Abstract
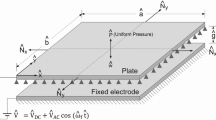
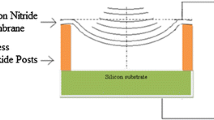
An analytical study of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs) with circular microplates has been carried out. The study comprises one-sided (single electrode back-plate) and two-sided (double electrode back-plate) systems, and derives universal correction factors for pull-in voltage and critical displacement to be used in lumped element model (LEM) analysis. We employ von Karman plate theory and the single-mode Galerkin decomposition method to solve the equations. Consequently, voltage–deflection relations have been derived. By comparing results from plate theory with LEM, it is concluded: (1) for the one-sided CMUT by neglecting geometrical nonlinearity, we find \(\frac{{{V_{\text {Pull in - P}}}}}{{{V_{\text {Pull in - LEM}}}}} = 1.327\) and the ratio of critical displacement derived from plate theory over critical displacement from LEM is always 1.882. (2) For the one-sided CMUT including geometrical nonlinearity \(\frac{{{V_{\text {Pull in} - P}}}}{{{V_{\text {Pull in - LEM}}}}} = 1.45\) and critical displacement from plate theory over critical displacement from LEM is 1.792, for a specific set of parameters. (3) For the two-sided CMUT, there is no differences in using linear nor nonlinear analysis and \(\frac{{{V_{\text {Pull in - P}}}}}{{{V_{\text {Pull in - LEM}}}}} = 1.276\). For all studied cases, finite element (FE) analysis has been performed to validate the analytical outcomes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saadatmand M, Kook J (2019) Multi-objective optimization of a circular dual back-plate MEMS microphone: tradeoff between pull-in voltage, sensitivity and resonance frequency. Microsyst Technol 25(8):2937–2947
Rochus V, Wang B, Tilmans HAC, Chaudhuri AR, Helin P, Severi S, Rottenberg X (2016) Fast analytical design of MEMS capacitive pressure sensors with sealed cavities. Mechatronics 40:244–250
Liu J, Martin DT, Kadirvel K, Nishida T, Cattafesta L, Sheplak M, Mann BP (2008) Nonlinear model and system identification of a capacitive dual-backplate MEMS microphone. J Sound Vib 309(1):276–292
Jian L 2007) Nonlinear dynamics of a dual-backplate capacitive MEMS microphone. PhD thesis, Citeseer
Liu J, Martin DT, Nishida T, Cattafesta LN, Sheplak M, Brian MP (2008) Harmonic balance nonlinear identification of a capacitive dual-backplate MEMS microphone. J Microelectromech Syst 17(3):698–708
Rombach P, Müllenborn M, Klein U, Rasmussen K (2002) The first low voltage, low noise differential silicon microphone, technology development and measurement results. Sens Actuators A Phys 95(2):196–201
Martin DT (2007) Design, fabrication, and characterization of a MEMS dual-backplate capacitive microphone. PhD thesis, University of Florida
Martin D, Liu J, Kadirvel K, Fox R, Sheplak M, Nishida T (2006) Development of a MEMS dual backplate capacitive microphone for aeroacoustic measurements. In: 44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p 1246
Batra RC, Porfiri M, Spinello D (2007) Review of modeling electrostatically actuated microelectromechanical systems. Smart Mater Struct 16(6):R23
Batra RC, Porfiri M, Spinello D (2008) Vibrations and pull-in instabilities of microelectromechanical von Kármán elliptic plates incorporating the Casimir force. J Sound Vib 315(4):939–960
Faris WF (2003) Nonlinear dynamics of annular and circular plates under thermal and electrical loadings
Vogl GW, Nayfeh AH (2005) A reduced-order model for electrically actuated clamped circular plates. J Micromech Microeng 15(4):684
Ahmad B, Pratap R (2010) Elasto-electrostatic analysis of circular microplates used in capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers. IEEE Sens J 10(11):1767–1773
Chao PCP, Chiu CW, Tsai CY (2006) A novel method to predict the pull-in voltage in a closed form for micro-plates actuated by a distributed electrostatic force. J Micromech Microeng 16(5):986
Jallouli A, Kacem N, Bourbon G, Le Moal P, Walter V, Lardies J (2016) Pull-in instability tuning in imperfect nonlinear circular microplates under electrostatic actuation. Phys Lett A 380(46):3886–3890
Aggarwal S, Paul BE, DasGupta A, Chatterjee D (2017) Experimental characterization of piezoelectrically actuated micromachined silicon valveless micropump. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 21(1):2
Younis MI (2011) MEMS linear and nonlinear statics and dynamics, vol 20. Springer, Berlin
Shavezipur M, Hashemi SM, Nieva P, Khajepour A (2010) Development of a triangular-plate MEMS tunable capacitor with linear capacitance–voltage response. Microelectron Eng 87(9):1721–1727
Medina L, Gilat R, Krylov S (2017) Modeling strategies of electrostatically actuated initially curved bistable micro plates. Int J Solids Struct 118:1–13
Wygant IO, Kupnik M, Khuri-Yakub BT (2018) An analytical model for capacitive pressure transducers with circular geometry. J Microelectromech Syst 27(3):448–456
Sajadi B, Goosen H, van Keulen F (2018) Electrostatic instability of micro-plates subjected to differential pressure: a semi-analytical approach. Int J Mech Sci 138:210–218
Pelesko JA, Chen XY (2003) Electrostatic deflections of circular elastic membranes. J Electrostat 57(1):1–12
Siddique JI, Deaton R, Sabo E, Pelesko JA (2011) An experimental investigation of the theory of electrostatic deflections. J Electrostat 69(1):1–6
Engholm M, Pedersen T (2016) Modeling of plates with multiple anisotropic layers and residual stress. Sens Actuators A Phys 240:70–79
la Cour MF, Christiansen TL, Jensen JA, Thomsen EV (2015) Electrostatic and small-signal analysis of CMUTs with circular and square anisotropic plates. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 62(8):1563–1579
Skrzypacz P, Kadyrov S, Nurakhmetov D, Wei D (2019) Analysis of dynamic pull-in voltage of a graphene MEMS model. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 45:581–589
Talebian S, Rezazadeh G, Fathalilou M, Toosi B (2010) Effect of temperature on pull-in voltage and natural frequency of an electrostatically actuated microplate. Mechatronics 20(6):666–673
Saeedivahdat A, Abdolkarimzadeh F, Feyzi A, Rezazadeh G, Tarverdilo S (2010) Effect of thermal stresses on stability and frequency response of a capacitive microphone. Microelectron J 41(12):865–873
Younis MI, Abdel-Rahman EM, Nayfeh A (2003) A reduced-order model for electrically actuated microbeam-based MEMS. J Microelectromech Syst 12(5):672–680
Milad S, Alireza S (2018) Nonlinear vibration analysis of a circular micro-plate in two-sided NEMS/MEMS capacitive system by using harmonic balance method. Acta Mech Sin 1–15
Elishakoff I, Ruta GC, Stavsky Y (2006) A novel formulation leading to closed-form solutions for buckling of circular plates. Acta Mech 185(1–2):81–88
Jia XL, Yang J, Kitipornchai S, Lim CW (2012) Resonance frequency response of geometrically nonlinear micro-switches under electrical actuation. J Sound Vib 331(14):3397–3411
Guyader J-L (2013) Vibration in continuous media. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Pedro Manuel Calas Lopes Pacheco, D.Sc.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
In Eq. (20) coefficients \({K_{11}}-{K_{16}}\) are:
Appendix 2
In Eq. (23) coefficients \({K_{21}} - {K_{24}}\) are:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadatmand, M., Kook, J. Differences between plate theory and lumped element model in electrostatic analysis of one-sided and two-sided CMUTs with circular microplates. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02551-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02551-8