Abstract
An efficient and novel modeling approach is proposed in this paper for identifying proteins or genes involved in melanoma skin cancer. Two types of classifiers are modeled, based on the chemical structure and hydropathy property of amino acids. These classifiers are further implemented using NI LabVIEW–based hardware kit to observe the real-time response for proper diagnosis. The phase responses, pole-zero diagrams, and transient responses are examined to screen out the genes related to melanoma from healthy genes. The performance of the proposed classifier is measured using various performance measurement metrics in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, etc. The classifier is experimented along with a color code scheme on skin genes and illustrates the superiority in comparison with traditional methods by achieving 94% of classification accuracy with 96% of sensitivity.
Graphical abstract

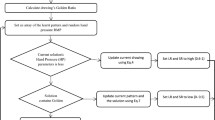
An equivalent electrical model is developed for designing melanoma classifier. Initially, each amino acid is modeled using the RC passive circuit depending on their physicochemical structure and hydropathy nature, to form a gene structure model. The melanoma-related genes are detected by phase, transient, and color code analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sampath G (2006) RLC (M) circuit models of protein structure: analysis, visualization, shape synthesis, and pattern matching. In: 40th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems. IEEE, pp 1623–1628
Ainuddin U, Khurram M, Hasan SR (2019) Cloning the λ switch: digital and Markov representations of the lambda phage Infected E. coli bacterium. IEEE transactions on NanoBioscience
Marshall R (2009) Modeling DNA/RNA strings using resistor—capacitor (rc) ladder networks. Comput J 53(6):644–660
Alam S, Hasan SR (2016) A gene–protein–miRNA electronic oscillator. IEEE Transac Circuits Systems II: Express Briefs 64(9):1007–1011
Grib NV, Berashevich JA, Borisenko VE (2006) Equivalent electrical network of the DNA molecule. Russ Microelectron 35(6):398–404
Jerant AF, Johnson JT, Demastes Sheridan C, Caffrey TJ (2000) Early detection and treatment of skin cancer. Am Fam Physician 62(2)
Stratigos A, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Malvehy J, Del Marmol V, Pehamberger H, Peris K, Becker JC, Zalaudek I, Saiag P, Middleton MR (2015) Diagnosis and treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline. Eur J Cancer 51(14):1989–2007
Friedman RJ, Rigel DS, Kopf AW (1985) Early detection of malignant melanoma: the role of physician examination and self-examination of the skin. CA Cancer J Clin 35(3):130–151
Roy T (2019) Analysis of cancer gene attributes using electrical sensor. Gene 685:62–69
Roy T, Barman S (2015) Performance analysis of network model to identify healthy and cancerous colon genes. IEEE J Biomedical Health Inform 20(2):710–716
Roy T, Barman S (2016) Modeling of cancer classifier to predict site of origin. IEEE transactions on nanobioscience 15(5):481–487
Mignone P, Pio G, D’Elia D, Ceci M (2020) Exploiting transfer learning for the reconstruction of the human gene regulatory network. Bioinformatics 36(5):1553–1561
Kim BH, Yu K, Lee PC (2020) Cancer classification of single-cell gene expression data by neural network. Bioinformatics 36(5):1360–1366
Barracchia EP, Pio G, D’Elia D, Ceci M (2020) Prediction of new associations between ncRNAs and diseases exploiting multi-type hierarchical clustering. BMC bioinformatics 21(1):1–24
Linos E, Katz KA, Colditz GA (2016) Skin Cancer—the importance of prevention. JAMA Intern Med 176(10):1435–1436
D'Orazio J, Jarrett S, Amaro-Ortiz A, Scott T (2013) UV radiation and the skin. Int J Mol Sci 14(6):12222–12248
Li C, Athar M (2016) Ionizing radiation exposure and basal cell carcinoma pathogenesis. Radiat Res 185(3):217–228
Athar M, Li C, Kim AL, Spiegelman VS, Bickers DR (2014) Sonic hedgehog signaling in basal cell nevus syndrome. Cancer Res 74(18):4967–4975
McClellan DA (2012) Detecting molecular selection on single amino acid replacements. Int J Bioinforma Res Appl 8(1/2):67–80
National Institutes of Health government web site. [Online], Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
Cancer Genome Anatomy Project. [Online], Available: http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/
Gostev M, Faulconbridge A, Brandizi M, Fernandez-Banet J, Sarkans U, Brazma A, Parkinson H (2011) The BioSample database (BioSD) at the european bioinformatics institute. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D64–D70
Nelson DL, Lehninger AL, Cox MM (2008) Lehninger principles of biochemistry. Macmillan
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157(1):105–132
Temes GC, LaPatra JW (1977) Introduction to circuit synthesis and design. McGraw-Hill Companies
Kollar IS, Franklin G, Pintelon R. On the equivalence of z-domain and s-domain models in system identification (1996) InQuality Measurement: The Indispensable Bridge between Theory and Reality (No Measurements? No Science!. In: IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference and IMEKO Tec. IEEE 1, pp. 14–19
ASCII Character Chart [Online], Available: https://www.eso.org/~ndelmott/ascii.html
Nair BS (2004) Digital signal processing: theory, analysis and digital-filter design. PHI Learning Pvt, Ltd
Marshall RG (2014) OMNIGENE software system. United States patent US 8:787,626
Stranzl T, Larsen MV, Lund O, Nielsen M, Brunak S (2012) The cancer exome generated by alternative mRNA splicing dilutes predicted HLA class I epitope density. PloS one 25 7(9):e38670
Das D, Mitra CK (2011) Signals in the promoter regions of several cancerous genes
Kennedy C, ter Huurne J, Berkhout M, Gruis N, Bastiaens M, Bergman W, Willemze R, Bavinck JN (2001) Melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene variants are associated with an increased risk for cutaneous melanoma which is largely independent of skin type and hair color. J Investig Dermatol 117(2):294–300
Uribe P, Gonzalez S (2011) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy. Pathol Res Prac 207(6):337–342
Han J, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ (2007) Polymorphisms in the MTHFR and VDR genes and skin cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 28(2):390–397
Omholt K, Platz A, Ringborg U, Hansson J (2001) Cytoplasmic and nuclear accumulation of β-catenin is rarely caused by CTNNB1 exon 3 mutations in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Int J Cancer 92(6):839–842
Vita M, Henriksson M (2006) The Myc oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human cancer. In: seminars in cancer biology. Academic Press 16(4):318–330
Glatz-Krieger K, Pache M, Tapia C, Fuchs A, Savic S, Glatz D, Mihatsch M, Meyer P (2006) Anatomic site-specific patterns of gene copy number gains in skin, mucosal, and uveal melanomas detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Virchows Arch 449(3):328–333
South AP, Purdie KJ, Watt SA, Haldenby S, Den Breems NY, Dimon M, Arron ST, Kluk MJ, Aster JC, McHugh A, Xue DJ (2014) NOTCH1 mutations occur early during cutaneous squamous cell carcinogenesis. J Investig Dermatol 134(10):2630–2638
De Villiers EM, Ruhland A, Šekaric P (1999) Human papillomaviruses in non-melanoma skin cancer. In: seminars in cancer biology. Academic Press 9(6):413–422
Gomez Lira M, Mazzola S, Tessari G, Malerba G, Ortombina M, Naldi L, Remuzzi G, Boschiero L, Forni A, Rugiu C, Piaserico S (2007) Association of functional gene variants in the regulatory regions of COX-2 gene (PTGS2) with nonmelanoma skin cancer after organ transplantation. Br J Dermatol 157(1):49–57
Coussens LM, Tinkle CL, Hanahan D, Werb Z (2000) MMP-9 supplied by bone marrow–derived cells contributes to skin carcinogenesis. Cell 103(3):481–490
Kuusisto KM, Bebel A, Vihinen M, Schleutker J, Sallinen SL (2011) Screening for BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, BRIP1, RAD50, and CDH1 mutations in high-risk Finnish BRCA1/2-founder mutation-negative breast and/or ovarian cancer individuals. Breast Cancer Res 13(1):R20
Ericson K, Gan C, Cheong I, Rago C, Samuels Y, Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW, Huso DL, Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N (2010) Genetic inactivation of AKT1, AKT2, and PDPK1 in human colorectal cancer cells clarifies their roles in tumor growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(6):2598–2603
Han J, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ (2007) Polymorphisms in the MTHFR and VDR genes and skin cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 28(2):390–397
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Marini A, Nambiar S, Hassan M, Tannapfel A, Ruzicka T, Hengge UR (2006) Epigenetic silencing of the PTEN gene in melanoma. Cancer Res 66(13):6546–6552
Wu H, Larribère L, Sun Q, Novak D, Sachindra S, Granados K, Umansky V, Utikal J (2018) Loss of neural crest-associated gene FOXD1 impairs melanoma invasion and migration via RAC1B downregulation. Int J Cancer 143(11):2962–2972
Melzer C, Hass R, Lehnert H, Ungefroren H (2019) RAC1B: a rho GTPase with versatile functions in malignant transformation and tumor progression. Cells 8(1):21
Baune BT, Konrad C, Suslow T, Domschke K, Birosova E, Sehlmeyer C, Beste C (2010) The Reelin (RELN) gene is associated with executive function in healthy individuals. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94(4):446–451
Roehe R, Plastow GS, Knap PW (2003) Quantitative and molecular genetic determination of protein and fat deposition. Homo 54(2):119–131
Grehan S, Allan C, Tse E, Walker D, Taylor JM (2001) Expression of the apolipoprotein E gene in the skin is controlled by a unique downstream enhancer. J Investig Dermatol 116(1):77–84
Takeuchi T, Liang SB, Matsuyoshi N, Zhou S, Miyachi Y, Sonobe H, Ohtsuki Y (2002) Loss of T-cadherin (CDH13, H-cadherin) expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Lab Investig 82(8):1023–1029
Takahashi T, Yamaguchi E, Furuya K, Kawakami Y (2001) The ACE gene polymorphism and cough threshold for capsaicin after cilazapril usage. Respir Med 95(2):130–135
Schroeder P, Gremmel T, Berneburg M, Krutmann J (2008) Partial depletion of mitochondrial DNA from human skin fibroblasts induces a gene expression profile reminiscent of photoaged skin. J Investig Dermatol 128(9):2297–2303
Edqvist PH, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Danielsson A, Edlund K, Uhlén M, Pontén F (2015) Expression of human skin-specific genes defined by transcriptomics and antibody-based profiling. J Histochem Cytochem 63(2):129–141
Martin JC, Wolk K, Bériou G, Abidi A, Witte-Händel E, Louvet C, Kokolakis G, Drujont L, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC, Sabat R (2017) Limited presence of IL-22 binding protein, a natural IL-22 inhibitor, strengthens psoriatic skin inflammation. J Immunol 198(9):3671–3678
Jacobs LC, Hamer MA, Gunn DA, Deelen J, Lall JS, Van Heemst D, Uh HW, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Griffiths CE, Beekman M (2015) A genome-wide association study identifies the skin color genes IRF4, MC1R, ASIP, and BNC2 influencing facial pigmented spots. J Investig Dermatol 135(7):1735–1742
Makrantonaki E, Brink TC, Zampeli V, Elewa RM, Mlody B, Hossini AM, Hermes B, Krause U, Knolle J, Abdallah M, Adjaye J (2012) Identification of biomarkers of human skin ageing in both genders. Wnt signalling-a label of skin ageing? PLoS One 7(11):e50393
Li L, Sun L, Gao F, Jiang J, Yang Y, Li C, Gu J, Wei Z, Yang A, Lu R, Ma Y (2010) Stk40 links the pluripotency factor Oct4 to the Erk/MAPK pathway and controls extraembryonic endoderm differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(4):1402–1407
Smart MC, Dedoussis G, Louizou E, Yannakoulia M, Drenos F, Papoutsakis C, Maniatis N, Humphries SE, Talmud PJ (2010) APOE, CETP and LPL genes show strong association with lipid levels in Greek children. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20(1):26–33
Kyrkou A, Soufi M, Bahtz R, Ferguson C, Bai M, Parton RG, Hoffmann I, Zerial M, Fotsis T, Murphy C (2013) RhoD participates in the regulation of cell-cycle progression and centrosome duplication. Oncogene 32(14):1831–1842
Belfer I, Segall SK, Lariviere WR, Smith SB, Dai F, Slade GD, Rashid NU, Mogil JS, Campbell CM, Edwards RR, Liu Q (2013) Pain modality-and sex-specific effects of COMT genetic functional variants. PAIN® 154(8):1368–1376
Roy, T. and Bhattacharjee, P. (2020). A LabVIEW-based real-time modeling approach for detection of abnormalities in cancer cells. Gene Reports, Elsevier, In press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100788
M. Kumari and S. M. Rezaul Hasan, "A Low Duty Cycle Burst-Mode Telemeter Signal Generation Technique for VHF Insect Tracking and Its CMOS Implementation," in IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 833-837, March 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2947696
I. A. A. Al-Darkazly and S. M. R. Hasan, "Extra-Low-Frequency Pulse Stimulated Conformational Change in Blood-Cell Proteins and Consequent Immune Activity Transformation," in IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine, vol. 8, pp. 1-13, 2020, Art no. 4100113, https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2020.2963894
Roy, T. and Barman, S. (2017). Prediction of Homo sapiens Cancer Cells by Electrical Network Modeling of Amino Acid Sequence. International Journal of Bioinformatics Research and Applications, Inderscience, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 75-93. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBRA.2017.082057
Roy, T. and Barman, S. (2016). Design and development of cancer regulatory system by modeling electrical network of gene. Microsystem Technologies, Springer, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 2641-2653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2548-x
Acknowledgments
The working facility is provided by the University of Engineering and Management, Kolkata-700156.
Funding
The authors would like to thank DST, Science and Engineering Research Board (EEQ/2017/000293), Govt. of India, for funding the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, T., Bhattacharjee, P. Performance analysis of melanoma classifier using electrical modeling technique. Med Biol Eng Comput 58, 2443–2454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02241-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02241-6