Abstract
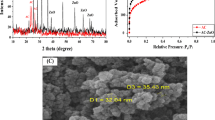
Kaolin-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (K-NZVI) was synthesized via a green synthesis method, in which leaf extract of Ruellia tuberosa was used as a reducing agent. The synthesized K-NZVI was used for decolorization of Reactive Black 5 (RB5), an azo dye widely used in textile industry. The XRD patterns of the K-NZVI particles show the characteristic peaks of Fe0, indicating that Fe0 nanoparticles (NZVI) were successfully synthesized on the kaolin surface. The SEM, TEM images and EDS elemental mapping show that the NZVI particles are well dispersed on the kaolin surface, thus, reducing the extent of NZVI aggregation. Batch experiments for decolorization of RB5 were carried out to investigate the effects of process parameters including solution pH, initial dye concentration and contact time. The results show that high decolorization efficiencies are obtained in acidic pH. Increasing initial dye concentration causes the decolorization efficiency to decrease, whereas increasing contact time results in higher efficiency. Furthermore, after five cycles of reuse of K-NZVI, the decolorization efficiency slightly decreases, indicating high reusability and stability of K-NZVI. The disappearance of the characteristic peaks of RB5 solution recorded by a UV–Vis spectrophotometer indicates cleavage of the azo bonds and, thus, the decomposition of RB5 in the solution. From a kinetic analysis performed at various RB5 concentrations, the decolorization process of RB5 by K-NZVI is well fit by the pseudo-first-order kinetic model.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghaly, A.E.; Ananthashankar, R.; Alhattab, M.; Ramakrishnan, V.V.: Production, characterization and treatment of textile effluents: a critical review. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 5, 1–19 (2014)
Lucas, M.S.; Amaral, C.; Sampaio, A.; Peres, J.A.; Dias, A.A.: Biodegradation of the diazo dye Reactive Black 5 by a wild isolate of Candida oleophila. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 39, 51–55 (2006)
Franciscon, E.; Grossman, M.J.; Paschoal, J.A.R.; Reyes, F.G.R.; Durrant, L.R.: Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive sulfonated azo dyes by a newly isolated Brevibacterium sp. strain VN-15. Springerplus 1, 1–10 (2012)
Zhu, H.; Jiang, R.; Fu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Yao, J.; Xiao, L.; Zeng, G.: Effective photocatalytic decolorization of methyl orange utilizing TiO2/ZnO/chitosan nanocomposite films under simulated solar irradiation. Desalination 286, 41–48 (2012)
Garg, S.K.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, S.K.; Tiwari, J.K.: Biodecolorization of textile dye effluent by Pseudomonas putida SKG-1 (MTCC10510) under the conditions optimized for monoazo dye orange II color removal in simulated minimal salt medium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 74, 24–35 (2012)
Qu, Y.; Cao, X.; Ma, Q.; Shi, S.; Tan, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.: Aerobic decolorization and degradation of Acid Red B by a newly isolated Pichia sp TCL. J. Hazard. Mater. 223–224, 31–38 (2012)
Alqaragully, M.B.: Removal of textile dyes (Maxilon Blue, and Methyl Orange) by date stones activated carbon. Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 1, 48–59 (2014)
dos Santos, A.B.; Cervantes, F.J.; van Lier, J.B.: Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile wastewaters: perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 2369–2385 (2007)
Farooq, M.U.; Jalees, M.I.; Iqbal, A.; Zahra, N.; Kiran, A.: Characterization and adsorption study of biosorbents for the removal of basic cationic dye: kinetic and isotherm analysis. Desalination Water Treat. 160, 333–342 (2019)
Hashim, K.S.; Al-Saati, N.H.; Alquzweeni, S.S.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Kot, P.; Kraidi, L.; Hussein, A.H.; Alkhaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Alwash, R.: Decolourization of dye solutions by electrocoagulation: an investigation of the effect of operational parameters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 584, 012024 (2019)
Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; Longo, M.A.; Sanroman, M.A.: Electro-Fenton decoloration of dyes in a continuous reactor: a promising technology in colored wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 155, 62–67 (2009)
Chen, C.H.; Chang, C.F.; Liu, S.M.: Partial degradation mechanisms of malachite green and methyl violet B by Shewanella decolorationis NTOU1 under anaerobic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 177, 281–289 (2010)
Kamat, P.V.; Meisel, D.: Nanoscience opportunities in environmental remediation. C. R. Chim. 6, 999–1007 (2003)
Gang, X.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Y.J.; Gao, P.; Su, Y.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Chen, J.B.: Simultaneous removal of aniline, antimony and chromium by ZVI coupled with H2O2: implication for textile wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 368, 840–848 (2019)
Tian, J.; Jin, J.; Chiu, P.C.; Cha, D.K.; Guo, M.; Imhoff, P.T.: A pilotscale, bi-layer bioretention system with biochar and zero-valent iron for enhanced nitrate removal from storm water. Water Res. 148, 378–387 (2019)
Wang, M.; Cheng, W.; Wan, T.; Hu, B.W.; Zhu, Y.L.; Song, X.F.; Sun, Y.B.: Mechanistic investigation of U(VI) sequestration by zerovalent iron/activated carbon composites. Chem. Eng. J. 362, 99–106 (2019)
Salam, M.A.; Fageeh, O.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Obaid, A.Y.: Removal of nitrate ions from aqueous solution using zero-valent iron nanoparticles supported on high surface area nanographenes. J. Mol. Liq. 212, 708–715 (2015)
Lee, H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, S.C.: Application of recycled zero-valent iron nanoparticle to the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. J. Nanomater. 2015, 1–8 (2015)
Lapeyrouse, N.; Liu, M.; Zou, S.; Booth, G.; Yestrebsky, C.L.: Remediation of chlorinated alkanes by vitamin B12 and zero-zalent iron. J. Chem. 2019, 1–8 (2019)
Shoiful, A.; Ueda, Y.; Nugroho, R.; Honda, K.: Degradation of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water by iron (Fe)-based materials. J. Water Process. Eng. 11, 110–117 (2016)
El-Temsah, Y.S.; Sevcu, A.; Bobcikova, K.; Cernik, M.; Joner, E.J.: DDT degradation efficiency and ecotoxicological effects of two types of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water and soil. Chemosphere 144, 2221–2228 (2016)
Gunawardana, B.; Singhal, N.; Swedlund, P.: Degradation of chlorinated phenols by zero valent iron and bimetals of iron: a review. Environ. Eng. Res. 16, 187–203 (2011)
Minella, M.; Sappa, E.; Hanna, K.; Barsotti, F.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Vione, D.: Considerable Fenton and photo-Fenton reactivity of passivated zero-valent iron. RSC Adv. 6, 86752–86761 (2016)
Azzam, A.M.; El-Wakeelb, S.T.; Mostafaa, B.B.; El-Shahat, M.F.: Removal of Pb, Cd, Cu and Ni from aqueous solution using nano scale zero valent iron particles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 2196–2206 (2016)
Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Wu, S.: Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by different surface-modified biochars: acid washing, nanoscale zero-valent iron and ferric iron loading. Bioresour. Technol. 261, 142–150 (2018)
Barreto-Rodrigues, M.; Silveira, J.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J.: Synthesis, characterization and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron in the degradation of the azo dye Disperse Red 1. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 628–634 (2017)
Shojaei, S.; Shojaei, S.: Optimization of process variables by the application of response surface methodology for dye removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 4601–4610 (2019)
Simsek, U.B.; Turabik, M.: Decolorization mechanisms of an anionic dye by using zero-valent iron nanoparticles: application of response surface modeling for the optimization process. Desalination Water Treat. 81, 303–314 (2017)
Fan, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, M.: Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 904–910 (2009)
Saxe, J.P.; Lubenow, B.L.; Chiu, P.C.; Huang, C.P.; Cha, D.K.: Enhanced biodegradation of azo dyes using an integrated elemental iron-activated sludge system: I. Evaluation of system performance. Water Environ. Res. 78, 19–25 (2006)
Chang, M.C.; Shu, H.Y.; Yu, H.H.; Sung, Y.C.: Reductive decolourization and total organic carbon reduction of the diazo dye CI Acid Black 24 by zero-valent iron powder. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 81, 1259–1266 (2006)
Sravanthi, K.; Ayodhya, D.; Swamy, P.Y.: Green synthesis, characterization of biomaterial-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles for contaminated water treatment. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 9, 1–11 (2018)
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, S.; Hou, S.: Migration experiment and numerical simulation of modified nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) in porous media. J. Hydrol. 579, 1–11 (2019)
Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C.: Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 533, 76–81 (2015)
Chang, C.; Lian, F.; Zhu, L.: Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of gamma-HCH by nZVI/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles with activated carbon support. Environ. Pollut. 159, 2507–2514 (2011)
Qiu, M.; Chen, C.: Treatment of dye C.I. Reactive Red 15 in aqueous solution using the activated carbon supported zero valent iron. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 17, 949–952 (2018)
Kim, S.A.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Lee, K.J.; Park, Y.J.; Shea, P.J.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, B.T.: Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by a zeolite nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. Chem. Eng. J. 217, 54–60 (2013)
Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.: Decoloration of acid violet red B by bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: reactivity, characterization, kinetics and reaction pathway. Appl. Clay Sci. 93–94, 56–61 (2014)
Li, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.: Enhanced removal of Ni(II) by nanoscale zero valent iron supported on Na-saturated bentonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 497, 43–49 (2017)
Shahwan, T.; Üzüm, Ç.; Eroğlu, A.E.; Lieberwirth, I.: Synthesis and characterization of bentonite/iron nanoparticles and their application as adsorbent of cobalt ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 47, 257–262 (2010)
Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Lu, X.Q.; Chen, Z.: Removal of Pb(II) from water using synthesized kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 163, 243–248 (2010)
Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, C.; Li, T.; Liu, J.: Synthesis, characterization and aging study of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and its application for Ni(II) adsorption. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 421–432 (2014)
Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.: Synthesis of kaolin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and its degradation mechanism of Direct Fast Black G in aqueous solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 61, 433–438 (2015)
Fang, S.; Yang, N.; Qiu, M.; Huang, C.: Degradation of dye C.I. Reactive Red 15 in aqueous solution by kaolinite supported zero valent iron. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 18, 963–968 (2019)
Jalees, M.I.; Farooq, M.U.; Basheer, S.; Asghar, S.: Removal of heavy metals from drinking water using chikni mitti (kaolinite): isotherm and kinetics. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 6351–6359 (2019)
Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.: Kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution: reactivity, characterization and mechanism. Water Res. 45, 3481–3488 (2011)
Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.: Multifunctional kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron used for the adsorption and degradation of crystal violet in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 398, 59–66 (2013)
Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Ok, Y.S.: Review on nano zero valent iron (nZVI): from synthesis to environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 287, 618–632 (2016)
Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C.: Green zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the degradation of amoxicillin. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 1109–1118 (2017)
Kumar, R.; Singh, N.; Pandey, S.N.: Potential of green synthesized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for remediation of lead-contaminated water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3943–3950 (2015)
Fahmy, H.M.; Mohamed, F.M.; Marzouq, M.; El-Din Mustafa, A.B.; Alsoudi, A.M.; Ali, O.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mahmoud, F.A.: Review of green methods of iron nanoparticles synthesis and applications. Bionanoscience 8, 491–503 (2018)
Devatha, C.P.; Thalla, A.K.; Katte, S.Y.: Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using different leaf extracts for treatment of domestic waste water. J. Clean. Prod. 139, 1425–1435 (2016)
Kheshtzar, R.; Berenjian, A.; Ganji, N.; Taghizadeh, S.M.; Maleki, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Ghasemi, Y.; Alireza, E.: Response surface methodology and reaction optimization to product zero-valent iron nanoparticles for organic pollutant remediation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 21, 1–8 (2019)
Huang, L.; Weng, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.: Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles by various tea extracts: comparative study of the reactivity. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 130, 295–301 (2014)
Tandon, P.K.; Shukla, R.C.; Singh, S.B.: Removal of arsenic(III) from water with clay-supported zerovalent iron nanoparticles synthesized with the help of tea liquor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 10052–10058 (2013)
Truskewycz, A.; Shukla, R.; Ball, A.S.: Iron nanoparticles synthesized using green tea extracts for the fenton-like degradation of concentrated dye mixtures at elevated temperatures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 4409–4417 (2016)
Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R.: Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 466–467, 210–213 (2014)
Machado, S.; Stawiński, W.; Slonina, P.; Pinto, A.R.; Grosso, J.P.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C.: Application of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles to the remediation of soils contaminated with ibuprofen. Sci. Total Environ. 461–462, 323–329 (2013)
Mystrioti, C.; Xanthopoulou, T.D.; Tsakiridis, P.; Papassiopi, N.; Xenidis, A.: Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 539, 105–113 (2016)
Eslami, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Biparva, P.: Green synthesis of safe zero valent iron nanoparticles by Myrtus communis leaf extract as an effective agent for reducing excessive iron in iron-overloaded mice, a thalassemia model. RSC Adv. 8, 26144–26155 (2018)
Pattanayak, M.; Mohapatra, D.; Nayak, P.L.: Green synthesis and characterization of zero valent iron nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Syzygium aromaticum (clove). Middle East J. Sci. Res. 18, 623–626 (2013)
Rajendrakumar, N.; Vasantha, K.; Murugan, M.; Mohan, V.R.: Antioxidant activity of tuber of Ruellia tuberosa L. (Acanthaceae). Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 6, 97–103 (2014)
Singh, M.; Dasgupta, M.; Biswas, S.: Leaf extract of cracker plant (Ruellia tuberosa Linn) induces metal chelating activity and DNA strands break: implications for its antioxidant-prooxidant property. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 15, 319–325 (2015)
Chen, F.A.; Wu, A.B.; Shieh, P.; Kuo, D.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.: Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of Ruellia tuberosa. Food Chem. 94, 14–18 (2006)
Cheong, B.E.; Waslim, M.Z.; Lem, F.F.; Teoh, P.L.: Antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities of Sabah Ruellia tuberosa. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 3, 20–24 (2013)
Phakeovilay, C.; Disadee, W.; Sahakitpichan, P.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Kittakoop, P.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kanchanapoom, T.: Phenylethanoid and flavone glycosides from Ruellia tuberosa L. J. Nat. Med. 67, 228–233 (2013)
Hashim, K.S.; Hussein, A.H.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Kot, P.; Kraidi, L.; Alkhaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Alwash, R.: Effect of initial pH value on the removal of reactive black dye from water by electrocoagulation (EC) method. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1294, 072017 (2019)
Nagajyothi, P.; Pandurangan, M.; Kim, D.H.; Sreekanth, T.; Shim, J.: Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and their catalytic and in vitro anticancer activities. J. Cluster Sci. 28, 245–257 (2017)
Zghari, B.; Doumenq, P.; Romane, A.; Boukir, A.: GC-MS, FTIR and 1H, 13C NMR structural analysis and identification of phenolic compounds in olive mill wastewater extracted from oued oussefrou effluent (Beni Mellal-Morocco). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 8, 4496–4509 (2017)
Senthilkumar, S.R.; Sivakumar, T.: Green tea (Camellia sinensis) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles and studies on their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6, 461–465 (2014)
Khoo, L.W.; Mediani, A.; Zolkeflee, N.K.Z.; Leong, S.W.; Ismail, I.S.; Khatib, A.; Shaari, K.; Abas, F.: Phytochemical diversity of Clinacanthus nutans extracts and their bioactivity correlations elucidated by NMR based metabolomics. Phytochem. Lett. 14, 123–133 (2015)
Pariyani, R.; Ismail, I.S.; Azam, A.A.; Abas, F.; Shaari, K.: Identification of the compositional changes in Orthosiphon stamineus leaves triggered by different drying techniques using 1H NMR metabolomics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 97, 4169–4179 (2017)
Mystrioti, C.; Sparis, D.; Papasiopi, N.; Xenidis, A.; Dermatas, D.; Chrysochoou, M.: Assessment of polyphenol coated nano zero valent iron for hexavalent chromium removal from contaminated waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 94, 302–307 (2015)
Khan, M.I.; Khan, H.U.; Azizli, K.; Sufian, S.; Man, Z.; Siyal, A.A.; Muhammad, N.; Faiz ur Rehman, M.: The pyrolysis kinetics of the conversion of Malaysian kaolin to metakaolin. Appl. Clay Sci. 146, 152–161 (2017)
Singhal, R.K.; Gangadhar, B.; Basu, H.; Manisha, V.; Naidu, G.R.K.; Reddy, A.V.R.: Remediation of malathion contaminated soil using zero valent iron nano-particles. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 3, 76–82 (2012)
dos Santos, F.S.; Lago, F.R.; Yokoyama, L.; Fonseca, F.V.: Synthesis and characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles supported on SBA-15. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 6, 178–183 (2017)
Su, L.; Liu, C.; Liang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Zhen, G.; Chai, X.; Sun, X.: Performance evaluation of zero-valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) for high-concentration H2S removal from biogas at different temperatures. RSC Adv. 8, 13798–13805 (2018)
Üzüm, Ç.; Shahwan, T.; Eroğlu, A.E.; Hallam, K.R.; Scott, T.B.; Lieberwirth, I.: Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 43, 172–181 (2009)
Yahaya, S.; Jikan, S.S.; Badarulzaman, N.A.; Adamu, A.D.: Chemical composition and particle size analysis of kaolin. Traektoriâ Nauki Path Sci. 3, 1001–1004 (2017)
Mohsen, Q.; El-maghraby, A.: Characterization and assessment of Saudi clays raw material at different area. Arab. J. Chem. 3, 271–277 (2010)
Chang, S.H.; Wang, K.S.; Chao, S.J.; Peng, T.H.; Huang, L.C.: Degradation of azo and anthraquinone dyes by a low-cost Fe0/air process. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 1127–1133 (2009)
He, Y.; Gao, J.F.; Feng, F.Q.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.Z.; Wang, S.Y.: The comparative study on the rapid decolorization of azo, anthraquinone and triphenylmethane dyes by zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 179, 8–18 (2012)
Lin, Y.T.; Weng, C.H.; Chen, F.T.: Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron. Sep. Purif. Technol. 64, 26–30 (2008)
Venkatapathy, R.; Bessingpas, D.G.; Canonica, S.; Perlinger, J.A.: Kinetics models for trichloroethylene transformation by zero-valent iron. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 37, 139–159 (2002)
Zhang, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, F.: Decolorisation of CI Reactive Black 8 by zero-valent iron powder with/without ultrasonic irradiation. Color. Technol. 123, 203–208 (2007)
Mbarek, W.B.; Azabou, M.; Pineda, E.; Fiol, N.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Khitouni, M.: Rapid degradation of azo-dye using Mn-Al powders produced by ball-milling. RSC Adv. 7, 12620–12628 (2017)
Deng, H.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Mao, Z.: Reductive performance of ZVI/Cu polyscale particle to decolorize reactive black 5. Microsc. Res. Tech. 82, 134–143 (2019)
Oliver-Tolentino, M.A.; Jiménez-Álvarez, E.; de Jesús Martínez-Ortiz, M.; García-Báez, E.; Franco-Hernández, M.O.; Guzmán-Vargas, A.: Effective electro-fenton degradation of reactive black 5 dye using modified electrode with Cu-zeolites. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 17, 71–75 (2014)
Nisar, N.; Aleem, A.; Saleem, F.; Aslam, F.; Shahid, A.; Chaudhry, H.; Malik, K.; Albaser, A.; Iqbal, A.; Qadri, R.; Yang, Y.: Reduction of reactive red 241 by oxygen insensitive azoreductase purified from a novel strain Staphylococcus KU898286. PLoS ONE 12, 1–18 (2017)
Asses, N.; Ayed, L.; Hkiri, N.; Hamdi, M.: Congo red decolorization and detoxification by Aspergillus niger: removal mechanisms and dye degradation pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 1–9 (2018)
Ahangaran, F.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Nouri, S.: urface modification of Fe3O4@SiO2 microsphere by silane coupling agent. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 1–5 (2013)
Quintelas, C.; Figueiredo, H.; Tavares, T.: The effect of clay treatment on remediation of diethylketone contaminated wastewater: uptake, equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 1241–1248 (2011)
Sharma, G.; Jeevanandam, P.: Synthesis of self-assembled prismatic iron oxide nanoparticles by a novel thermal decomposition route. RSC Adv. 3, 189–200 (2013)
Shin, M.C.; Choi, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Baek, K.: Effect of surfactant on reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron. Desalination 223, 299–307 (2008)
Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.: Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res. 45, 886–892 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Faculty of Science and Technology, Prince of Songkla University, for the instruments and facilities used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khunjan, U., Kasikamphaiboon, P. Green Synthesis of Kaolin-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Using Ruellia tuberosa Leaf Extract for Effective Decolorization of Azo Dye Reactive Black 5. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 383–394 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04831-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04831-w