Abstract
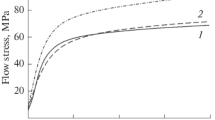
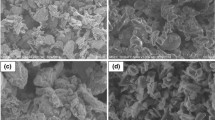
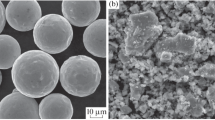
In order to strengthen pure tin and improve its dry sliding resistance, Sn/SiC and Sn/Zn composites were fabricated via a powder metallurgy route. Microstructure, hardness and pin-on-disk wear resistance of pure tin and the fabricated composites were compared to those of Sn–7.5Sb–3.5Cu Babbitt alloy. The dominant wear mechanism at different applied loads was determined by analyzing worn surfaces and wear debris in each case. The results showed that the hardening effect of Zn was much higher than that of SiC. The hardening role of Zn in the tin matrix was ascribed to the direct load transfer mechanism. Microscopic studies of the worn surfaces revealed that the pure tin was susceptible to surface fatigue wear and plowing damage, depending on the normal load applied during the wear test. In the case of Sn/SiC composite and the Babbitt alloy, delamination wear mechanism resulting from subsurface crack propagation controlled the wear rate. While the highest hardness and the lowest coefficient of friction were obtained for the Babbitt alloy, the Sn/Zn composite exhibited the highest wear resistance at a constant applied load, indicating the importance of asperity contact type in the wear process.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma SC. Tribology in machine components. In: Menezes PL, Nosonovsky M, Ingole SP, Kailas SV, Lovell MR, editors. Tribology for Scientists and Engineers: from Basics to Advanced Concepts. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 821.
Jenabali Jahromi SA, Moazami Goudarzi M, Nazarboland A. Failure analysis of GE-F9 gas turbine journal bearings. Iran J Sci Technol Trans B Eng. 2008;32(B1):61.
Harnoy A. Bearing Design in Machinery: Engineering Tribology and Lubrication. 1st ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2002. 275.
Kingsbury GR. Friction and wear of sliding bearing materials. In: Torren GE, editor. ASM Handbook, Volume 18, Friction, Lubrication, and Wear Technology. Geauga: ASM International; 1992. 741.
Dean RR, Evans CJ. Plain bearing materials: the role of tin. Tribol Int. 1976;9(3):101.
Moazami Goudarzi M, Jenabali Jahromi SA, Nazarboland A. Investigation of characteristics of tin-based white metals as a bearing material. Mater Des. 2009;30(6):2283.
Dong Q, Yin Z, Li H, Zhang X, Jiang D, Zhong N. Effects of Ag micro-addition on structure and mechanical properties of Sn–11Sb–6Cu Babbitt. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2018;722:225.
Zhang D, Zhao F, Li Y, Li P, Zeng Q, Dong G. Study on tribological properties of multi-layer surface texture on Babbitt alloys surface. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;390:540.
Ni Y, Li X, Dong G, Tong Z, Mei T. The combined effect of La and heat treatment on the tribological performances of tin-Babbitt alloy. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. 2019;233(7):1117.
Zhang D, Ho JKL, Dong G, Zhang H, Hua M. Tribological properties of tin-based Babbitt bearing alloy with polyurethane coating under dry and starved lubrication conditions. Tribol Int. 2015;90:22.
Alcover Junior PRC, Pukasiewicz AGM. Evaluation of microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of a Babbitt alloy deposited by arc and flame spray processes. Tribol Int. 2019;131:148.
Smart RF, Ellwood EC. Sintering of tin powder. Nature. 1958;181:833.
Eastwood BJ, Robins DA. Some properties of tin prepared from tin powder by extrusion. Powder Metall. 1964;7(14):99.
Ferguson BL, Roberts PR. Extrusion of metal powders. In: Eisen WB, Ferguson BL, German RM, Iacocca R, Lee PW, Madan D, Moyer K, Sanderow H, Trudel Y, editors. ASM Handbook, Volume 7, Powder Metal Technologies and Applications. Geauga: ASM International; 1998. 621.
Chawla N, Shen YL. Mechanical behavior of particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Adv Eng Mater. 2001;3(6):357.
Dai LH, Ling Z, Bai YL. Size-dependent inelastic behavior of particle-reinforced metal-matrix composites. Compos Sci Technol. 2001;61(8):1057.
Matucha KH. Materials Science and Technology, Structure and Properties of Nonferrous Alloys. Weinheim: Wiley; 1996. 36.
Moazami-Goudarzi M, Akhlaghi F. Wear behavior of Al 5252 alloy reinforced with micrometric and nanometric SiC particles. Tribol Int. 2016;102:28.
Zum Gahr KH. Microstructure and Wear of Materials. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1987. 80.
Menezes P, Nosonovsky M, Ingole SP, Kailas SV, Lovell MR. Tribology for Scientists and Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Concepts. 1st ed. New York: Springer; 2013. 71.
Babu MVS, Krishna AR, Suman KNS. Review of journal bearing materials and current trends. Am J Mater Sci Technol. 2015;4(2):72.
Sturk RK, Whitney WJ. Fluid Film Bearing Materials. In: Wang QJ, Chung Y-W, editors. Encyclopedia of Tribology. Boston: Springer; 2013. 1200.
Ludema KC. Friction, Wear, Lubrication: A Textbook in Tribology. 1st ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1996. 150.
Torrance AA. A new approach to the mechanics of abrasion. Wear. 1981;67(2):233.
Suh NP. The delamination theory of wear. Wear. 1973;25(1):111.
Rouhi M, Moazami-Goudarzi M, Ardestani M. Comparison of effect of SiC and MoS2 on wear behavior of Al matrix composites. Trans Nonferr Metal Soc. 2019;29(6):1169.
Rowson DM, Wu YL. The sequential observation of the pitting process in discs. Wear. 1981;70(3):383.
Stachowiak GW, Batchelor AW, Stachowiak GB. 10—Wear particle analysis. In: Stachowiak GW, Batchelor AW, Stachowiak GB, editors. Tribology Series. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2004. 253.
Xu K, Luxmoore AR, Deravi F. Comparison of shape features for the classification of wear particles. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 1997;10(5):485.
Chen LH, Rigney DA. Transfer during unlubricated sliding wear of selected metal systems. Wear. 1985;105(1):47.
Arab M, Marashi SPH. Graphene nanoplatelet (GNP)-incorporated AZ31 magnesium nanocomposite: microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties. Tribol Lett. 2018;66(4):156.
Czichos H. Chapter 1—introduction to friction and wear. In: Friedrich K, editor. Composite Materials Series. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1986. 1.
Moazami-Goudarzi M, Nemati A. Tribological behavior of self lubricating Cu/MoS2 composites fabricated by powder metallurgy. Trans Nonferr Metal Soc. 2018;28(5):946.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, F., Moazami-Goudarzi, M. & Najafi, H. Microstructures, hardening and tribological behaviors of tin matrix composites reinforced with SiC and Zn particles. Rare Met. 40, 2584–2592 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01535-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01535-w