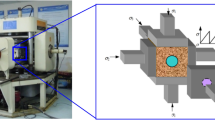
Abstract
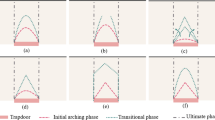
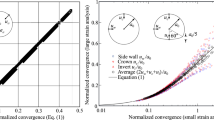
To determine the distribution of active earth pressure on retaining walls, a series of model tests with the horizontally translating rigid walls are designed. Particle image velocimetry is used to study the movement and shear strain during the active failure of soil with height H and friction angle ϕ. The test results show that there are 3 stages of soil deformation under retaining wall translation: the initial stage, the expansion stage and the stability stage. The stable sliding surface in the model tests can be considered to be composed of two parts. Within the height range of 0.82H–1.0H, it is a plane at an angle of π/4+ϕ/2 to the horizontal plane. In the height range of 0–0.82H, it is a curve between a logarithmic spiral and a plane at an angle of π/4+ϕ/2 to the horizontal. A new method applicable to any sliding surface is proposed for active earth pressure with the consideration of arching effect. The active earth pressure is computed with the actual shape of the slip surface and compared with model test data and with predictions obtained by existing methods. The comparison shows that predictions from the newly proposed method are more consistent with the measured data than the predictions from the other methods.
摘要
为研究挡土墙主动土压力分布规律,本文开展了刚性挡土墙平动模型试验,利用颗粒图像测速 技术研究高度为H、内摩擦角为ϕ 的无黏性土体在主动破坏过程中的位移和剪应变发展规律。试验结 果表明,挡土墙发生平移时的土体变形可划分三个阶段:初始阶段,发展阶段和稳定阶段。稳定阶段 的土体滑裂面由两部分组成,在0.82H~1.0H 高度范围内,滑裂面为与水平面成π/4+ϕ/2 的平面,在 0~0.82H 高度范围内的滑裂面为曲面,该曲面处在对数螺旋面和与水平面成π/4+ϕ/2 的平面所夹区域 之中。本文考虑土拱效应,基于差分法提出了适用于任意滑裂面形状的主动土压力计算方法,并根据 实际滑裂面计算了土体主动土压力理论值。在此基础上,将本文方法得到的理论值与实验数据及其他 方法计算的理论值进行对比,验证了本文所提出方法的有效性。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Y Z. Distribution of earth pressure on a retaining wall [J]. Geotechnique, 2000, 50(1): 83–88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2000.50.1.83.
YANG Gui, WANG Yang-yang, LIU Yan-chen. Analysis of active earth pressure on retaining walls based on curved sliding surface [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(8): 2182–2188. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.08.004. (in Chinese)
CAO Zhen-ming. Active earth pressure analysis on retaining wall with sliding surface of filling curve [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1995, 8(1): 7–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19721/j.cnki.10017372.1995.s1.002. (in Chinese)
WANG Kui-hua, MA Shao-jun, WU Wen-bing. Active earth pressure of cohesive soil backfill on retailing wall with curved sliding surface [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(5): 732–738. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.05.004. (in Chinese)
YANG Ming-hui, DAI Xia-bin, ZHAO Ming-hua, LUO Hong. Calculation of active earth pressure for limited soils with curved sliding surface [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(7): 2029–2035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.07.024. (in Chinese)
TSAGARELI Z V. Experimental investigation of the pressure of a loose medium on retaining walls with a vertical back face and horizontal backfill surface [J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 1965, 2(4): 197–200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01706095.
HARROP-WILLIAMS K. Arch in soil arching [J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1989, 115(3): 415–419. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:3(302).
FANG Y S, ISHIBASHI I. Static earth pressures with various wall movements [J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1986, 112(3): 317–333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1986)112:3(317).
GOEL S, PATRA N R. Effect of arching on active earth pressure for rigid retaining walls considering translation mode [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 8(2): 123–133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2008)8:2(123).
PAIK K H, SALGADO R. Estimation of active earth pressure against rigid retaining walls considering arching effects [J]. Geotechnique, 2003, 53(7): 643–654. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2003.53.7.643.
KHOSRAVI M H, PIPATPONGSA T, TAKEMURA J. Theoretical analysis of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls under translation mode [J]. Soils and Foundations, 2016, 56(4): 664–675. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2016.07.007.
KHOSRAVI M H, KARGAR A R, AMINI M. Active earth pressures for non-planar to planar slip surfaces considering soil arching [J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018: 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2018.1503439.
ZHOU Y T, CHEN Q, CHEN F. Active earth pressure on translating rigid retaining structures considering soil arching effect [J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(8): 910–926. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2016.1229225.
ZHOU Q Y, ZHOU Y T, WANG X M. Estimation of active earth pressure on a translating rigid retaining wall considering soil arching effect [J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 2018, 48(3): 541–548. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-017-0252-8.
RAO P, CHEN Q, ZHOU Y, NIMBALKAR S, CHIARO G. Determination of active earth pressure on rigid retaining wall considering arching effect in cohesive backfill soil [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2015, 16(3): 1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000589.
WHITE D J, TAKE W A, BOLTON M D. Soil deformation measurement using particle image velocimetry (PIV) and photogrammetry [J]. Geotechnique, 2003, 53(7): 619–631. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.53.7.619.37383.
WHITE D, RANDOLPH M, THOMPSON B. An image-based deformation measurement system for the geotechnical centrifuge [J]. International Journal of Physical Modelling in Geotechnics, 2005, 5(3): 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/ijpmg.2005.050301.
MAHMOUDIMEHRIZI M, DAGHIGH Y, NAZARIAFSHAR J. Physical modeling of the helical anchor walls’ behavior using particle image velocity [J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 2019: 1–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-019-00397-z.
SALEHI ALAMDARI N, KHOSRAVI M, KATEBI H. Distribution of lateral active earth pressure on a rigid retaining wall under various motion modes [J]. International Journal of Mining and Geo-Engineering, 2020, 54(1): 15–25. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22059/ijmge.2019.280916.594805.
NIEDOSTATKIEWICZ M, LESNIEWSKA D, TEJCHMAN J. Experimental analysis of shear zone patterns in cohesionless for earth pressure problems using particle image velocimetry [J]. Strain, 2011, 47: 218–231. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1305.2010.00761.x
KHOSRAVI M H, PIPATPONGSA T, TAKEMURA J. Experimental analysis of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls under translation mode [J]. Géotechnique, 2013, 63(12): 1020–1028. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.12.P.021.
PATEL S, DEB K. Study of active earth pressure behind a vertical retaining wall subjected to rotation about the base [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(4): 402–408. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001639.
NAZHAT Y, AIREY D. The kinematics of granular soils subjected to rapid impact loading [J]. Granular Matter, 2015, 17(1): 1–20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-014-0544-y.
AUBRAM D. Development and experimental validation of an arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) method for soil mechanics [J]. Geotechnik, 2015, 38(3): 193–204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/gete.201400030.
ZENG L, XIAO L Y, ZHANG J H, FU H Y. The Role of Nanotechnology in Subgrade and Pavement Engineering: A Review [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2020, 20: 4607–4618. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.18491.
ZHANG J H, LI F, ZENG L, PENG J H, LI J. Numerical simulation of the moisture migration of unsaturated clay embankments in southern China considering stress state [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020: 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01916-6.
ZENG L, YAO X F, ZHANG J H, GAO Q F, CHEN J C, GUI Y T. Ponded infiltration and spatial-temporal prediction of the water content of silty mudstone [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020: 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01880-1.
YING Hong-wei, ZHANG Jin-hong, WANG Xiao-gang, LI Bing-he, ZHU Wei. Experimental analysis of passive earth pressure against rigid retaining wall under translation mode for finite soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(6): 978–986. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201606002. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51978084, 51678073) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2020JJ4605) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project(2019IC13) supported by the International Cooperation and Development Project of Double First-Class Scientific Research in Changsha University of Science & Technology, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Zm., Liu, Zf., Liu, Xh. et al. Improved method for determining active earth pressure considering arching effect and actual slip surface. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 2032–2042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4428-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4428-5