Abstract
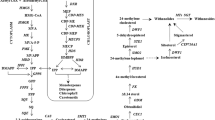
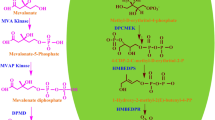
Sesquiterpenoid Zerumbone, the principal secondary metabolite in Zingiber zerumbet Smith, has been identified as the putative molecule conferring resistance against soft-rot causative, Pythium myriotylum. Metabolic precursors for sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis namely, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and DMAPP, are generated either from cytosolic mevalonic acid (MVA) and/or the plastidal methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. Evaluation of expression pattern of regulatory genes of MEP and MVA pathway following P. myriotylum infection revealed that while transcripts of MVA regulatory gene, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR), did not show significant changes, biphasic expression pattern was observed for MEP pathway regulatory genes, viz., 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductase (DXR) and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) as well for ZzTPS (terpene synthase) and Farnesyl phosphate synthase (FPS) compared with uninfected control. Contribution of the two pathways in zerumbone biosynthesis was evaluated in axenic tissue culture raised Z. zerumbet plantlets using MVA and MEP pathway specific inhibitors, mevinolin (MEV) and fosmidomycin (FOS) respectively. Results generated by regulatory gene and metabolite analysis are informative with respect to the role of plastidial IPP pool generated via MEP pathway in zerumbone biosynthesis and the possible redirection of flux in the event of metabolic perturbations mediated by chemical inhibitors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baby S, Dan M, Thaha ARM, Johnson AJ, Kurup R, Balakrishnapillai P, Lim CK (2009) High content of zerumbone in volatile oils of Zingiber zerumbet from southern India and Malaysia. Flavour Fragr J 24(6):301–308
Bick JA, Lange BM (2003) Metabolic cross talk between cytosolic and plastidial pathways of isoprenoid biosynthesis: unidirectional transport of intermediates across the chloroplast envelope membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys 415(2):146–154
CABI (2014) Zingiber zerumbet (shampoo ginger). CAB International, Wallingford http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/57539 (accessed 20 June 2018)
Chen F, Tholl D, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E (2011) The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom. Plant J 66(1):212–229
Cheng A, Wang L, Sun Y, Hongxiang Lou H (2013) Identification and expression analysis of key enzymes of the terpenoids biosynthesis pathway of a liverwort Plagiochasma appendiculatum by EST analysis. Acta Physiol Plant 35:107–118
Cusido RM, Palazon J, Bonfill M, Exposito O, Moyano E, Pinol MT (2007) Source of isopentenyl diphosphate for taxol and baccatin III biosynthesis in cell cultures of Taxus baccata. Biochem Eng J 33:159–167
De-Eknamkul W, Potduang B (2003) Biosynthesis of beta-sitosterol and stigmasterol in Croton sublyratus proceeds via a mixed origin of isoprene units. Phytochemistry 62(3):389–398
Dudareva N, Andersson S, Orlova I, Gatto N, Reichelt M, Rhodes D, Boland W, Gershenzon J (2005) The nonmevalonate pathway supports both monoterpene and sesquiterpene formation in snapdragon flowers. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 102(3):933–938
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227
Hemmerlin A, Hoeffler J-F, Meyer O, Tritsch D, Kagan IA, Grosdemange-Billiard C, Rohmer M, Bach TJ (2003) Cross-talk between the cytosolic mevalonate and the plastidial methylerythritol phosphate pathways in tobacco bright yellow-2 cells. J Biol Chem 278:26666–26676
Huang R, O’Donnell AJ, Barboline JJ, Barkman TJ (2016) Convergent evolution of caffeine in plants by co-option of exapted ancestral enzymes. PNAS 113(38):10613–10618
Kadowaki N, Ho S, Antonenko S, Malefyt RW, Kastelein RA, Bazan F, Liu Y-J (2001) Subsets of human dendritic cell precursors express different Toll-like receptors and respond to different microbial antigens. J Exp Med 194(6):863–870
Kanchiswamy CN, Malnoy M, Maffei ME (2015) Chemical diversity of microbial volatiles and their potential for plant growth and productivity. Front Plant Sci 6:151
Kavitha PG, Nair P, Aswati Nair R, Jayachandran BK, Sabu M, Thomas G (2005) AFLP polymorphism and Pythium response in Zingiber species. In: Kesavachandran R et al (eds) Recent trends in horticultural biotechnology. New India Publishing Agency, New Delhi, pp 232–234
Keerthi D, Geethu C, Aswati Nair R, Pillai P (2014) Metabolic profiling of Zingiber zerumbet following Pythium myriotylum infection: investigations on the defensive role of the principal secondary metabolite, Zerumbone. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(5):2593–2603
Koga AY, Beltrame FL, Pereira AV (2016) Several aspects of Zingiber zerumbet: a review. Braz J Pharmacognosy 26(3):385–391
Köksal M, Jin Y, Coates RM, Croteau R, Christianson DW (2011) Taxadiene synthase structure and evolution of modular architecture in terpene biosynthesis. Nature 469(7328):116–120
Kuzuyama T, Shimizu T, Takahashi S, Seto H (1998) Fosmidomycin, a specific inhibitor of 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in the nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 39:7913–7916
Laule O, Fürholz A, Chang HS, Zhu T, Wang X, Heifetz PB, Gruissem W, Lange M (2003) Crosstalk between cytosolic and plastidial pathways of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 100(11):6866–6871
Li S, Zhang P, Zhang M, Fu C, Zhao C, Dong Y, Guo A, Yu L (2012) Transcriptional profile of Taxus chinensis cells in response to methyl jasmonate. BMC Genomics 13:295
Mansouri H, Salari F (2014) Influence of mevinolin on chloroplast terpenoids in Cannabis sativa. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20(2):273–277
Martin DM, Gershenzon J, Bohlmann J (2003) Induction of volatile terpene biosynthesis and diurnal emission by methyl jasmonate in foliage of Norway spruce. Plant Physiol 132(3):1586–1599
May B, Lange BM, Wüst M (2013) Biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes in grape berry exocarp of Vitis vinifera L.: evidence for a transport of farnesyl diphosphate precursors from plastids to the cytosol. Phytochemistry 95:135–144
Ming JC, Vera R, Chalchat JC (2011) Chemical composition of the essential oil from rhizomes, leaves and flowers of Zingiber zerumbet Smith from Reunion Island. J Essent Oil Res 15(3):202–205
Nagegowda DA (2010) Plant volatile terpenoid metabolism: biosynthetic genes, transcriptional regulation and sub-cellular compartmentation. FEBS Lett 584:2965–2973
Okamoto S, Yu F, Harada H, Okajima T, Hattan J, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2011) A short-chain dehydrogenase involved in terpene metabolism from Zingiber zerumbet. FEBS J 278(16):2892–2900
Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Bonfill M, Morales C, Piñol MT (2003) Inhibition of paclitaxel and baccatin III accumulation by mevinolin and fosmidomycin in suspension cultures of Taxus baccata. J Biotechnol 101(2):157–163
Pazouki L, Niinemets Ü (2016) Multi-substrate terpene synthases: their occurrence and physiological significance. Front Plant Sci 7(1019):1–16
Peter P, Aswati RN, Divakaran K, Ganapathy G (2019) Evaluating type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and terpene synthase (TPS) expression in incompatible interactions of Zingiber zerumbet to Pythium myriotylum Drechsler. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 52:1161–1176
Ramakrishna A, Ravishankar GA (2011) Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav 6(11):1720–1731
Rodríguez-Concepción M, Boronat A (2002) Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids: a metabolic milestone achieved through genomics. Plant Physiol 130(3):1079–1089
Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Gruissem W (1999) Arachidonic acid alters tomato HMG expression and fruit growth and induces 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase-independent lycopene accumulation. Plant Physiol 119:41–48
Sallaud C, Rontein D, Onillon S, Jabès F, Duffé P, Giacalone C, Tissier A (2009) A novel pathway for sesquiterpene biosynthesis from Z,Z-Farnesyl pyrophosphate in the wild tomato Solanum habrochaites. Plant Cell 21(1):301–317
Salzman R, Fujita T, Zhu-Salzman K, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (1999) An improved RNA isolation method for plant tissues containing high levels of phenolic compounds or carbohydrates. Plant Mol Biol Report 17(1):11–17
Savoi S, Wong DCJ, Arapitsas P, Miculan M, Bucchetti B, Peterlunger E, Fait A, Mattivi F, Castellarin SD (2016) Transcriptome and metabolite profiling reveals that prolonged drought modulates the phenylpropanoid and terpenoid pathway in white grapes (Vitis vinifera L.). BMC Plant Biol 16:67
Srivastava M, Sharma S, Misra P (2016) Elicitation based enhancement of secondary metabolites in Rauwolfia serpentina and Solanum khasianum hairy root cultures. Pharmacogn Mag 12(3):S315–S320
Steliopoulos P, Wust M, Adam KP, Mosandl A (2002) Biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene germacrene D in Solidago canadensis: 13C and 2H labeling studies. Phytochemistry 60:13–20
Strack D, Fester T (2006) Isoprenoid metabolism and plastid reorganization in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots. New Phytol 172:22–34
Sulaiman MR, Mohamad TAST, Mossadeq WMS, Moin S, Yusof M, Mokhtar AF, Zakaria ZA, Israf DA, Lajis N (2010) Antinociceptive activity of the essential oil of Zingiber zerumbet. Planta Med 76(2):107–112
Tholl D (2015) Biosynthesis and biological functions of terpenoids in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 148(1):63–106
Tholl D, Lee S (2011) Terpene specialized metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Arabidopsis Book 9:e0143
Towler MJ, Weathers PJ (2007) Evidence of artimisnin production from IPP stemming from both the mevalonate and the non-mevalonate pathways. Plant Cell Rep 26:2129–2136
Vranová E, Coman D, Gruissem W (2013) Network analysis of the MVA and MEP pathways for isoprenoid synthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:665–700
Walter M, Floss D, Strack D (2010) Apocarotenoids: hormones, mycorrhizal metabolites and aroma volatiles. Planta 232:1–17
Wang Y-D, Yuan Y-J, Lu M, Wu J-C, Jiang J-L (2003) Inhibitor studies of isopentenyl pyrophosphate biosynthesis in suspension cultures of the yew Taxus chinensis var. mairei. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 37:39–43
Wildung MR, Croteau RB (2005) Genetic engineering of peppermint for improved essential oil composition and yield. Transgenic Res 14:365–372
Wölwer-Rieck U, May B, Lankes C, Wüst M (2014) Methylerythritol and mevalonate pathway contributions to biosynthesis of mono-, sesqui-, and diterpenes in glandular trichomes and leaves of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. J Agric Food Chem 62(11):2428–2435
Wu S, Schalk M, Clark A, Miles RB, Coates R, Chappell J (2006) Redirection of cytosolic or plastidic isoprenoid precursors elevates terpene production in plants. Nat Biotechnol 24(11):1441–1447
Yang D, Du X, Liang X, Han R, Liang Z, Liu Y, Liu F, Zhao J (2012) Different roles of the Mevalonate and Methylerythritol phosphate pathways in cell growth and Tanshinone production of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. PLoS One 7(11):1–9
Yob NJ, Jofrry SM, Affandi MM, The LK, Salleh MZ, Zakaria ZA (2011) Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Smith: a review of its ethnomedicinal, chemical, and pharmacological uses. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011(1):1–8
Yu F, Harada H, Yamasaki K, Okamoto S, Hirase S, Tanaka Y, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2008a) Isolation and functional characterization of a β-eudesmol synthase, a new sesquiterpene synthase from Zingiber zerumbet Smith. FEBS Lett 582(5):565–572
Yu F, Okamto S, Nakasone K, Adachi K, Matsuda S, Harada H, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2008b) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of α-humulene synthase, a possible key enzyme of zerumbone biosynthesis in shampoo ginger (Zingiber zerumbet Smith). Planta 227(6):1291–1299
Yu F, Okamoto S, Harada H, Yamasaki K, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2011) Zingiber zerumbet CYP71BA1 catalyzes the conversion of alpha-humulene to 8-hydroxy- alpha-humulene in zerumbone biosynthesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(6):1033–1040
Zhi L, Yu LJ, Li CY, Zhao CF (2005) Effects of fosmidomycin and lovastatin treatment on taxol biosynthesis in suspension culture cells of Taxus chinensis. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 31(2):199–204
Acknowledgments
KD acknowledges the research fellowship received from Ministry of Human Resource and Development (MHRD), Government of India. Authors are grateful to NITC CUK for the research facilities extended.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology-Science and Engineering Research Board (DST-SERB) for research grant (no. EMR/2016/002229).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RAN conceived and designed the experiments. RAN and KD performed the experiment. RAN, KD, and PP analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Message
• Biphasic expression observed for methylerythritol (MEP) pathway regulatory genes in Zingiber zerumbet following Pythium myriotylum infection.
• Metabolite analysis of in vitro plantlets treated with mevinolin (MEV) and fosmidomycin (FOS) reveals 54-fold decrease in zerumbone following FOS treatment.
• Identified plastidial IPP flux contributing more towards zerumbone biosynthesis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, A.R., Divakaran, K. & Pillai, P. Evidence for Methylerythritol Pathway (MEP) Contributions to Zerumbone Biosynthesis as Revealed by Expression Analysis of Regulatory Genes and Metabolic Inhibitors Studies. Plant Mol Biol Rep 38, 370–379 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01202-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01202-5