the year-old infant: Early sex differences. Child Development, 40(1), 21–31. https://doi.org/10.2307/1127152.
Golombok, S., Rust, J., Zervoulis, K., Golding, J., & Hines, M. (2012). Continuity in sex-typed behavior from preschool to adolescence: A longitudinal population study of boys and girls aged 3–13 years. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 41(3), 591–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-011-9784-7.
Gonzalez, A. M., Dunlop, W. L., & Baron, A. S. (2016). Malleability of implicit associations across development. Developmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12481.
Greif, E. B. (1980). Sex differences in parent-child conversations. Women's Studies International Quarterly, 3(2–3), 253–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-0685(80)92281-2.
Haines, E. L., Deaux, K., & Lofaro, N. (2016). The times they are a-changing … or are they not? A comparison of gender stereotypes, 1983–2014. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 40(3), 353–363. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361684316634081.
Halim, M. L. D., Ruble, D. N., Tamis-LeMonda, C. S., Shrout, P. E., & Amodio, D. M. (2017). Gender Attitudes in Early Childhood: Behavioral consequences and cognitive antecedents. Child Development, 88(3), 882–899. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12642.
Hwang, C. P. (1978). Mother-infant interaction; effects of sex of infant on feeding behaviour. Early Human Development, 2(4), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3782(78)90061-0.
Johnston, D. W., Schurer, S., & Shields, M. A. (2014). Maternal gender role attitudes, human capital investment, and labour supply of sons and daughters. Oxford Economic Papers, 66(3), 631–659.
Kagesten, A., Gibbs, S., Blum, R. W., Moreau, C., Chandra-Mouli, V., Herbert, A., et al. (2016). Understanding factors that shape gender attitudes in early adolescence globally: a mixed-methods systematic review. PLoS ONE, 11, 157.
Kane, E. W. (2006). "No way my boys are going to be like that!": Parents' responses to children's gender nonconformity. Gender & Society, 20(2), 149–176. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891243205284276.
Kelly, K. R. (2016). Mother-child conversations and child memory narratives: The roles of child gender and attachment. Psychology of Language and Communication, 20(1), 48–72. https://doi.org/10.1515/plc-2016-0003.
Koenig, M. A., & Harris, P. L. (2005). The role of social cognition in early trust. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(10), 457–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2005.08.006.
Kohlberg, L. A. (1966). A cognitive-developmental analysis of children's sex-role concepts and attitudes. In E. E. Maccoby (Ed.), The development of sex differences (pp. 82–173). Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Kuebli, J., Butler, S., & Fivush, R. (1995). Mother-child talk about past emotions: Relations of maternal language and child gender over time. Cognition and Emotion, 9(2–3), 265–283. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699939508409011.
Leaper, C., Anderson, K. J., & Sanders, P. (1998). Moderators of gender effects on parents' talk to their children: A meta-analysis. Developmental Psychology, 34(1), 3–27. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.34.1.3.
Leaper, C., Leve, L., Strasser, T., & Schwartz, R. (1995). Mother-child communication sequences: Play activity, child gender, and marital status effects. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 41(3), 307–327.
Lindahl, L. B., & Heimann, M. (1997). Research report: Social proximity in early mother-infant interactions: Implications for gender differences? Infant and Child Development, 6(2), 83–88.
Lindahl, L. B., & Heimann, M. (2002). Social proximity in Swedish mother-daughter and mother-son interactions in infancy. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 20(1), 37–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646830220106794.
Lindsey, E. W., Cremeens, P. R., & Caldera, Y. M. (2010). Gender differences in mother-toddler and father-toddler verbal initiations and responses during a caregiving and play context. Sex Roles, 63(5–6), 399–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-010-9803-5.
Lytton, H., & Romney, D. M. (1991). Parents' differential socialization of boys and girls: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 109(2), 267. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.109.2.267.
MacPhee, D., & Prendergast, S. (2019). Room for improvement: Girls’ and boys’ home environments are still gendered. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 80(5–6), 332–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-018-0936-2.
Malatesta, C. Z., & Haviland, J. M. (1982). Learning display rules: The socialization of emotion expression in infancy. Child Development, 53(4), 991–1003. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129139.
Martin, C. L., & Halverson, C. F. (1981). A schematic processing model of sex typing and stereotyping in children. Child Development, 52(4), 1119–1134. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129498.
Martin, J. L., & Ross, H. S. (2005). Sibling aggression: Sex differences and parents' reactions. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29(2), 129–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650250444000469.
Martin, K. A. (2005). William wants a doll. Can he have one? Feminists, child care advisors, and gender-neutral child rearing. Gender & Society, 19(4), 456–479. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891243204272968.
Masur, E. F. (1987). Imitative interchanges in a social context: Mother-infant matching behavior at the beginning of the second year. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 33(4), 453–472.
Mesman, J., & Groeneveld, M. G. (2017). Gendered parenting in early childhood: Subtle but unmistakable if you know where to look. Child Development Perspectives, 12, 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12250.
Miller, D. I., Nolla, K. M., Eagly, A. H., & Uttal, D. H. (2018). The development of children's gender-science stereotypes: A meta-analysis of 5 decades of U.S. Draw-a-scientist studies. Child Development, 89(6), 1943–1955. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13039.
Mondschein, E. R., Adolph, K. E., & Tamis-LeMonda, C. S. (2000). Gender bias in mothers' expectations about infant crawling. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 77(4), 304–316. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.2000.2597.
Morrongiello, B. A., & Dawber, T. (1999). Parental influences on toddlers' injury-risk behaviors: Are sons and daughters socialized differently? Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 20(2), 227–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0193-3973(99)00015-5.
Morrongiello, B. A., McArthur, B. A., Goodman, S., & Bell, M. (2015). Don't touch the gadget because it's hot! Mothers' and children's behavior in the presence of a contrived hazard at home: Implications for supervising children. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 40(1), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsu056.
Nguyen, H.-H. D., & Ryan, A. M. (2008). Does stereotype threat affect test performance of minorities and women? A meta-analysis of experimental evidence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(6), 1314–1334. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012702.
O'Brien, M., & Huston, A. C. (1985). Development of sex-typed play behavior in toddlers. Developmental Psychology, 21(5), 866–871. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.21.5.866.
Piira, T., Champion, G. D., Bustos, T., Donnelly, N., & Lui, K. (2007). Factors associated with infant pain response following an immunization injection. Early Human Development, 83(5), 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2006.06.007.
Pruden, S. M., & Levine, S. C. (2017). Parents’ spatial language mediates a sex difference in preschoolers’ spatial-language use. Psychological Science, 28(11), 1583–1596. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797617711968.
Raag, T., & Rackliff, C. L. (1998). Preschoolers' awareness of social expectations of gender: Relationships to toy choices. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 38(9–10), 685–700. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018890728636.
Reese, E., Haden, C. A., & Fivush, R. (1996). Mothers, fathers, daughters, sons: Gender differences in autobiographical reminiscing. Research on Language and Social Interaction, 29(1), 27–56. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327973rlsi2901_3.
Reilly, D., & Neumann, D. L. (2013). Gender-role differences in spatial ability: A meta-analytic review. Sex Roles, 68(9), 521–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-013-0269-0.
Robinson, J., Little, C., & Biringen, Z. (1993). Emotional communication in mother-toddler relationships: Evidence for early gender differentiation. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 39(4), 496–517.
Roger, K. M., Rinaldi, C. M., & Howe, N. (2012). Mothers' and fathers' internal state language with their young children: An examination of gender differences during an emotions task. Infant and Child Development, 21(6), 646–666. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.1762.
Rothman, B. K. (1986). The Tentative Pregnancy: Prenatal Diagnosis and the Future of Motherhood. New York, NY: Penguin Books.
Sandnabba, N. K., & Ahlberg, C. (1999). Parents' attitudes and expectations about children's cross-gender behavior. Sex Roles, 40(3), 249–263. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018851005631.
Serbin, L. A., Poulin-Dubois, D., Colburne, K. A., Sen, M. G., & Eichstedt, J. A. (2001). Gender stereotyping in infancy: Visual preferences for and knowledge of gender-stereotyped toys in the second year. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 25(1), 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650250042000078.
Sidorowicz, L. S., & Lunney, G. S. (1980). Baby X revisited. Sex Roles, 6(1), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00288362.
Smith, C., & Lloyd, B. (1978). Maternal behavior and perceived sex of infant: Revisited. Child Development, 49(4), 1263–1265. https://doi.org/10.2307/1128775.
Smith, P. K., & Daglish, L. (1977). Sex differences in parent and infant behavior in the home. Child Development, 48(4), 1250–1254. https://doi.org/10.2307/1128482.
Suizzo, M. A., & Bornstein, H. M. (2006). French and European American child-mother play: Culture and gender considerations. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 30(6), 498–508. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025406071912.
Sung, J., Fausto-Sterling, A., Garcia Coll, C., & Seifer, R. (2013). The dynamics of age and sex in the development of mother-infant vocal communication between 3 and 11 months. Infancy, 18(6), 1135–1158. https://doi.org/10.1111/infa.12019.
Tenenbaum, H. R., & Leaper, C. (2003). Parent-child conversations about science: The socialization of gender inequities? Developmental Psychology, 39(1), 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.39.1.34.
Weinberg, M. K., Tronick, E. Z., Cohn, J. F., & Olson, K. L. (1999). Gender differences in emotional expressivity and self-regulation during early infancy. Developmental Psychology, 35(1), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.35.1.175.
Will, J. A., Self, P. A., & Datan, N. (1976). Maternal behavior and perceived sex of infant. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 46(1), 135–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-0025.1976.tb01234.x.
Wood, E., Desmarais, S., & Gugula, S. (2002). The impact of parenting experience on gender stereotyped toy play of children. Sex Roles, 47(1–2), 39–49.
Zosuls, K. M., Miller, C. F., Ruble, D. N., Martin, C. L., & Fabes, R. A. (2011). Gender development research in Sex roles: Historical trends and future directions. Sex Roles, 64(11–12), 826–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-010-9902-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Parenting and Family Support Centre is partly funded by royalties stemming from published resources of the Triple P—Positive Parenting Program, which is developed and owned by The University of Queensland (UQ). Royalties are also distributed to the Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences at UQ and contributory authors of published Triple P resources. Triple P International (TPI) Pty Ltd is a private company licenced by UQ, to publish and disseminate Triple P worldwide. The author of this report has no share or ownership of TPI. Dr Morawska receives royalties from TPI. TPI had no involvement in the study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of data, or writing of this report. Dr Morawska is an employee at UQ.
Ethical Approval
This study used data from published studies and no data was collected from individual participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morawska, A. The Effects of Gendered Parenting on Child Development Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 23, 553–576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-020-00321-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-020-00321-5