Abstract
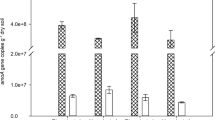
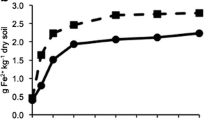
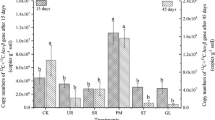
The biological nitrogen fixation in planted and nonplanted paddy soils was quantified using a chamber-based 15N2-labeling technique, and the active diazotrophs of soil were assessed by 15N2-DNA-stable isotope probing (SIP). In addition, the nanometer scale secondary ion mass spectrometry (NanoSIMS) was applied to analysis the 15N-enrichment of soil DNA in SIP fractions. 15N2-labeling experiment showed that BNF was 11.33 ± 1.90 kg N ha−1 in the rice-planted soil and 3.55 ± 1.18 kg N ha−1 in the nonplanted soil after 28-day labeling. The biologically fixed 15N was mainly (> 95%) recovered in the surface layer (0–0.5 cm) in the rice-planted soil. High throughput sequencing of nifH genes extracted from surface soil showed that the presence of rice affected the community composition of diazotrophs. The relative abundance of Nostocales and Stigonematales was significantly higher in rice-planted soil than in nonplanted soil (P < 0.05). After CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation, NanoSIMS images clearly showed that 15N was incorporated into soil DNA in the 15N2-labeling SIP gradient fractions. Analyses of nifH genes in 15N-enriched SIP gradient fractions suggested that Nostocales and Stigonematales were the major contributors to BNF in the rice-soil system. Taken together, these results have highlighted the contributions of cyanobacteria to the BNF in paddy fields and improved our understanding of the close relationship between rice plants and cyanobacteria.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auclair J, Lepine F, Villemur R (2012) A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to measure 13C-isotope enrichment for DNA stable-isotope probing. Can J Microbiol 58:287–292
Bei Q, Liu G, Tang H, Cadisch G, Rasche F, Xie Z (2013) Heterotrophic and phototrophic 15N2 fixation and distribution of fixed 15N in a flooded rice-soil system. Soil Biol Biochem 59:25–31
Birnie GD (1978) Isopycnic centrifugation in ionic media. In: Birnie GD, Rickwood D (eds) Centrifugal Separations in Molecular and Cell Biology. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 169–217
Bonnet S, Berthelot H, Turk-Kubo K, Cornet-Barthaux V, Fawcett S, Berman-Frank I, Barani A, Grégori G, Dekaezemacker J, Benavides M, Capone DG (2016) Diazotroph derived nitrogen supports diatom growth in the South West Pacific: a quantitative study using nanoSIMS. Limnol Oceanogr 61:1549–1562
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu S-F, Nelson TA (2007a) Stable isotope probing with 15N2 reveals novel noncultivated diazotrophs in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3196–3204
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu S-F, Nelson TA (2007b) Stable isotope probing with 15N achieved by disentangling the effects of genome G + C content and isotope enrichment on DNA density. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3189–3195
Burgmann H, Meier S, Bunge M, Widmer F, Zeyer J (2005) Effects of model root exudates on structure and activity of a soil diazotroph community. Environ Microbiol 7:1711–1724
Cadisch G, Espana M, Causey R, Richter M, Shaw E, Morgan JA, Rahn C, Bending GD (2005) Technical considerations for the use of 15N-DNA stable-isotope probing for functional microbial activity in soils. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:1424–1428
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Collavino MM, Tripp HJ, Frank IE, Vidoz ML, Calderoli PA, Donato M, Zehr JP, Aguilar OM (2014) NifH pyrosequencing reveals the potential for location-specific soil chemistry to influence N2-fixing community dynamics. Environ Microbiol 16:3211–3223
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Estrada GA, Baldani VLD, de Oliveira DM, Urquiaga S, Baldani JI (2013) Selection of phosphate-solubilizing diazotrophic Herbaspirillum and Burkholderia strains and their effect on rice crop yield and nutrient uptake. Plant Soil 369:115–129
Filho BD, Gano KA, Binz A, Lima RF, Aguilar LM, Ramirez A, Caballero-Mellado J, Sá E, Giongo A (2014) Rhizobia enhance growth in rice plants under flooding conditions. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 14:707–718
Finzi-Hart JA, Pett-Ridge J, Weber PK, Popa R, Fallon SJ, Gunderson T, Hutcheon ID, Nealson KH, Capone DG (2009) Fixation and fate of C and N in the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium using nanometer-scale secondary ion mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:6345–6350
Fish JA, Chai B, Wang Q, Sun Y, Brown CT, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2013) FunGene: the functional gene pipeline and repository. Front Microbiol 4:291
Foster RA, Kuypers MM, Vagner T, Paerl RW, Musat N, Zehr JP (2011) Nitrogen fixation and transfer in open ocean diatom-cyanobacterial symbioses. ISME J 5:1484–1493
Gaby JC, Buckley DH (2012) A comprehensive evaluation of PCR primers to amplify the nifH gene of nitrogenase. PLoS One 7:e42149
Guerquin-Kern J-L, Wu T-D, Quintana C, Croisy A (2005) Progress in analytical imaging of the cell by dynamic secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS microscopy). Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj 1724:228–238
Habte M, Alexander M (1980) Nitrogen fixation by photosynthetic bacteria in lowland rice culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:342–347
James E (2000) Nitrogen fixation in endophytic and associative symbiosis. Field Crop Res 65:197–209
Ji SH, Gururani MA, Chun SC (2014) Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting endophytic diazotrophic bacteria from Korean rice cultivars. Microbiol Res 169:83–98
Khan ZU, Begum ZNT, Mandal R, Hossain MZ (1994) Cyanobacteria in rice soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 10:296–298
Knauth S, Hurek T, Brar D, Reinhold-Hurek B (2005) Influence of different Oryza cultivars on expression of nifH gene pools in roots of rice. Environ Microbiol 7:1725–1733
Laborte AG, de Bie KC, Smaling EM, Moya PF, Boling AA, Van Ittersum MK (2012) Rice yields and yield gaps in Southeast Asia: Past trends and future outlook. Eur J Agron 36:9–20
Ladha JK, Reddy PM (2003) Nitrogen fixation in rice systems: state of knowledge and future prospects. Plant Soil 252:151–167
Lee K-K, Castro T, Yoshida T (1977) Nitrogen fixation throughout growth, and varietal differences in nitrogen fixation by the rhizosphere of rice planted in pots. Plant Soil 48:613–619
Li R, Watanabe MM (2002) DNA base composition of planktonic species of Anabaena (Cyanobacteria) and its taxonomic value. J Gen Appl Microbiol 48:77–82
Lueders T, Manefield M, Friedrich MW (2004) Enhanced sensitivity of DNA- and rRNA-based stable isotope probing by fractionation and quantitative analysis of isopycnic centrifugation gradients. Environ Microbiol 6:73–78
Ma J, Bei Q, Wang X, Lan P, Liu G, Lin X, Liu Q, Lin Z, Liu B, Zhang Y, Jin H, Hu T, Zhu J, Xie Z (2019) Impacts of Mo application on biological nitrogen fixation and diazotrophic communities in a flooded rice-soil system. Sci Total Environ 649:686–694
Mårtensson L, Díez B, Wartiainen I, Zheng W, El-Shehawy R, Rasmussen U (2009) Diazotrophic diversity, nifH gene expression and nitrogenase activity in a rice paddy field in Fujian, China. Plant Soil 325:207–218
Martínez-Pérez C, Mohr W, Löscher CR, Dekaezemacker J, Littmann S, Yilmaz P, Lehnen N, Fuchs BM, Lavik G, Schmitz RA, LaRoche J, Kuypers MMM (2016) The small unicellular diazotrophic symbiont, UCYN-A, is a key player in the marine nitrogen cycle. Nat Microbiol 1:16163
Neufeld JD, Vohra J, Dumont MG, Lueders T, Manefield M, Friedrich MW, Murrell JC (2007) DNA stable-isotope probing. Nat Protoc 2:860–866
Nilsson M, Bhattacharya J, Rai AN, Bergman B (2002) Colonization of roots of rice (Oryza sativa) by symbiotic Nostoc strains. New Phytol 156:517–525
Parks DH, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P, Beiko RG (2014) STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30:3123–3124
Pepe-Ranney C, Koechli C, Potrafka R, Andam C, Eggleston E, Garcia-Pichel F, Buckley DH (2016) Non-cyanobacterial diazotrophs mediate dinitrogen fixation in biological soil crusts during early crust formation. ISME J 10:287–298
Poly F, Monrozier LJ, Bally R (2001) Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res Microbiol 152:95–103
Prasanna R, Nayak S (2007) Influence of diverse rice soil ecologies on cyanobacterial diversity and abundance. Wetl Ecol Manag 15:127–134
Prasanna R, Jaiswal P, Nayak S, Sood A, Kaushik BD (2009) Cyanobacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of rice and its ecological significance. Indian J Microbiol 49:89–97
Prasanna R, Chaudhary V, Gupta V, Babu S, Kumar A, Singh R, Shivay YS, Nain L (2013) Cyanobacteria mediated plant growth promotion and bioprotection against Fusarium wilt in tomato. Eur J Plant Pathol 136:337–353
Priya H, Prasanna R, Ramakrishnan B, Bidyarani N, Babu S, Thapa S, Renuka N (2015) Influence of cyanobacterial inoculation on the culturable microbiome and growth of rice. Microbiol Res 171:78–89
Radajewski S, Ineson P, Parekh NR, Murrell JC (2000) Stable-isotope probing as a tool in microbial ecology. Nature 403:646–649
Radajewski S, McDonald IR, Murrell JC (2003) Stable-isotope probing of nucleic acids: a window to the function of uncultured microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:296–302
Rana A, Joshi M, Prasanna R, Shivay YS, Nain L (2012) Biofortification of wheat through inoculation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and cyanobacteria. Eur J Soil Biol 50:118–126
Rangel-Castro JI, Killham K, Ostle N, Nicol GW, Anderson IC, Scrimgeour CM, Ineson P, Meharg A, Prosser JI (2005) Stable isotope probing analysis of the influence of liming on root exudate utilization by soil microorganisms. Environ Microbiol 7:828–838
Roger P-A, Santiago-Ardales S, Reddy P, Watanabe I (1987) The abundance of heterocystous blue-green algae in rice soils and inocula used for application in rice fields. Biol Fertil Soils 5:98–105
Shu W, Pablo GP, Jun Y, Danfeng H (2012) Abundance and diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in rhizosphere and bulk paddy soil under different duration of organic management. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:493–503
Slodzian G, Daigne B, Girard F, Boust F, Hillion F (1992) Scanning secondary ion analytical microscopy with parallel detection. Biol Cell 74:43–50
Song T, Martensson L, Eriksson T, Zheng W, Rasmussen U (2005) Biodiversity and seasonal variation of the cyanobacterial assemblage in a rice paddy field in Fujian, China. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:131–140
Tan Z, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2003) Effect of N-fertilization, plant genotype and environmental conditions on nifH gene pools in roots of rice. Environ Microbiol 5:1009–1015
Tirol AC, Roger PA, Watanabe I (1982) Fate of nitrogen from a blue-green alga in a flooded rice soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 28:559–569
Tu Q, Zhou X, He Z, Xue K, Zhou J (2015) The diversity and co-occurrence patterns of N2-fixing communities in a CO2-enriched grassland ecosystem. Microb Ecol 71:604–615
Ventura W, Watanabe I (1983) 15N dilution technique of assessing the contribution of nitrogen fixation to rice plant. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 29:123–131
Wang Q, Quensen JF 3rd, Fish JA, Lee TK, Sun Y, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2013) Ecological patterns of nifH genes in four terrestrial climatic zones explored with targeted metagenomics using FrameBot, a new informatics tool. MBio 4:e00592–e00513
Wang X, Liu B, Ma J, Zhang Y, Hu T, Zhang H, Feng Y, Pan H, Xu Z, Liu G, Lin X, Zhu J, Bei Q, Xie Z (2019) Soil aluminum oxides determine biological nitrogen fixation and diazotrophic communities across major types of paddy soils in China. Soil Biol Biochem 131:81–89
Warembourg FR (1993) Nitrogen fixation in soil and plant systems. In: Knowles R, Blackburn TH (eds) Nitrogen isotope techniques. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 127–156
Wartiainen I, Eriksson T, Zheng W, Rasmussen U (2008) Variation in the active diazotrophic community in rice paddy-nifH PCR-DGGE analysis of rhizosphere and bulk soil. Appl Soil Ecol 39:65–75
Wilhelm R, Szeitz A, Klassen TL, Mohn WW (2014) Sensitive, efficient quantitation of 13C-enriched nucleic acids via ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for applications in stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7206–7211
Woebken D, Burow LC, Prufert-Bebout L, Bebout BM, Hoehler TM, Pett-Ridge J, Spormann AM, Weber PK, Singer SW (2012) Identification of a novel cyanobacterial group as active diazotrophs in a coastal microbial mat using NanoSIMS analysis. ISME J 6:1427–1439
Xu Y, Zinner E, Gallino R, Heger A, Pignatari M, Lin Y (2015) Sulfur isotope compositions of submicrometer SiC grains from the Murchison meteorite. Astrophys J 799:156
Xu Y, Ge Y, Song J, Rensing C (2019) Assembly of root-associated microbial community of typical rice cultivars in different soil types. Biol Fertil Soils 56:249–260
Xun W, Li W, Huang T, Ren Y, Xiong W, Miao Y, Ren W, Li D, Shen Q, Zhang R (2018) Long-term agronomic practices alter the composition of asymbiotic diazotrophic bacterial community and their nitrogen fixation genes in an acidic red soil. Biol Fertil Soils 54:329–339
Zhang J, Kobert K, Flouri T, Stamatakis A (2014) PEAR: a fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 30:614–620
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yufang Sun for help on 15N-enrichment analysis of gas samples, and our colleagues from the research group (other than the authors) for help on the DNA-SIP experiment. We are grateful for computation resources from the High Performance Computing System at National Engineering Laboratory of Soil Pollution Control and Remediation Technologies, CAS Key Laboratory of Soil Environment and Pollution Remediation, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Prof Paolo Nannipieri and the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31870500, 41501273), the Special Project on the Basis of National Science and Technology of China (2015FY110700), the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-EW-409), and Technology Supporting Project of Jiangsu Province (BE2013451).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
An overview of the experimental setup and used procedures (PDF 340 kb)
Fig. S2
15N-enrichment of N2 in the 15 N2-labeled chamber (DOCX 93 kb)
Fig. S3
NanoSIMS images (12C14N− and 12C15N−/12C14N−) of soil DNA in the 15 N2-labeling gradient fractions (#1~#12) from 15 N2-DNA-SIP. The colored bars indicate the total ion counts of 12C14N− and the isotopic ratio of 12C15N−/12C14N− in a 30 × 30 μm2 area. Scale bars represent 2 μm. The white outlines indicate regions of hot spots, which were used to estimate the highest 15 N−/14 N− ratios of the DNA. The 15 N enrichment of DNA in SIP gradient fractions was depicted in atom% 15 N (DOCX 1973 kb)
Fig. S4
The nifH gene copy numbers in each SIP gradient fraction derived from 15 N2-labeling and nonlabeling treatments (DOCX 46 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
ESM 2
(DOCX 40 kb)
ESM 3
(DOCX 20 kb)
ESM 4
(DOCX 19 kb)
ESM 5
(DOCX 16 kb)
ESM 6
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Bei, Q., Yang, W. et al. Unveiling of active diazotrophs in a flooded rice soil by combination of NanoSIMS and 15N2-DNA-stable isotope probing. Biol Fertil Soils 56, 1189–1199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01497-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01497-2