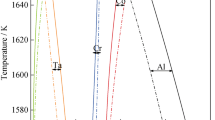
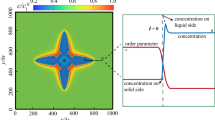
Abstract
In the present study, a two-dimensional phase field model coupled with Lattice Boltzmann method (PF-LBM) is proposed to predict the dendritic growth and motion in the melt of Fe-C binary alloy, where the phase field method (PF) is used to calculate the dendritic growth, including the phase field and the concentration field, and the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is used to calculate the flow field. The dendrite motion is determined by Newton’s Second Law and tracked by Lagrangian point in a Cartesian coordinate system. Later, the model validations were performed with the benchmark of a solid particle settlement in a stagnant fluid and particle motion in a shear flow, and the results show that the present model is capable of predicting the solid particle motion in the fluid flow. Finally, the model is adopted to investigate the dendritic growth and motion in a forced fluid flow (laminar flow or rotational flow), and the dendrite settlement in a terrestrial environment. The results show that when the forced fluid flow is a laminar flow, the free dendrite would be driven to translate, and the relative velocity between the dendrite and flow fluid decreases, resulting in weak influence of fluid flow on the dendritic growth. When the forced fluid flow is a rotational fluid flow, the dendrite would centrifugally rotate on the domain center with a counterclockwise self-spinning, and the rotation radius becomes larger and larger. For the case of dendrite settlement in a terrestrial environment, the relative movement between the dendrite and melt promotes the downward branch growth, but inhibits the upward branch growth, and two vortices form at the wake region of dendrite. Therefore, the settling dendrite shows a significant asymmetrical morphology.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ludwig, M. Wu and A. Kharicha: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 4854-4867
H. Combeau, M. Založnik, S. Hans and P. E. Richy: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 289-304.
G. Lesoult, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 413-414, pp. 19-29.
M. C. Flemings: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 833-841.
T. Schenk, H. NguyenThi, J. Gastaldi, G. Reinhart, V. Cristiglio, N. Mangelinck-Noël, H. Klein, J. Härtwig, B. Grushko, B. Billia and J. Baruchel: J. Cryst. Growth, 2005, 275, 201-208.
H. Yasuda, Y. Yamamoto, N. Nakatsuka, M. Yoshiya, T. Nagira, A. Sugiyama, I. Ohnaka, K. Uesugi and K. Umetani: Int. J. Cast Metal Res., 2013, vol. 22, pp. 15-21.
H. Yasuda, T. Nagira, M. Yoshiya, N. Nakatsuka, A. Sugiyama, K. Uesugi and K. Umetani: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 402–408.
C. R. Swaminathan and V. R. Voller: Metall. Trans. B, 1992, vol. 23, pp. 651-664.
J. Caldwell and C.-C. Chan: Appl. Math. Model., 2000, vol. 24, pp. 45-53.
V. R. Voller: Int. J Heat Mass Trans., 2008, vol. 51, pp. 823-834.
J. A. Spittle and S. G. R. Brown: J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 3989-3994.
Y. H. Shin and C. P. Hong: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 359-367.
M. F. Zhu, S. Y. Lee and C. P. Hong: Phys. Rev. E, 2004, vol. 69, pp. 061610.
M. F. Zhu, T. Dai, S. Y. Lee and C. P. Hong: Comput. Math. Appl., 2008, vol. 55, pp. 1620-1628.
S. Luo, M. Zhu and S. Louhenkilpi: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 823-830.
T. M. Rodgers, J. D. Madison and V. Tikare: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2017, vol. 135, pp. 78-89.
A. M. Ferrenberg and R. H. Swendsen: Phys. Rev. Lett., 1998, vol. 61, pp. 2635-2638.
Y. Saito and T. Ueta: Phys. Rev. A, 1989, vol. 40, pp. 3408-3419.
D. Juric and G. Tryggvason: J. Comput. Phys., 1996, vol. 123, pp. 127-148.
M. Nakagawa, Y. Natsume and K. Ohsasa: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 909-913.
Y. Yang, J. W. Garvin and H. S. Udaykumar: Int. J Heat Mass Trans., 2005, vol 48, pp. 5270-5283.
S.Pan, and M. Zhu: Acta Metall., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 340-352.
H. S. Udaykumar, S. Marella and S. Krishnan: Int. J Heat Mass Trans., 2003, vol. 46, pp. 2615-2627.
J. H. Jeong, N. Goldenfeld and J. A. Dantzig: Phys. Rev. E, 2001, vol. 64, pp. 041602.
T. Suzuki, M. Ode, S. G. Kim and W. T. Kim: J. Cryst. Growth, 2002, 237-239, 125-131.
S. G. Kim, W. T. Kim and T. Suzuki: Phys. Rev. E, 1999, vol. 60, pp. 7186-7197.
S. G. Kim, W. T. Kim and T. Suzuki: Phys. Rev. E, 1998, vol. 58, pp. 3316-3323.
W. J. Boettinger, J. A. Warren, C. Beckermann and A. Karma: Rev. Mater. Res., 2002, vol. 32, pp. 163-194.
C. Beckermann, H. J. Diepers, I. Steinbach, A. Karma and X. Tong: J. Comput. Phys., 1999, vol. 154, pp. 468-496.
S. Luo and M. Y. Zhu: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 71, pp. 10-18.
W. Wang, S. Luo and M. Zhu: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 95, pp. 136-148.
D. Chatterjee and S. Chakraborty: Phys Lett. A, 2006, 351, 359-367.
D. Sun, M. Zhu, S. Pan and D. Raabe: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 1755-1767.
B. Jelinek, M. Eshraghi, S. Felicelli and J. F. Peters: Comput. Phys Commun., 2014, 185, 939-947.
35. A. Zhang, J. Du, Z. Guo, Q. Wang and S. Xiong: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 3603-3615.
J. Zhang: Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2011,vol. 10, pp. 1-28.
R. H. H. Abadi,, M.H. Rahimian and A. Fakhari: J. Comput. Phys., 2018, vol. 374, pp. 668-691.
H. Liang, Z. H. Chai, B. C. Shi, Z. L. Guo and T. Zhang: Phys. Rev. E, 2014, 90, 063311.
P. M. Raja, S. Sarkara, S. Chakrabortya, G. Phanikumarb, P. Duttaa and K. Chattopadhyay: Int. J Heat Fluid Fl., 2002, vol. 23, pp. 298-307.
Chakraborty N, Chakraborty S (2007) Int J Heat Mass Trans 50(9):1805-1822.
W. Miller, I. Rasin and S. Succi: Physica A, 2006, vol. 362, pp. 78-83.
M. Do-Quang and G. Amberg: J. Comput. Phys., 2008, vol. 227, pp. 1772-1789.
S. Karagadde, A. Bhattacharya, G. Tomar and P. Dutta: J. Comput. Phys., 2012, vol. 231, pp. 3987-4000.
D. Medvedev, F. Varnik and I. Steinbach: Procedia Comput. Sci., 2013, vol. 18, pp. 2512-2520.
R. Rojas, T. Takaki and M. Ohno: J. Comput. Phys., 2015, vol. 298, pp. 29-40.
T. Takaki, R. Sato, R. Rojas, M. Ohno and Y. Shibuta: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2018, vol. 147, pp. 124-131.
X. B. Qi, Y. Chen, X. H. Kang, D. Z. Li and T. Z. Gong: Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, pp. 45770.
L. Rátkai, T. Pusztai and L. Gránásy: npj Compu. Mater., 2019, vol. 5, pp. 113.
E. G. Flekkøy: Phys. Rev. E, 1993, vol. 47, pp. 4247-4257.
O. Behrend, R. Harris and P. B. Warren: Phys. Rev. E, 1994, vol. 50, pp. 4586-4595.
J. Feng, H. H. Hu and D. D. Joseph: J. Fluid Mech., 1994, vol. 277, pp. 271-301.
L. Liu, S. Pian, Z. Zhang, Y. Bao, R. Li and H. Chen: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2018, vol. 146, pp. 9-17.
X. H. Wang and Y. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 800-812.
M. Ode, T. Suzuki, S. G. Kim and W. T. Kim: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2000, vol. 1, pp. 43-49.
S. Okano, T. Nishimura, H. Ooi and T. Chino: J-STAGE, 1975, vol. 61, pp. 2982-2990.
K. Murakami, H. Aihara and T. Okamoto: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 933-939.
W. Kurz, B. Giovanola and R. Trivedi: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 823-830.
58. P. Bouissou and P. Pelcé: Phys. Rev. A, 1989, vol. 40, pp. 6673-6680.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of National Key Research and Development Plan (Grant Nos. 2017YFB0304100, 2016YFB0300105), National Natural Science of China (Grant Nos. 51674072, 51704151, 51804067) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. N182504014, N170708020, N172503013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted February 21, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, S., Wang, P., Wang, W. et al. PF-LBM Modelling of Dendritic Growth and Motion in an Undercooled Melt of Fe-C Binary Alloy. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2268–2284 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01925-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01925-6