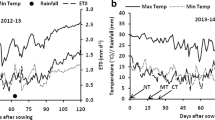
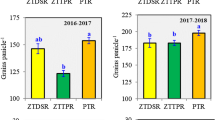
Abstract
Low productivity of rainfed lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) in the post-harvest rice fallows due to soil moisture stress is a major concern in the lower Indo-Gangetic plains. We hypothesized that adjusting sowing dates with proper tillage can optimize the microenvironment for rainfed lentil allowing higher seed yield and improving soil biology. A 2-year field experiment was laid out following a split-plot design during 2014–2016 integrating three lentil sowing dates (early, S1; mid, S2; and late, S3) with two tillage practices (zero tillage, ZT, and conventional tillage, CT) in an Inceptisol of West Bengal, India. The objective was to examine various physiological (relative leaf water content (RLWC), leaf area index (LAI)) and biochemical (chlorophyll, carbohydrate, free amino acids, phenol, proline) changes in lentil, soil biology (soil microbial biomass carbon (SMBC), dehydrogenase activity (DHA)), and lentil yield attributes (grain yield, seed index). When sown early, S1, lentils produced ~ 47% and 15% higher grain yield and ~ 23% and 18% higher seed index over S3 and S2, respectively. Delayed sowing (S3) induced early maturity, severe moisture stress that resulted in lower RLWC (14%), LAI (49%), chlorophyll (37%), and carbohydrate (33%) content compared to S1. SMBC and DHA were significantly higher at S1, specifically under ZT, but had negative correlation with phenol, amino acids, and proline. Our experiment concludes that early sowing of lentil coupled with zero tillage can mitigate soil moisture stress in the relay-cropped, rainfed lentil and provide an optimum microenvironment to facilitate sustainable production of lentil in the region.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ZT:
-
Zero tillage
- CT:
-
Conventional tillage
- RLWC:
-
Relative leaf water content
- LAI:
-
Leaf area index
- TAW:
-
Total available water
- RAW:
-
Readily available water
- RZSM:
-
Root zone soil moisture
- SMBC:
-
Soil microbial biomass carbon
- DHA:
-
Dehydrogenase activity
References
Abi-Ghanem R, Carpenter-Boggs L, Smith JL (2011) Cultivar effects on nitrogen fixation in peas and lentils. Biol Fertil Soils 47:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0492-6
Amirnia R, Ghiyasi M, Siavash Moghaddam S, Rahimi A, Damalas CA, Heydarzadeh S (2019) Nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria plus mycorrhizal fungi improve seed yield and quality traits of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik). J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:592–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00058-3
Anjum SA, Xie X, Wang L, Saleem MF, Man C, Lei W (2011) Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. Afr J Agric Res 6:2026–2032. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR10.027
Araya T, Nyssen J, Govaert B, Deckers J, Cornelis WM (2015) Impacts of conservation agriculture-based farming systems on optimizing seasonal rainfall partitioning and productivity on vertisols in the Ethiopian drylands. Soil Tillage Res 148:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.11.009
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Asha S, Rao KN (2002) Effect of simulated water logging on the levels of amino acids in groundnut at the time of sowing. Indian J Plant Physiol 7:288–291
Ashraf MF, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant biotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59(2):206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.12.006
Balota EL, Filho AC, Andrade DS, Dick RP (2004) Long-term tillage and crop rotation effects on microbial biomass and C and N mineralization in a Brazilian Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res 77:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2003.12.003
Bandyopadhyay PK, Singh KC, Mondal NR, Ghosh PK, Kumar N, Basu PS, Singh SS (2016) Effects of stubble length of rice in mitigating soil moisture stress and on yield of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) in rice-lentil relay crop. Agric Water Manag 173:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.05.009
Banerjee K, Krishnan P, Mridha N (2018) Application of thermal imaging of wheat crop canopy to estimate leaf area index under different moisture stress conditions. Biosyst Eng 166:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2017.10.012
Barrs HD, Weatherly PE (1962) A re-examination of relative turgidity for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428
Bates IS, Waldern RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bhaduri D, Purakayastha TJ, Patra AK, Singh M, Wilson BR (2017) Biological indicators of soil quality in a long-term rice–wheat system on the Indo-Gangetic plain: combined effect of tillage–water–nutrient management. Environ Earth Sci 76:202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6513-0
Blessing CH, Mariette S, Kaloki P, Bramley H (2018) Profligate and conservative: water use strategies in grain legumes. J Exp Bot 69(3):349–369. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx415
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf118
Blum A (2017) Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support plant production. Plant Cell Environ 40(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12800
Cakmak I (2000) Possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 146:185–205
Cevik S, Akpinar G, Yilizli A, Kasap M, Karosmanoglu K, Unyayar S (2019) Comparative physiological and leaf proteome analysis between drought-tolerant chickpea Cicer reticulatum and drought-sensitive chickpea C. arietinum. J Biosci 44(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9836-4
Chakraborty U, Dutta S, Chakraborty B (2001) Drought induced biochemical changes in young tea leaves. Indian J Plant Physiol 6:103–106
Chaturvedi RK, Raghubansi AS (2018) Leaf size and specific leaf area of tropical deciduous tree increase with elevation in soil moisture content. Int J Hydrol 2(4):466–469. https://doi.org/10.15406/ijh.2018.02.00112
Colmer TD, Voesenek LACJ (2009) Flooding tolerance: suites of plant traits in variable environments. Funct Plant Biol 36:665–681. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP09144
DACFW (2014) Department of Agriculture, Cooperation and farmers welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India. http://agricoop.nic.in/annual-report
Das A, Lal R, Patel DP, Ramkrushna GI, Layek J, Ngachan SV, Ghosh PK, Bordoloi J, Kumar M (2014) Effects of tillage and biomass on soil quality and productivity of lowland rice cultivation by small scale farmers in north eastern India. Soil Tillage Res 143:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.05.012
Das SK, Jana K (2015) Effect of foliar spray of water soluble fertilizer at pre flowering stage on yield of pulses. Agric Sci Dig 35(4):275–279. https://doi.org/10.18805/asd.v35i4.688
Daughtry CST (1990) Direct measurements of canopy structure. Remote Sens Rev 5:45–60
Diakhate S, Badiane-Ndour NY, Founoune-Mboup H, Diatta S, Fall AF, Hernandez RR, Cournac L, Dick R, Chapuis-Lardy L (2016) Impact of simulated drought stress on soil microbiology, and nematofauna in a native shrub + millet intercropping system in Senegal. Open J Soil Sci 6:189–203. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojss.2016.612018
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Esfahani MN, Sulieman S, Schulze J, Shinozaki KY, Shinozaki K, Tran LP (2014) Mechanisms of physiological adjustment of N2 fixation in Cicer arietinum L. (chickpea) during early stages of water deficit: single or multi-factor controls. Plant J 79(6):964–980. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12599
FAO (2016) FAOSTAT statistics database - agriculture. http://faostat3.fao.org/browse/Q/QC/E
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra SMA (2009) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212
Filippou P, Bouchagier P, Skotti E, Fotopoulos V (2014) Proline and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species metabolism is involved in the tolerant response of the invasive plant species Ailanthus altissima to drought and salinity. Environ Exp Bot 97:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.09.010
Franco-Andreu L, Gomez I, Parrado J, Garcis C, Hernandez T, Tejada M (2017) Soil biology changes as a consequence of organic amendments subjected to a severe drought. Land Degrad Dev 28(3):897–905. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2663
Ganesan K, Xu B (2017) Polyphenol-rich lentils and their health promoting effects. Int J Mol Sci 18:2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112390
Grossiord C, Sevanto S, Limousin JM, Meir P, Maurizio M, Pangle RE, Pockman WT, Salmon Y, Zweifel R, McDowell NG (2018) Manipulative experiments demonstrate how long-term soil moisture changes alter controls of plant water use. Environ Exp Bot 152:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.12.010
Gunes A, Inal A, Adak MS, Alpaslan M, Bagci EG, Erol T, Pilbeam DJ (2007) Mineral nutrition of wheat, chickpea and lentil as affected by mixed cropping and soil moisture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 78:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-006-9075-1
Hamada AM (2000) Amelioration of drought stress by ascorbic acid, thiamine or aspirin in wheat plants. Indian J Plant Physiol 5:358–364
Hanlan TG, Ball RA, Vandenberg A (2006) Canopy growth and biomass partitioning to yield in short-season lentil. Can J Plant Sci 86:109–119. https://doi.org/10.4141/P05-029
Jenkinson DS, Ladd JN (1981) Microbial biomass in soil - measurement and turnover. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil Biochem, vol 5. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 415–471
Jha P, Hati KM, Dalal RC, Dang YP, Kopittke PM, Menzies NW (2020) Soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a Vertisol following 50 years of no-tillage, crop stubble retention and nitrogen fertilization. Geoderma 358:113996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113996
Jin K, Cornelis WM, Schiettecatte W, Lu J, Yao Y, Wu H, Gabriels D, De Neve S, Cai D, Jin J, Hartmann R (2007) Effects of different management practices on the soil–water balance and crop yield for improved dryland farming in the Chinese loess plateau. Soil Tillage Res 96:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2007.05.002
Kantwa SR, Ahlawat IPS, Gangaiah B (2005) Effect of land configuration, post-monsoon irrigation and phosphorus on performance of sole and intercropped pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). Indian J Agron 50:278–280
Kar G, Kumar A (2009) Evaluation of post-rainy season crops with residual soil moisture and different tillage methods in rice-fallow of eastern India. Agric Water Manag 96:931–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2009.01.002
Kasturibai KV, Rajagobal V (2000) Osmotic adjustment as a mechanism for drought tolerance in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Indian J Plant Physiol 5:320–323
Kesli Y, Adak M (2012) Effects of different harvest time and sulfur fertilization on amino acid composition of lentil. J Plant Nutr 35:1693–1704. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.698350
Kim JY, Mahé A, Brangeon J, Prioul JL (2000) A maize vacuolur invertase, IVR2, is induced by water stress. Organ/tissue specificity and diurnal modulation of expression. Plant Physiol 124:71–84
Klein D, Loh TC, Goulding RL (1971) A rapid procedure to evaluate the dehydrogenase activity of soils low in organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 3:385–387
Kusvuran S (2012) Influence of drought stress on growth, ion accumulation and antioxidative enzymes in okra genotypes. Int J Agric Biol 14(3):401–406
Lampurlanes J, Angas P, Cantero-Martinez C (2002) Tillage effects on water storage during fallow: and on barley root growth and yield in two contrasting soils of the semi-arid Segarra region in Spain. Soil Tillage Res 65:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(01)00285-9
Lenssen AW, Johnson GD, Carlson GR (2007) Cropping sequence and tillage system influences annual crop production and water use in semiarid Montana, USA. Field Crop Res 100:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2006.05.004
Mafakheri A, Siosemardeh AF, Bahramnejad B, Struik PC, Sohrabi Y (2010) Effect of drought stress on yield, proline and chlorophyll contents in three chick pea cultivars. Aus J Crop Sci 4(8):580–585
Mahfouz H, Megawer EA, Maher A, Shaaban A (2020) Integrated effect of planting dates and irrigation regimes on morpho-physiological response, forage yield and quality, and water use efficiency of clitoria (Clitoria ternatea L.) in arid region. Arch. Agron Soil Sci 66(2):152–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1605165
Malick EP, Singh MB (1980) Plant enzymology and hittoenzymology (1st Edn.) Kalyani publishers: New Delhi; 286
Manzoni S, Schimel JP, Porpporato A (2012) Responses of soil microbial communities to water stress: results from a meta-analysis. Ecology 93(4):930–938. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0026.1
Mathobo R, Marais D, Steyn M (2017) The effect of drought stress on yield, leaf gaseous exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agric Water Manag 180:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.11.005
Matus A, Derksen DA, Walley FL, Loeppky HA, Van Kessel C (1997) The influence of tillage and crop rotation on nitrogen fixation in lentil and pea. Can J Plant Sci 77:197–200
Mina BL, Saha S, Kumar N, Srivastava AK, Gupta HS (2008) Changes in soil nutrient content and enzymatic activity under conventional and zero-tillage practices in an Indian sandy clay loam soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 82:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9189-8
Moharana PC, Biswas DR, Ghosh A, Sarkar A, Bhattacharyya R, Meena MD (2020) Effects of crop residues composts on the fractions and forms of organic carbon and nitrogen in subtropical Indian conditions. Soil Res 58:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR19091
Mondal MMA, Puteh AB, Malek MA, Roy S, Yusop MR (2013) Contribution of morpho-physiological traits on yield of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik). Aus J Crop Sci 7(8):1167–1172
Moore S, Stein WH (1948) Photometric ninhydrin method for use in the chromatography of amino acids. J Biol Chem 176:367–388
Morgan JM (1984) Osmoregulation and water stress in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35:299–319
Moussa HR, Abdel-Aziz SM (2008) Comparative response of drought tolerant and drought sensitive maize genotypes to water stress. Aus J Crop Sci 1(1):31–36
Obia A, Cornelissen G, Martinsen V, Smebye AB, Mulder J (2020) Conservation tillage and biochar improve soil water content and moderate soil temperature in a tropical Acrisol. Soil Tillage Res 197:104521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104521
Palta JA, Nandwal AS, Kumari S, Turner NC (2005) Foliar nitrogen applications increase the seed yield and protein content in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) subject to terminal drought. Aust J Agric Res 56:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR04118
Ramanjulu S, Sudhakar C (2000) Proline metabolism during dehydration in two mulberry genotypes with contrasting drought tolerance. J Plant Physiol 157:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(00)80139-X
Rao SD, Dhuppar P, Biyan SC, Chintapalli B (2011) Emerging trends in lentil crop production system, profitability and global concern. Proceedings of the International Conference on Economics and Business: Analysis and Application EBA DEI, Agra
Rawat N, Sharma M, Suyal DC, Singh DK, Joshi D, Singh P, Goel R (2019) Psyhcrotolerant bio-inoculants and their co-inoculation to improve Cicer arietinum growth and soil nutrient status for sustainable mountain agriculture. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00064-5
Reddy AA (2009) Pulses production technology: status and way forward. Economic Political Weekly 44:73–80
Richard LA (1949) Pressure membrane apparatus construction and use. Agril Engg 28:451–454
Rodrigues MÂ, Grade V, Barroso V, Pereira A, Cassol LC, Arrobas M (2020) Chestnut response to organo-mineral and controlled-release fertilizers in rainfed growing conditions. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:380–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00119-7
Roy T, Biswas DR, Ghosh A, Patra AK, Singh RD, Sarkar A, Biswas SS (2019) Dynamics of culturable microbial fraction in an Inceptisol under short-term amendment with municipal sludge from different sources. Appl Soil Ecol 136:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.12.024
Sanaullah M, Blagodatskaya E, Chabbi A, Rumpel C, Kuzyakov Y (2011) Drought effects on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of grasses depend on plant community composition. Appl Soil Ecol 48(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2011.02.004
Sangakkara UR (2004) Effect of tillage and moisture levels on growth, yield and nodulation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) and mungbean (Phaseolus radiatus) in the dry season. Indian J Agron 49:60–63
Sankar B, Jaleel CA, Manivannan P, Kishorekumar A, Somasundaram R, Panneerselvam R (2007) Drought induced biochemical modifications and proline metabolism in Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. Acta Bot Croat 66(1):43–56
Sarkar A, Biswas DR, Datta SC, Roy T, Biswas SS, Ghosh A, Saha M, Moharana PC, Bhattacharyya R (2020) Synthesis of poly(vinyl alcohol) and liquid paraffin-based controlled release nitrogen-phosphorus formulations for improving phosphorus use efficiency in wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00249-3
Sarma RK, Saikia R (2014) Alleviation of drought stress in mung bean by strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa GGRJ21. Plant and Soil 377(1-2):111-126
Schimel J, Schaeffer SM (2012) Microbial control over carbon cycling in soil. Front Microbiol 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00348
Shah P, Mohammad W, Shah SM, Iqbal MM (2004) Yields and N2 fixation of lentil and chickpea as influenced by tillage and P levels under rain-fed conditions. Sarhad J Agric 20:243–249
Sharifi P, Mohammadkhani N (2016) Effects of drought stress on photosynthesis factors in wheat genotypes during anthesis. Cereal Res Commun 44(2):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1556/0806.43.2015.054
Singh AK, Meena MK, Bharati RC (2011) Sulphur and zinc nutrient management in rice-lentil cropping system. In: Proceedings of International Conference on , research for rural and agricultural development. CPRS, Patna, Bihar, pp 66–67
Singh G, Marwaha TS, Kumar D (2009) Effect of resource conserving techniques on soil microbiological activities parameters under long term maize (Zea mays) – wheat (Triticum aestivum) crop rotation. Indian J Agric Sci 79:94–100
Singh KC (2015) Rooting behaviour and actual evapotranspiration of lentil under different tillage and residue management. PhD thesis, Department of Agricultural Chemistry and Soil Science, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Mohanpur, India
Srinivasarao C, Kundu S, Grover M, Manjunath M, Sudhanshu SK, Patel JJ, Singh SR, Singh RP, Patel MM, Arunachalam A, Soam SK (2018) Effect of long term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial activities in semi-arid and sub-humid rainfed agricultural systems. Trop Ecol 59(1):99–108
Suryapani S, Umar S, Malik AA, Ahmad A (2013) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation by lentil improves biochemical characteristics and yield of intercropped wheat under low fertilizer input. J Crop Improv 27:53–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2012.727134
Thomas H, Howarth CJ (2000) Five ways to stay green. J Exp Bot 51:329–337
Torabian S, Farhangi-Abroz S, Denton MD (2019) Do tillage systems influence nitrogen fixation in legumes? A review. Soil Tillage Res 185:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.09.006
Turfani V, Narducci V, Durazzo A, Galli V, Carcea M (2017) Technological, nutritional and functional properties of wheat bread enriched with lentil or carob flours. LWT-Food Sci Technol 78:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.12.030
Ullmann KS, Meisner MH, Williams NM (2016) Impact of tillage on the crop pollinating, ground-nesting bee, Peponapis pruinosa in California. Agric Ecosyst Environ 232:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.08.002
Venkateswarlu B, Malaviya DD (2004) Performance of groundnut as influenced by land configurations and fertilizer management under rainfed conditions of south Saurashtra. Andhra Agric J 5:292–295
Walia MK, Krausz RF, Cook RL (2018) Does tillage or fertilizer provide resilience to extreme weather in southern Illinois? Agron J 110(5):2091–2097. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.11.0641
Wijewardana C, Reddy KR, Alsajri FA, Irby JT, Krutz J, Golden B (2018) Quantifying soil moisture deficit effects on soybean yield and yield components distribution pattern. Irrig Sci 36(4–5):241–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-018-0580-1
Wilkinson SC, Anderson JM, Scardelis SP, Tisiafouli M, Taylor A, Wolters V (2002) PLFA profiles of microbial communities in decomposing conifer litters subject to moisture stress. Soil Biol Biochem 34:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00168-7
Yadav SK, Jyothi Lakshmi N, Maheswari M, Vanaja M, Venkateswarlu B (2005) Influence of water deficit at vegetative, anthesis and grain filling stages on water relation and grain yield in sorghum. Indian J Plant Physiol 10:20–24
Zhu JK (2016) Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167(2):313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.029
Zuber SM, Villamil VB (2016) Meta-analysis approach to assess effect of tillage on microbial biomass and enzyme activities. Soil Biol Biochem 97:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.011
Availability of Data
All research data can be accessed by contacting the corresponding author at asiari2012@gmail.com
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All of the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Madhumonti Saha, P.K. Bandyopadhyay, Abhijit Sarkar, R. Nandi, and K.C. Singh. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Madhumonti Saha and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Conceptualization, Madhumonti Saha; Methodology, Madhumonti Saha and P.K. Bandyopadhyay;
Formal analysis and investigation: Madhumonti Saha, Abhijit Sarkar, R. Nandi, K.C. Singh
Writing—original draft preparation: Madhumonti Saha
Writing—review and editing: P.K. Bandyopadhyay, Abhijit Sarkar, Debankur Sanyal
Data curation: P.K. Bandyopadhyay, Abhijit Sarkar, R. Nandi, K.C. Singh
Resources: P.K. Bandyopadhyay
Visualization and supervision: P.K. Bandyopadhyay
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, M., Bandyopadhyay, P.K., Sarkar, A. et al. Understanding the Impacts of Sowing Time and Tillage in Optimizing the Micro-Environment for Rainfed Lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) Production in the Lower Indo-Gangetic Plain. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 2536–2551 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00319-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00319-6