Abstract
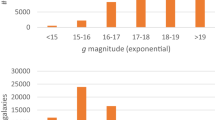
The distribution of spin directions of \(\sim 6.4\cdot 10^{4}\) SDSS spiral galaxies with spectra was examined, and compared to the distribution of \(\sim 3.3\cdot 10^{4}\) Pan-STARRS galaxies. The analysis shows a statistically significant asymmetry between the number of SDSS galaxies with opposite spin directions, and the magnitude and direction of the asymmetry changes with the direction of observation and with the redshift. The redshift dependence shows that the distribution of the spin direction of SDSS galaxies becomes more asymmetric as the redshift gets higher. Fitting the distribution of the galaxy spin directions to a quadrupole alignment provides fitness with statistical significance \(>5\sigma \), which grows to \(>8\sigma \) when just galaxies with \(z>0.15\) are used. Similar analysis with Pan-STARRS galaxies provides dipole and quadrupole alignments nearly identical to the analysis of SDSS galaxies, showing that the source of the asymmetry is not necessarily a certain unknown flaw in a specific telescope system. While these observations are clearly provocative, there is no known error that could exhibit itself in such form. The data analysis process is fully automatic, and uses deterministic and symmetric algorithms with defined rules. It does not involve either manual analysis that can lead to human perceptual bias, or machine learning that can capture human biases or other subtle differences that are difficult to identify due to the complex nature of machine learning processes. Also, an error in the galaxy annotation process is expected to show consistent bias in all parts of the sky, rather than change with the direction of observation to form a clear and definable pattern.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghanim, N., Armitage-Caplan, C., Arnaud, M., Ashdown, M., Atrio-Barandela, F., Aumont, J., Baccigalupi, C., Banday, A., Barreiro, R., Bartlett, J., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 571, 27 (2014)
Ben-David, A., Kovetz, E.D., Itzhaki, N.: Astrophys. J. 748(1), 39 (2012)
Bengaly, C.A., Maartens, R., Santos, M.G.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018(04), 031 (2018)
Bennett, C.L., Bay, M., Halpern, M., Hinshaw, G., Jackson, C., Jarosik, N., Kogut, A., Limon, M., Meyer, S., Page, L., et al.: Astrophys. J. 583(1), 1 (2003)
Biagetti, M., Orlando, G.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020(7), 5 (2020)
Blum, R.D., Burleigh, K., Dey, A., Schlegel, D.J., Meisner, A.M., Levi, M., Myers, A.D., Lang, D., Moustakas, J., Patej, A., et al.: In: American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts# 228, vol. 228, 2016
Bohmer, C.G., Mota, D.F.: Phys. Lett. B 663(3), 168 (2008)
Campanelli, L., Cea, P., Tedesco, L.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(13), 131302 (2006)
Campanelli, L., Cea, P., Tedesco, L.: Phys. Rev. D 76(6), 063007 (2007)
Chechin, L.: Astron. Rep. 60(6), 535 (2016)
Cline, J.M., Crotty, P., Lesgourgues, J.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2003(09), 010 (2003)
Cooray, A., Melchiorri, A., Silk, J.: Phys. Lett. B 554(1-2), 1 (2003)
Dojcsak, L., Shamir, L.: New Astron. 28, 1 (2014)
Efstathiou, G.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 343(4), 95 (2003)
Ellis, G.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 11(4), 281 (1979)
Eriksen, H.K., Hansen, F.K., Banday, A.J., Górski, K.M., Lilje, P.B.: Astrophys. J. 605(1), 14 (2004)
Feng, B., Zhang, X.: Phys. Lett. B 570(3-4), 145 (2003)
Font-Ribera, A., McDonald, P., Mostek, N., Reid, B.A., Seo, H.-J., Slosar, A.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014(05), 023 (2014)
Gödel, K.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 21(3), 447 (1949)
Gordon, C., Hu, W.: Phys. Rev. D 70(8), 083003 (2004)
Gruppuso, A.: Phys. Rev. D 76(8), 083010 (2007)
Hoehn, C., Shamir, L.: Astron. Notes 335(2), 189 (2014)
Hu, W., White, M.: arXiv preprint, arXiv:astro-ph/9706147 (1997)
Iye, M., Sugai, H.: Astrophys. J. 374, 112 (1991)
Iye, M., Tadaki, K., Fukumoto, H.: Astrophys. J. 886(2), 133 (2019)
Javanmardi, B., Kroupa, P.: Astron. Astrophys. 597, 120 (2017)
Javanmardi, B., Porciani, C., Kroupa, P., Pflam-Altenburg, J.: Astrophys. J. 810(1), 47 (2015)
Jiménez, J.B., Maroto, A.L.: Phys. Rev. D 76(2), 023003 (2007)
Kroupa, P.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 29(4), 395 (2012)
Kuminski, E., Shamir, L.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 223(2), 20 (2016)
Land, K., Slosar, A., Lintott, C., Andreescu, D., Bamford, S., Murray, P., Nichol, R., Raddick, M.J., Schawinski, K., Szalay, A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 388(4), 1686 (2008)
Lee, J.H., Pak, M., Song, H., Lee, H.-R., Kim, S., Jeong, H.: Astrophys. J. 884(2), 104 (2019)
Longo, M.J.: Phys. Lett. B 699(4), 224 (2011)
Mészáros, A.: Astron. Notes 340(7), 564 (2019)
Ozsváth, I., Schücking, E.: Nature 193(4821), 1168 (1962)
Ozsvath, I., Schücking, E.: Class. Quantum Gravity 18(12), 2243 (2001)
Piao, Y.-S.: Phys. Rev. D 71(8), 087301 (2005)
Piao, Y.-S., Feng, B., Zhang, X.: Phys. Rev. D 69(10), 103520 (2004)
Puerari, I., Garcia-Gomez, C., Garijo, A.: arXiv preprint, arXiv:astro-ph/9709236 (1997)
Rodrigues, D.C.: Phys. Rev. D 77(2), 023534 (2008)
Shamir, L.: Astrophys. J. 736(2), 141 (2011a)
Shamir, L.: The Astrophysics Source Code Library, 1105 (2011b)
Shamir, L.: Phys. Lett. B 715(1-3), 25 (2012)
Shamir, L.: Galaxies 1(3), 210 (2013)
Shamir, L.: arXiv preprint, arXiv:1601.04424v1 [astro-ph] (2016a)
Shamir, L.: Astrophys. J. 823(1), 32 (2016b)
Shamir, L.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 362(2), 33 (2017a)
Shamir, L.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 34, 44 (2017b)
Shamir, L.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 34, 011 (2017c)
Shamir, L.: Open Astron. J. 29(1), 15 (2020a)
Shamir, L.: In: 236th AAS Meeting, vol. 336, p. 02 (2020b)
Shamir, L.: Astron. Notes 341(3), 324 (2020c)
Sivaram, C., Arun, K.: Open Astron. J. 5, 7 (2012)
Slosar, A., Land, K., Bamford, S., Lintott, C., Andreescu, D., Murray, P., Nichol, R., Raddick, M.J., Schawinski, K., Szalay, A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 392(3), 1225 (2009)
Smoot, G.F., Gorenstein, M.V., Muller, R.A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 39(14), 898 (1977)
Sofue, Y.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 44, 1 (1992)
Timmis, I., Shamir, L.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 231(1), 2 (2017)
Weeks, J., Luminet, J.-P., Riazuelo, A., Lehoucq, R.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 352(1), 258 (2004)
Yu, H.-R., Motloch, P., Pen, U.-L., Yu, Y., Wang, H., Mo, H., Yang, X., Jing, Y.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 124(10), 101302 (2020)
Zhe, C., Xin, L., Sai, W.: Chin. Phys. C 39(5), 055101 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by NSF grants AST-1903823 and IIS-1546079. Funding for the Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV has been provided by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science, and the Participating Institutions. SDSS-IV acknowledges support and resources from the Center for High-Performance Computing at the University of Utah. The SDSS web site is www.sdss.org.
SDSS-IV is managed by the Astrophysical Research Consortium for the Participating Institutions of the SDSS Collaboration including the Brazilian Participation Group, the Carnegie Institution for Science, Carnegie Mellon University, the Chilean Participation Group, the French Participation Group, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, The Johns Hopkins University, Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (IPMU) / University of Tokyo, the Korean Participation Group, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP), Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie (MPIA Heidelberg), Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik (MPA Garching), Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), National Astronomical Observatories of China, New Mexico State University, New York University, University of Notre Dame, Observatário Nacional / MCTI, The Ohio State University, Pennsylvania State University, Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, United Kingdom Participation Group, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, University of Arizona, University of Colorado Boulder, University of Oxford, University of Portsmouth, University of Utah, University of Virginia, University of Washington, University of Wisconsin, Vanderbilt University, and Yale University.
The Pan-STARRS1 Surveys (PS1) and the PS1 public science archive have been made possible through contributions by the Institute for Astronomy, the University of Hawaii, the Pan-STARRS Project Office, the Max-Planck Society and its participating institutes, the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Garching, The Johns Hopkins University, Durham University, the University of Edinburgh, the Queen’s University Belfast, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network Incorporated, the National Central University of Taiwan, the Space Telescope Science Institute, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under Grant No. NNX08AR22G issued through the Planetary Science Division of the NASA Science Mission Directorate, the National Science Foundation Grant No. AST-1238877, the University of Maryland, Eotvos Lorand University (ELTE), the Los Alamos National Laboratory, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamir, L. Patterns of galaxy spin directions in SDSS and Pan-STARRS show parity violation and multipoles. Astrophys Space Sci 365, 136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-020-03850-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-020-03850-1