Abstract
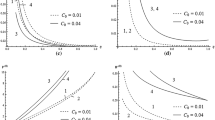
For the propagation of a shock (blast) in a self-gravitating perfect gas in case of spherical and cylindrical symmetry, an approximate analytical solution is investigated. The shock wave is considered to be a strong one, with the ratio \( \left( {\frac{C}{{V_{S} }}} \right)^{2} \) to be a small quantity, where \( c \) is the sound speed in an undisturbed medium and \( V_{S} \) is the shock wave velocity. The initial density in the undisturbed medium is taken to be varying according to a power law. To obtain the approximate closed-form similarity solution, the flow variables are expanded in a power series of \( \left( {\frac{C}{{V_{S} }}} \right)^{2} \). The first- and second-order approximations are discussed with the help of power series expansion. The analytical solutions are constructed for the first-order approximation. The distribution of the flow variables for first-order approximation in the flow field region behind the shock wave is shown in graphs for both the cylindrical and spherical geometries. The effect of flow parameters, namely, ambient density variation index \( \alpha \), adiabatic exponent \( \gamma \)and gravitational parameter \( G_{0} \), are studied on the flow variables and on the total energy of disturbance in the case of the first approximation to the solutions. It is shown that the total energy of the disturbance in the flow field region behind the shock wave decreases with an increase in initial density variation index or adiabatic exponent, i.e. shock strength increases with increase in the value of adiabatic exponent or initial density variation index. A comparison is also made between the solutions obtained for non-gravitating and self-gravitating gases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arad B., Gazit Y., Ludmirsk A. 1987, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 20, 360
Allen G. E., Chow K., DeLaney T., Filipovic M. D., Houck J. C., Pannuti T. G., Stage M. D. 2015, ApJ, 798, 82
Ashraf S., Ahmad Z. 1975, Ind. J. P. Appl. Math., 6, 1090
Bernstein I. B., Book D. L. 1978, ApJ, 225, 633
Bernstein I. B., Book D. L. 1980, ApJ, 240, 223
Bian F.-Y., Lou Y.-Q. 2005, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 363, 1315
Carrus P., Fox P., Haas F., Kopal Z. 1951, Astrophys. J., 113, 496
Chevalier R. A., Imamura J. 1982, ApJ, 261, 543
Coughlin E. R., Quataert E., Ro S. 2002, ApJ, 863, 158
Cowie L. L. 1977, Astrophys. J., 215, 226
Daghan D., Donmez O. 2016, Braz. J. Phys., 46, 321
Dessart L., Livne E., Waldman R. 2010, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc., 405, 2113
Deschner S. C., Ilenseer T. F., Duschl W. J. 2018, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 78, 80
Elmegreen B. G., Elmegreen D. M. 1978, ApJ, 220, 1051
Erpenbeck J. J. 1962, Phys. Fluids, 5, 604, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1706664
Gardner C. S., Kruskal M. D. 1964, Phys. Fluids, 7, 700, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1711271
Giuliani J. L. 1979, ApJ, 223, 280
Gorenstein P., Harden F. R. Jr., Tucker W. H. 1974, ApJ, 192, 661
Gretler W., Regenfelder R. 2005, Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids, 24, 205
Hugoniot H. 1887, J. Ec. Polytech., 57, 3
Isenberg P. A. 1977, ApJ, 217, 597
Korobeinikov V. P. 1956, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 109, 271
Korobeinikov V. P., Melnikova N. S., Ryazanov Y. V. 1962, The Theory of Point Explosion, U.S. Department of Commerce, Washington, D.C., Chap. 7 (English Translation)
Korobeinikov V. P. 1976, Problems in the theory of point explosion in gases, in Proceedings of the Steklov Institute of Mathematics, Volume 119, AMS, Providence, RI
Koo B. C., Mckee C. F. 1990, ApJ, 354, 513
Landau L. D., Lifshitz E. M. 1959, Fluid Mechanics, Pergamon, Oxford
Larson R. B. 1969a, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 145, 271
Larson R. B. 1969b, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 145, 405
Laumbach D. D., Probstein R. F. 1969, J. Fluid Mech. Part I, 35, 53
Laumbach D. D., Probstein R. F. 1970, Phys. Fluids, 13, 1178
Lerch I., Vasyliunas V. 1976, Astrophys. J., 210, 85
Leahy D. A., Ranasinghe S. 2016, ApJ, 817, 74
Lerche I., Vasyliunas V. M. 1976, ApJ, 210, 85
McCray R., Stein R. F., Kafatos M. 1975, ApJ, 196, 564
Mufson S. L. 1975, ApJ, 202, 372
Naidu G. N., Rao M. P. R., Yadav H. L. 1983, Astrophys. Space Sci., 89, 77
Nath G. 2010, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 10, 445
Nath G. 2011, Adv. Space Res., 37, 1463
Nath G. 2012a, Meccanica, 47, 1797
Nath G. 2012b, Ain Shams Eng. J., 3, 393
Nath G. 2013, Adv. Space Res., 52, 1304
Nath G. 2014a, J. Theor. Appl. Phys., 8, 331, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40094-014-0131-y
Nath G. 2014b, Shock Waves, 24, 415.
Nath G. 2015, Meccanica, 50, 1701
Nath G., 2016, Astrophys. Space Sci., 361, 31
Nath G. 2020, Indian J. Phys., https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-02001684-9
Nath G., Vishwakarma J. P., Srivastava V. K., Sinha A. K. (2013) J. Theo. Appl. Phys. 7, 15, https://doi.org/10.1186/2251-7235-7-15
Nath G., Dutta M., Pathak R. P. 2019, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sec. A Phys. Sci., https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00625-4
Nath G., Pathak R. P., Dutta M. 2018, Acta Astronautica, 142, 152
Nath G., Sinha A. K. 2011, Phys. Res. Inter., 2011, Article ID 782172, 8, https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/782172
Nath G., Singh S. 2019, J. Astrophys. Astron., 40, 50, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-019-9616-z
Nath G., Vishwakarma J. P. 2016, Acta Astronatica, 123, 200
Newman W. I. 1979, Astrop. Space Sci., 47, 99
Newman, W. I. (1980), Ap. J., 236, 880-888
Ostriker J. P. 1988, Rev. Mod. Phys., 60, 1
Penston, M. V. 1969a, M.N.R.A.S., 144, 425–448.
Penston, M. V.. 1969b, M.N.R.A.S., 145, 457–485.
Purohit S.C. 1974, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 36, 288
Rankine W. J. M. 1870, Roy. Soc. Lond. Philos. Ser. I, 160, 277
Ro S., Matzner C.D. 2017, Astrophys. J., 841, 1
Rogers M. H. 1957, Astrophys. J., 125, 478
Rosenau P., Frankenthal S. 1976, Phys. Fluids, 19, 1889
Sakurai A. 1953, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 8, 662
Sakurai A. 1954, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 9, 256
Sakurai A. 1956, J. Fluid. Mech., 1, 436
Sachdev P. L., Ashraf S. 1971, J. Appl. Math. Phys., 22, 1095
Sedov L. I. 1946, J. Appl. Maths. Mech., 10, 241
Sedov L. I. 1959, Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics, Academic Press, New York
Singh J. B., Vishwakarma P. R. 1983, Astrophys. Space Sci., 95, 99
Shao-Chi L. 1954, J. Appl. Phys., 25, 54
Shu F. H. 1977, ApJ, 214, 488
Solinger A., Rappaport S., Buff J. 1975, ApJ, 201, 381
Taylor G. 1946, Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 186, 273
Taylor G. 1950a, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A, 201, 159
Taylor G.I. (1950b), Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 2011065 175-186.
Truelove J. K, Klein R. I., McKee C. F., Holliman J. H., Howell L. H., Jeffrey A. G., Wood D. T. 1998, Astrophys. J., 495, 821
Vink J. 2012, Astron. Astrophys. Rev., 20, 49, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00159-011-0049-1
Vishwakarma J.P., Yadav A. K. 2003, Eur. Phys. J. B., 34, 247
Vishwakarma J. P., Nath G. 2006, Phys. Scr., 74, 493
Vishwakarma J. P., Nath G. 2007, Meccanica, 42, 331
Vishwakarma J. P., Nath G. 2009, Meccanica, 44, 239
Vishwakarma J. P., Nath G. 2012, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 17, 2382
Watanable M., Takayama K. 1991 Shock Waves, 1, 149
Waxman E., Shvarts D. 1993, PhFIA, 5, 1035
Winkler P. F., Clark G. W. 1974, ApJ (Lett.), 191, L67
Woltjer L. 1972, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 10, 129
Yan Z. Y., Zhang H. Q. 2001, J. Phys. A. Math. Gen., 34, 1785, https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/34/8/320
Zhuravskaya T. A., Levin V. A. 1996, J. Appl. Math. Mech., 60, 745
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nath, G. Approximate analytical solution for the propagation of shock waves in self-gravitating perfect gas via power series method: isothermal flow. J Astrophys Astron 41, 21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-020-09638-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-020-09638-7