Abstract
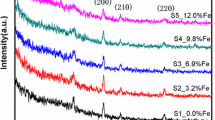
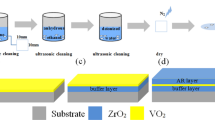
Vanadium dioxide (VO2) undergoes a reversible metal-insulator transition at low temperature, which has wide range of applications in smart windows and infrared detectors. However, the preparation of VO2 films with controllable phase on glass substrate is still limited. In this paper, it is shown that B-phase can be transformed into M-phase with monoclinic structure by inserting TiO2 buffer layer on glass substrate at low temperature of 400°C. This crystalline transformation might be attributed to that Ti atoms diffuse and form oxygen-deficient environments. Different thicknesses of buffer layers have different effect on characteristic of VO2 film. With 50-nm TiO2 buffer layer, the VO2|TiO2|glass film showed an abrupt resistance change with more than 2.5-order of magnitude across metal–insulator transition, and the visible-light transmittance value is as high as 55.5% with the solar modulation capability up to 8.6%. The current results are very important for the application in smart windows.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
F. J. Morin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 3, 34 (1959).
S. R. Popuri, A. Artemenko, and R. Decourt, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 6601 (2017).
J. S. Ke, S. F. Weng, and M. C. Wu, J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1 (2012).
M. M. Qazilbash, M. Brehm, B.-G. Chae, P.-C. Ho, G. O. Andreev, B.-J. Kim, S. J. Yun, A. V. Balatsky, M. B. Maple, F. Keilmann, H.-T. Kim, and D. N. Basov, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 318 (5857), 1750 (2007).
D. Hagrman, J. Zubieta, and C. J. Warren, J. Solid State Chem. 138, 178 (1998).
A. Zylbersztejn and N. F. Mott, Phys. Rev. B 11, 4383 (1975).
K. D. Rogers, J. A. Coath, and M. C. Lovell, J. Appl. Phys. 70, 1412 (1998).
G. Stefanovich, A. Pergament, and D. Stefanovich, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 8837 (2000).
E. E. Chain, Appl. Opt. 30, 2782 (1991).
H. S. Choi, J. S. Ahn, J. H. Jung, T. W. Noh, and D. H. Kim, Phys. Rev. B 54, 4621 (1996).
W. Li, S. Ji, and K. J. Qian, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 456, 166 (2015).
E. Strelcov, Y. Lilach, and A. Kolmakov, Nano Lett. 9, 2322 (2009).
S. Ni, H. Zeng, and X. Yang, J. Nanomater. 3, 218 (2011).
K. Chaoyang, Z. Cong, and Z. Liwei, Appl. Surf. Sci. 463, 704 (2019).
Y. Zhao, C. Chen, and X. Pan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 48, 7138 (2019).
Y. Muraoka and Z. Hiroi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 583 (2002).
K. Nagashima, T. Yanagida, H. Tanaka, and T. Kawai, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 026103 (2007).
S. Lee, I. N. Ivanov, and J. K. Keum, Sci. Rep. 60, 73112 (2016).
A. Srivastava, H. Rotella, and S. Saha, Appl. Mater. 3, 489 (2015).
P. Jin, G. Xu, and M. Tazawa, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. 77, 455 (2003).
J. Bian, M. Wang, and H. Sun, J. Mater. Sci. 51, 6149 (2016).
J. Jian, X. Wang, and L. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 9, 5319 (2017).
J. W. Ma, Y. R. Song, and G. Xu, Mech. Mater. 363, 370 (2013).
Z. Zhang, Y. Gao, and L. Kang, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 22214 (2010).
H. J. Zhou, J. H. Li, and X. Cao, Mater. Res. Innov. 19, S246 (2015).
H. Zong, C. Geng, and C. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 138 (2019).
Z. Ding, Y. Cui, and D. Wan, RSC Adv., 729496 (2017).
L. Xu, L. Shi, and X. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 3230 (2008).
Y. Zhang, X. Tan, and C. Huang, Mater. Res. Innov. 19, 295 (2015).
S. Chen, J. Liu, and L. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 18938 (2014).
M. Zhou, J. Bao, and M. Tao, Chem. Commun. 49, 6021 (2013).
D. Zhang, K. Yang, and Y. Li, J. Alloys Compd. 684, 719 (2016).
B. Zhu, H. Tao, and X. Zhao, Infrared Phys. Technol. 75, 22 (2016).
Funding
This work was sponsored by the Science and Technology Development Project of Henan Province (182102210028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Wang, S., Li, R. et al. The Effect of the Crystalline Structure Transformation in VO2|Glass by Inserting TiO2 Buffer Layer and Its Application in Smart Windows. Semiconductors 54, 929–935 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378262008014X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378262008014X