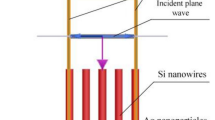
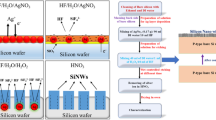
Abstract
Solar cell utilizes a small portion of solar spectrum leaving higher energy (> band gap, Eg) as thermalization loss and lower energy (< band gap, Eg) as absorption loss. Wavelength-sensitive engineered absorbing layer such as nanometric absorber holds huge potential in this context. Here in this work, a simple and hands-on strategy was devised to grow silicon nanowires (Si-NWs) on silicon wafer. Nanoparticles were achieved in the first step and used as seeds to directed growth of Si-NWs. As-grown Si-NWs with coverage ca. 6.5 × 108/cm2 were characterized through scanning electron microscope. To realize such Si-NWs as nanometric absorber in nanowire solar cell, a three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain simulation has been carried out. Considering the possibility of Si-NWs of different diameters as observed in experimental investigations, Si-NW of 50-, 100-, and 150-nm diameters was chosen in simulation. Two specific wavelengths, 700 and 1100 nm, were in prime focus to understand the characteristics of exciton generation within Si-NW. Confinement in exciton generation rate distribution at 700-nm solar spectrum for Si-NW of 150 nm was found to be most effective, whereas at 1100-nm wavelength Si-NW of 100 nm showed higher exciton generation rate distribution with the nanowire. Exciton generation line profiles along the center and edge were extracted, and comparative analysis was carried out for different diameters of Si-NW at 700- and 1100-nm wavelengths. Such experimental and correlated simulation is indispensable not only to reduce costs but also to understand and improve the cell efficiency using the light-trapping technique.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saga T (2010) Advances in crystalline silicon solar cell technology for industrial mass production. NPG Asia Mater 2(3):96–102
Hoffmann W (2006) PV solar electricity industry: market growth and perspective. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90(18–19):3285–3311
Zeng Y, Yang Q, Wan Y, Yang Z, Liao M, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Guo X, Wang Z, Gao P, Wu CH (2019) Numerical exploration for structure design and free-energy loss analysis of the high-efficiency polysilicon passivated-contact p-type silicon solar cell. Sol Energy 178:249–256
Battersby S (2019) News feature: the solar cell of the future. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(1):7–10
Höger I, Schaper M, Mette A, Lee BG, Fertig F, Lantzsch R, Peters S, Eidner A, Duncker K, Bartzsch M, Junghänel M (2018) Boosting module power by advanced interconnection and p-type Cz silicon solar cell efficiencies exceeding 22% in mass production. AIP Conf Proc 1999(1):110003
Polman A, Atwater HA (2012) Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics. Nat Mater 11(3):174
Yu L, Misra S, Wang J, Qian S, Foldyna M, Xu J, Shi Y, Johnson E, i Cabarrocas PR. (2014) Understanding light harvesting in radial junction amorphous silicon thin film solar cells. Sci Rep 4:4357
Kelzenberg MD, Boettcher SW, Petykiewicz JA, Turner-Evans DB, Putnam MC, Warren EL, Spurgeon JM, Briggs RM, Lewis NS, Atwater HA (2010) Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nat Mater 9(3):239–244
Boettcher SW, Spurgeon JM, Putnam MC, Warren EL, Turner-Evans DB, Kelzenberg MD, Maiolo JR, Atwater HA, Lewis NS (2010) Energy-conversion properties of vapor-liquid-solid–grown silicon wire-array photocathodes. Science 327(5962):185–187
Garnett E, Yang P (2010) Light trapping in silicon nanowire solar cells. Nano Lett 10(3):1082–1087
Jäger ST, Strehle S (2014) Design parameters for enhanced photon absorption in vertically aligned silicon nanowire arrays. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):1–6
Zhan Y, Zhao J, Zhou C, Alemayehu M, Li Y, Li Y (2012) Enhanced photon absorption of single nanowire α-Si solar cells modulated by silver core. Opt Express 20(10):11506–11516
Bencherif H, Dehimi L, Pezzimenti F, Della Corte FG (2019) Improving the efficiency of a-Si: H/c-Si thin heterojunction solar cells by using both antireflection coating engineering and diffraction grating. Optik 182:682–693
Ulbrich C, Gerber A, Hermans K, Lambertz A, Rau U (2013) Analysis of short circuit current gains by an anti-reflective textured cover on silicon thin film solar cells. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 21(8):1672–1681
Manzoor S, Zhengshan JY, Ali A, Ali W, Bush KA, Palmstrom AF, Bent SF, McGehee MD, Holman ZC (2017) Improved light management in planar silicon and perovskite solar cells using PDMS scattering layer. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 173:59–65
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213
Luo X, Tsai D, Gu M, Hong M (2019) Extraordinary optical fields in nanostructures: from sub-diffraction-limited optics to sensing and energy conversion. Chem Soc Rev 48(8):2458–2494
Fazio B, Artoni P, Iatì MA, D'andrea C, Faro MJ, Del Sorbo S, Pirotta S, Gucciardi PG, Musumeci P, Vasi CS, Saija R (2016) Strongly enhanced light trapping in a two-dimensional silicon nanowire random fractal array. Light: Sci Applic 5(4):e16062
Tsakalakos L, Balch JE, Fronheiser J, Shih MY, LeBoeuf SF, Pietrzykowski M, Codella PJ, Korevaar BA, Sulima O, Rand J, Davuluru A (2007) Strong broadband optical absorption in silicon nanowire films. J Nanophotonics 1(1):013552
Srivastava SK, Kumar D, Schmitt SW, Sood KN, Christiansen SH, Singh PK (2014) Large area fabrication of vertical silicon nanowire arrays by silver-assisted single-step chemical etching and their formation kinetics. Nanotechnology 25(17):175601
Wang X, Peng KQ, Pan XJ, Chen X, Yang Y, Li L, Meng XM, Zhang WJ, Lee ST (2011) High-performance silicon nanowire array photoelectrochemical solar cells through surface passivation and modification. Angew Chem 123(42):10035–10039
Dan Y, Seo K, Takei K, Meza JH, Javey A, Crozier KB (2011) Dramatic reduction of surface recombination by in situ surface passivation of silicon nanowires. Nano Lett 11(6):2527–2532
Tong J, Suo F, Ma J, Tobing LY, Qian L, Zhang DH (2019) [Opto-Electron Adv, 2019, 2 (1)] Surface plasmon enhanced infrared photodetection. Opto-Electronic Rep 3(01):a201901001
Gunawan O, Guha S (2009) Characteristics of vapor–liquid–solid grown silicon nanowire solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 93(8):1388–1393
Cao L, Fan P, Vasudev AP, White JS, Yu Z, Cai W, Schuller JA, Fan S, Brongersma ML (2010) Semiconductor nanowire optical antenna solar absorbers. Nano Lett 10(2):439–445
Sahoo MK, Kale P (2019) Integration of silicon nanowires in solar cell structure for efficiency enhancement: a review. J Mater 5(1):34–48
Krogstrup P, Jørgensen HI, Heiss M, Demichel O, Holm JV, Aagesen M, Nygard J, i Morral AF (2013) Single-nanowire solar cells beyond the Shockley–Queisser limit. Nat Photonics 7(4):306–310
Salhi B, Hossain MK, Mukhaimer AW, Al-Sulaiman FA (2016) Nanowires: a new pathway to nanotechnology-based applications. J Electroceram 37(1–4):34–49
Hossain MK, Salhi B, Mukhaimer AW (2017) Optical confinements in correlated spectral characteristics of vertically aligned silicon nanometric wires followed by a facile fabrication thereof. Plasmonics 12(5):1297–1304
Hossain MK, Salhi B, Mukhaimer AW, Al-Sulaiman FA (2016) Fabrication and optical simulation of vertically aligned silicon nanowires. Appl Nanosci 6(7):1031–1036
Wagner RS, Ellis WC (1964) Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl Phys Lett 4(5):89–90
Palik ED (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids I-III. Academic press handbook series, Elsevier science publishing, USA
Peng K, Wang X, Lee ST (2008) Silicon nanowire array photoelectrochemical solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 92(16):163103
Peng KQ, Wang X, Li L, Wu XL, Lee ST (2010) High-performance silicon nanohole solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 132(20):6872–6873
Tang J, Huo Z, Brittman S, Gao H, Yang P (2011) Solution-processed core–shell nanowires for efficient photovoltaic cells. Nat Nanotechnol 6(9):568–572
Tsakalakos L, Balch J, Fronheiser J, Korevaar BA, Sulima O, Rand J (2007) Silicon nanowire solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 91(23):233117
Liu Y, Sun N, Liu J, Wen Z, Sun X, Lee ST, Sun B (2018) Integrating a silicon solar cell with a triboelectric nanogenerator via a mutual electrode for harvesting energy from sunlight and raindrops. ACS Nano 12(3):2893–2899
Maryasin V, Rafhay Q, Bucci D, Michallon J, Kaminski-Cachopo A (2018) Opto-electrical simulation of III-V nanowire based tandem solar cells on Si. AIP Conf Proc 1999(1):120001 AIP Publishing
Hossain MK, Mukhaimer AW (2020) Nanoparticles-decorated silicon absorber: absorption depth profile characteristics within absorbing layer. Sol Energy 204:552–560
Acknowledgments
The authors like to thank the Center of Research Excellence in Renewable Energy (CoRERE), Research Institute, King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals (KFUPM), Dhahran 31261, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Funding
Mohammad Kamal Hossain acknowledges the funding support provided by the King Abdullah City for Atomic and Renewable Energy (KACARE) through project KACARE182-RFP-07.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, M.K., Salhi, B. & Mukhaimar, A. Fabrication and Spectral Characteristics of Silicon Nanowires for Efficient Solar Energy Harvesting. Plasmonics 16, 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01250-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01250-3