Abstract
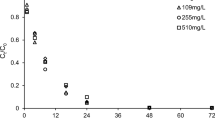
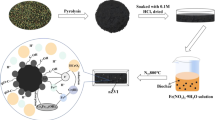
This study investigated the feasibility and mechanism of sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on biochar (S-nZVI@BC) for the removal of TCE in the scenario of groundwater remediation. The effects of some critical factors, including pyrolysis temperature of biochar, mass ratio of S-nZVI to BC, initial pH, typical groundwater compositions, co-contaminants, and particle aging time, on the TCE removal were examined. The results revealed that the different pyrolysis temperatures could change physicochemical properties of BC, which influenced the TCE adsorption and degradation by S-nZVI@BC. The mass ratio of S-nZVI to BC could determine the extent of adsorption and degradation of TCE. The total removal of TCE was not significantly influenced by the initial pH (3.0–9.0), but the degradation of TCE was enhanced at higher pH. Notably, the typical anions (SO42−, HCO3−, and HPO42−), humic acid, and co-contaminants (Cr(VI) and NO3−) in groundwater all slightly influenced the total removal of TCE, but markedly inhibited its degradation. Additionally, after exposure to air over different times (5 days, 10 days, 20 days, and 30 days), the reactivity of S-nZVI@BC composites was apparently decreased due to surface passivation. Nevertheless, the aged S-nZVI@BC composites still maintained relative high removal and degradation of TCE when the reaction time prolonged. Overall, the results showed that the S-nZVI@BC, combining the high adsorption capacity of BC and the high reductive capacity of S-nZVI, had a much better performance than the single S-nZVI or BC, suggesting that S-nZVI@BC is one promising material for the remediation of TCE-contaminated groundwater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Sung, J. K., Yang, J. E., & Ok, Y. S. (2012). Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresource Technology, 118, 536–544.
Butler, E. C., & Hayes, K. F. (2001). Factors influencing rates and products in the transformation of trichloroethylene by iron sulfide and iron metal. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3884–3891.
Chen, B., Zhou, D., & Zhu, L. (2008). Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 5137–5143.
Cheng, Y. J., Dong, H., Lu, Y., Hou, K., Wang, Y., Ning, Q., Li, L., Wang, B., Zhang, L., & Zeng, G. (2019). Toxicity of sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron to Escherichia coli in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 220, 523–530.
De Janeiro, R. (1990). The role of chloride and sulphate anions in the iron dissolution mechanism studied by impedance measurements. Electrochimica Acta, 35, 1003–1009.
Deng, J. M., Dong, H. R., Zhang, C., Jiang, Z., & Cheng, Y. J. (2018). Nanoscale zero-valent iron/biochar composite as an activator for Fenton-like removal of sulfamethazine. Separation and Purification Technology, 202, 130–137.
Dong, H., Zhao, F., Zeng, G., Tang, L., Fan, C., Zhang, L., Zeng, Y., He, Q., Xie, Y., & Wu, Y. (2016). Aging study on carboxymethyl cellulose-coated zero-valent iron nanoparticles in water: chemical transformation and structural evolution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 312, 234–242.
Dong, H., Deng, J., Xie, Y., Zhang, C., & Jiang, Z. (2017a). Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 332, 79–86.
Dong, H., Zhang, C., Hou, K., Cheng, Y., Deng, J., Jiang, Z., Tang, L., & Zeng, G. (2017b). Removal of trichloroethylene by biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Separation and Purification Technology, 188, 188–196.
Dong, H., Zhang, C., Deng, J., Jiang, Z., Zhang, L., Cheng, Y., Hou, K., Tang, L., & Zeng, G. (2018). Factors influencing degradation of trichloroethylene by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Water Research, 135, 1–10.
Dong, H., Wang, B., Li, L., Wang, Y., Ning, Q., Tian, R., Li, R., Chen, J., & Xie, Q. (2019). Activation of persulfate and hydrogen peroxide by using sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for oxidative degradation of sulfamethazine: a comparative study. Separation and Purification Technology, 218, 113–119.
Dong, H., Li, L., Wang, Y., Ning, Q., Wang, B., & Zeng, G. (2020). Aging of zero-valent iron-based nanoparticles in aqueous environment and the consequent effects on their reactivity and toxicity. Water Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1265.
Fan, D., O’Brien Johnson, G., Tratnyek, P. G., & Johnson, R. L. (2016). Sulfidation of nano zerovalent iron (nZVI) for improved selectivity during in-situ chemical reduction (ISCR). Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 9558–9565.
Giasuddin, A. B. M., Kanel, S. R., & Choi, H. (2007). Adsorption of humic acid onto nanoscale zerovalent iron and its effect on arsenic removal. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 2022–2027.
Guan, X., Sun, Y., Qin, H., Li, J., Lo, I. M. C., He, D., & Dong, H. (2015). The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994-2014). Water Research, 75, 224–248.
Han, Y., & Yan, W. (2016). Reductive dechlorination of trichloroethene by zero-valent iron nanoparticles: reactivity enhancement through sulfidation treatment. Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 12992–13001.
Hassan, S. M. (2000). Reduction of halogenated hydrocarbons in aqueous media: I. Involvement of sulfur in iron catalysis. Chemosphere, 40, 1357–1363.
Kilduff, J. E., & Karanfil, T. (2002). Trichloroethylene adsorption by activated carbon preloaded with humic substances: effects of solution chemistry. Water Research, 36, 1685–1698.
Kim, E. J., Murugesan, K., Kim, J. H., Tratnyek, P. G., & Chang, Y. S. (2013). Remediation of trichloroethylene by fes-coated iron nanoparticles in simulated and real groundwater: effects of water chemistry. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 9343–9350.
Li, D., Mao, Z., Zhong, Y., Huang, W., Wu, Y., & Peng, P. (2016). Reductive transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A by sulfidated nano zerovalent iron. Water Research, 103, 1–9.
Li, P., Lin, K., Fang, Z., Zhang, W., 2018. Degradation of nitrate and secondary pollution in drinking water by S-NZVI prepared from steel pickling waste liquor. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research. 0–1.
Li, R., Dong, H., Tian, R., Chen, J., & Xie, Q. (2020a). Activation of sulfite by different Fe0-based nanomaterials for oxidative removal of sulfamethazine in aqueous solution. Separation and Purification Technology, 250, 117230.
Li, Z., Sun, Y. Q., Yang, Y., Han, Y. T., Wang, T. S., Chen, J. W., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2020b). Biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron as an efficient catalyst for organic degradation in groundwater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 383, 121240.
Liang, B., Cheng, H. Y., Kong, D. Y., Gao, S. H., Sun, F., Cui, D., Kong, F. Y., Zhou, A. J., Liu, W. Z., Ren, N. Q., Wu, W. M., Wang, A. J., & Lee, D. J. (2013). Accelerated reduction of chlorinated nitroaromatic antibiotic chloramphenicol by biocathode. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 5353–5361.
Lipczynska-kochany, E., Consultant, E., Milburn, R.R., Nadarajah, N., 1994. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride in the presence of iron and sulphur containing compounds 6535.
Liu, Y., Phenrat, T., & Lowry, G. V. (2007). Effect of TCE concentration and dissolved groundwater solutes on NZVI-promoted TCE dechlorination and H2 evolution. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 7881–7887.
Liu, Z. L., Tian, D., Shen, F., Long, L. L., Zhang, Y. Z., Yang, G., Zeng, Y. M., Zhang, J., He, J. S., Zhu, Y., & Deng, S. H. (2019). Elucidating dominant factors of PO43−, Cd2+ and nitrobenzene removal by biochar: a comparative investigation based on distinguishable biochars. Chinese Chem Lett, 30, 2221–2224.
Mandal, S., Pu, S. Y., Adhikari, S., Ma, H., Kim, D. H., Bai, Y. C., & Hou, D. Y. (2020). Progress and future prospects in biochar composites: application and reflection in the soil environment. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1713030.
Ning, Q., Dong, H. R., Li, L., Wang, Y. Y., & Wang, B. (2020). Removal of trichloroethylene by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron coated with different stabilizers in aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Poll., 231, 161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04550-w.
Pang, H. W., Diao, Z. F., Wang, X. X., Ma, Y., Yu, S. J., Zhu, H. T., Chen, Z. S., Hu, B. W., Chen, J. R., & Wang, X. K. (2019). Adsorptive and reductive removal of U(VI) by Dictyophora indusiate-derived biochar supported sulfide NZVI from wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 366, 368–377.
Sarathy, V., Tratnyek, P. G., Nurmi, J. T., Baer, D. R., Amonette, J. E., Chun, C. L., Penn, R. L., & Reardon, E. J. (2008). Aging of iron nanoparticles in aqueous solution: effects on structure and reactivity. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 112, 2286–2293.
Shi, L. N., Zhang, X., & Chen, Z. L. (2011). Removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Research, 45, 886–892.
Su, Y., Adeleye, A. S., Keller, A. A., Huang, Y., Dai, C., Zhou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2015). Magnetic sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron (S-nZVI) for dissolved metal ion removal. Water Research, 74, 47–57.
Sun, Y. Q., Yu, I. K. M., Tsang, D. C. W., Cao, X. D., Lin, D. H., Wang, L. L., Graham, N. J. D., Alessi, D. S., Komarek, M., Ok, Y. S., Feng, Y. J., & Li, X. D. (2019). Multifunctional iron-biochar composites for the removal of potentially toxic elements, inherent cations, and hetero-chloride from hydraulic fracturing wastewater. Environment International, 124, 521–532.
Tanboonchuy, V., Grisdanurak, N., & Liao, C. H. (2012). Background species effect on aqueous arsenic removal by nano zero-valent iron using fractional factorial design. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 205–206, 40–46.
Tian, R., Dong, H., Chen, J., Li, R., & Xie, Q. (2020). Amorphous Co3O4 nanoparticles-decorated biochar as an efficient activator of peroxymonosulfate for the removal of sulfamethazine in aqueous solution. Separation and Purification Technology, 250, 117246.
Utsumi, S. (2006). New colorimetric determination of chloride using mercuric thiocyanate and ferric ion. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 25(3), 226–226.
Wang, Z., Zheng, H., Luo, Y., Deng, X., Herbert, S., & Xing, B. (2013). Characterization and influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission from agricultural soil. Environmental Pollution, 174, 289–296.
Wang, Y., Dong, H., Li, L., Tian, R., Chen, J., Ning, Q., Wang, B., Tang, L., & Zeng, G. (2019). Influence of feedstocks and modification methods on biochar’s capacity to activate hydrogen peroxide for tetracycline removal. Bioresource Technology, 291, 121840.
Wang, B., Dong, H. R., Li, L., Wang, Y. Y., Ning, Q., Tang, L., & Zeng, G. M. (2020). Influence of different co-contaminants on trichloroethylene removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemical Engineering Journal, 381, 122773.
Xie, L., & Shang, C. (2005). Role of humic acid and quinone model compounds in bromate reduction by zerovalent iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 1092–1100.
Yao, Y., Gao, B., Fang, J., Zhang, M., Chen, H., Zhou, Y., Creamer, A. E., Sun, Y., & Yang, L. (2014). Characterization and environmental applications of clay-biochar composites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, 136–143.
Yen, M. Y., Teng, C. C., Hsiao, M. C., Liu, P. I., Chuang, W. P., Ma, C. C. M., Hsieh, C. K., Tsai, M. C., & Tsai, C. H. (2011). Platinum nanoparticles/graphene composite catalyst as a novel composite counter electrode for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21, 12880–12888.
Zhang, D., Li, Y., Tong, S., Jiang, X., Wang, L., Sun, X., Li, J., Liu, X., & Shen, J. (2018). Biochar supported sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for the reduction of nitrobenzene. RSC Advances, 8, 22161–22168.
Zhang, W., Qian, L., Ouyang, D., Chen, Y., Han, L., & Chen, M. (2019a). Effective removal of Cr(VI) by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: enhanced adsorption and crystallization. Chemosphere, 221, 683–692.
Zhang, D. J., Shen, J. Y., Shi, H. F., Su, G. Y., Jiang, X. B., Li, J. S., Liu, X. D., Mu, Y., & Wang, L. J. (2019b). Substantially enhanced anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene by biochar stabilized sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: process and mechanisms. Environment International, 131, 105020.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51879100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14407 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Dong, H., Tian, R. et al. Remediation of Trichloroethylene-Contaminated Groundwater by Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Supported on Biochar: Investigation of Critical Factors. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04797-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04797-3